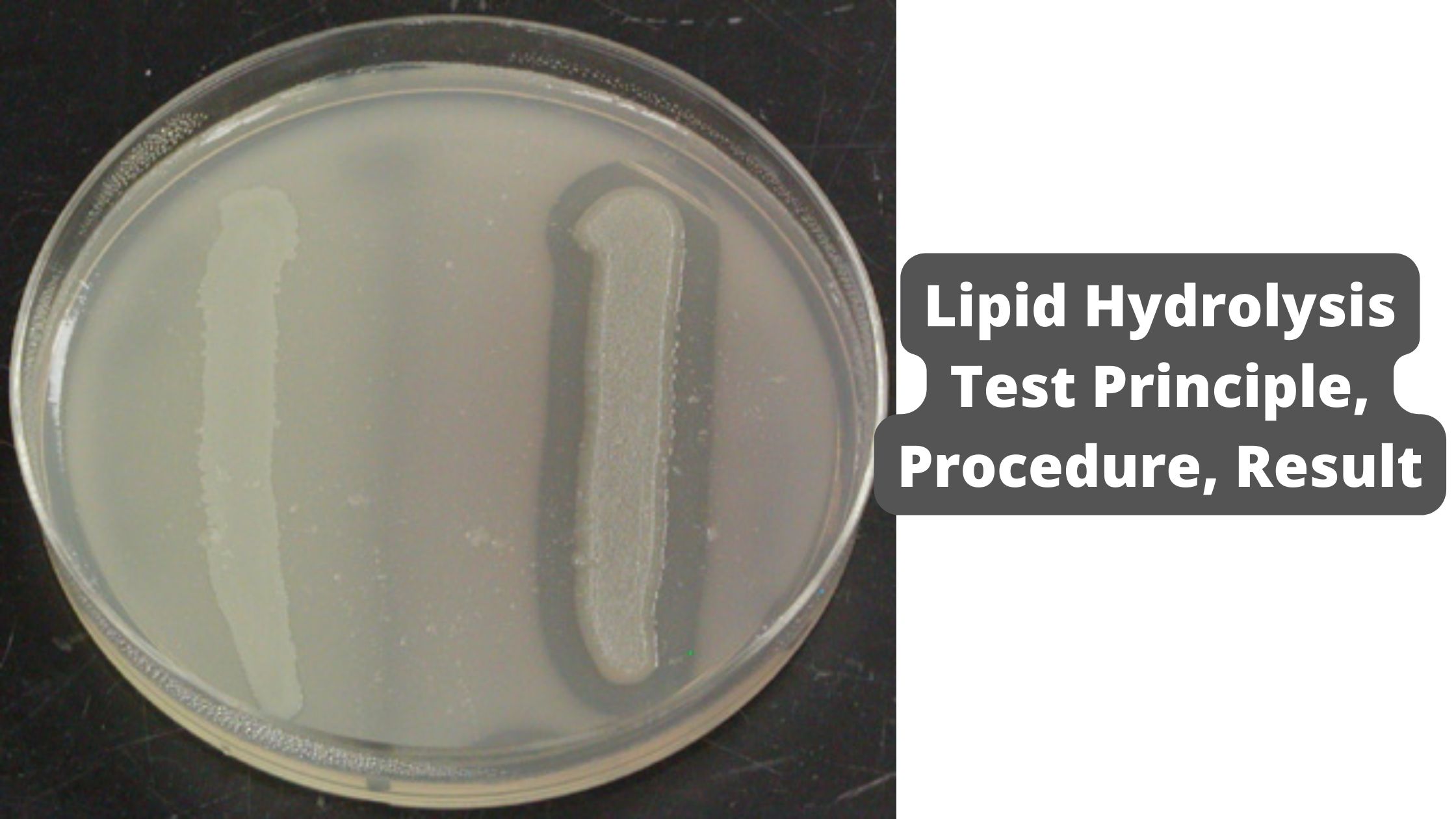
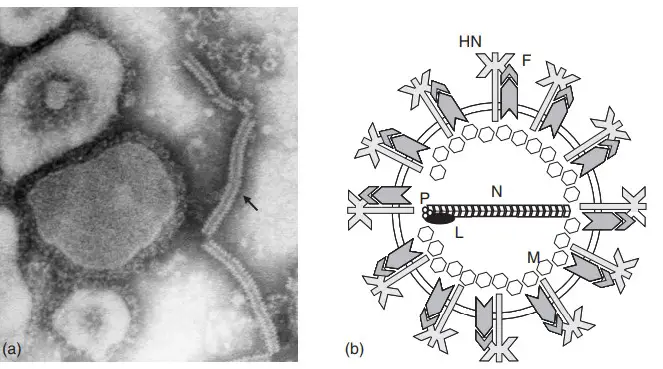
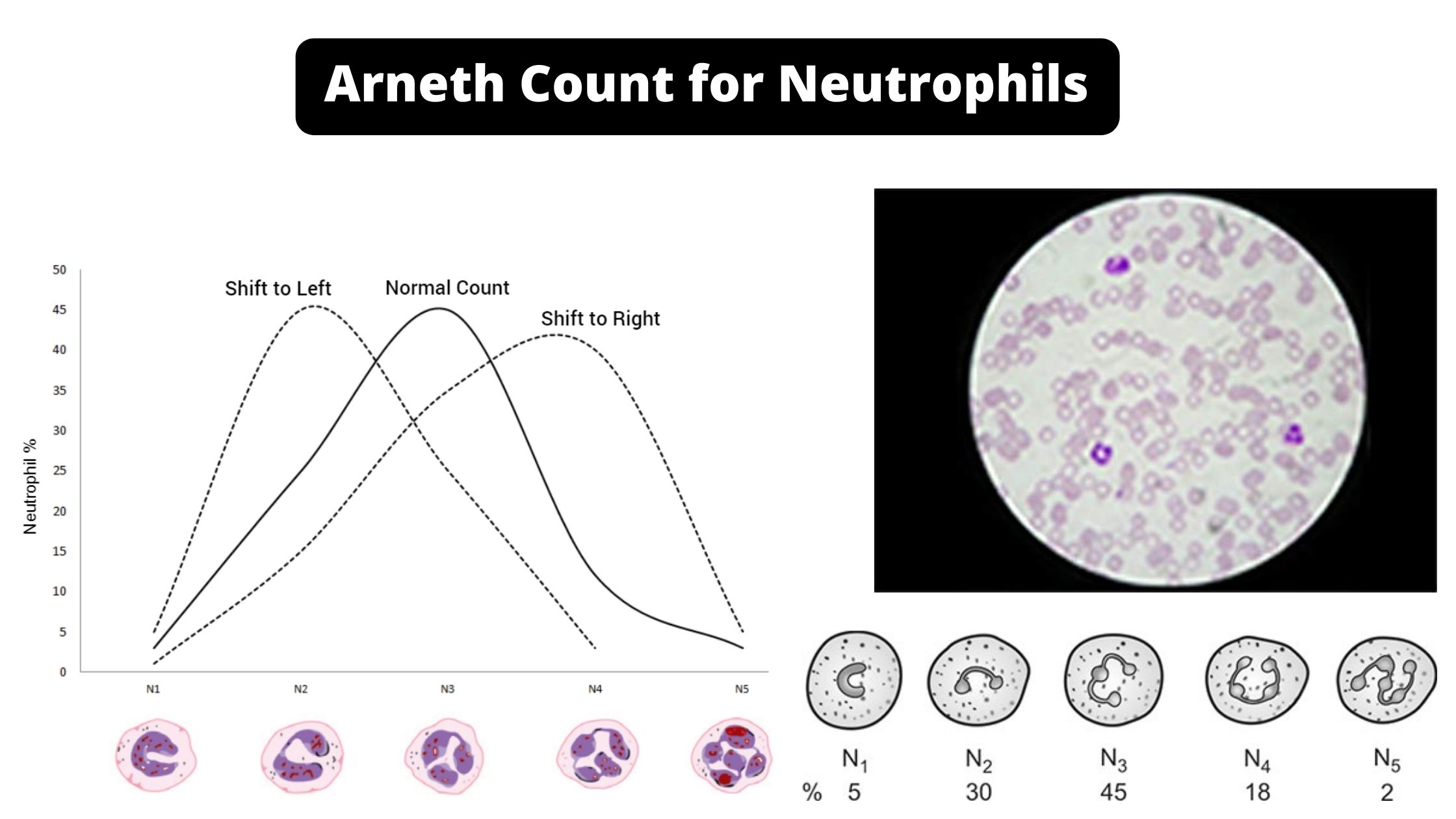
Lipid Hydrolysis Test – Principle, Procedure, Result
It is a biochemical test that is used to determine the ability of microorganism to produce and secrete the enzyme lipase. It is also referred to as lipase test. The complex lipids such as triglycerides are large molecules and these cannot pass through the bacterial cell membrane. Due to this reason some bacteria releases the … Read more