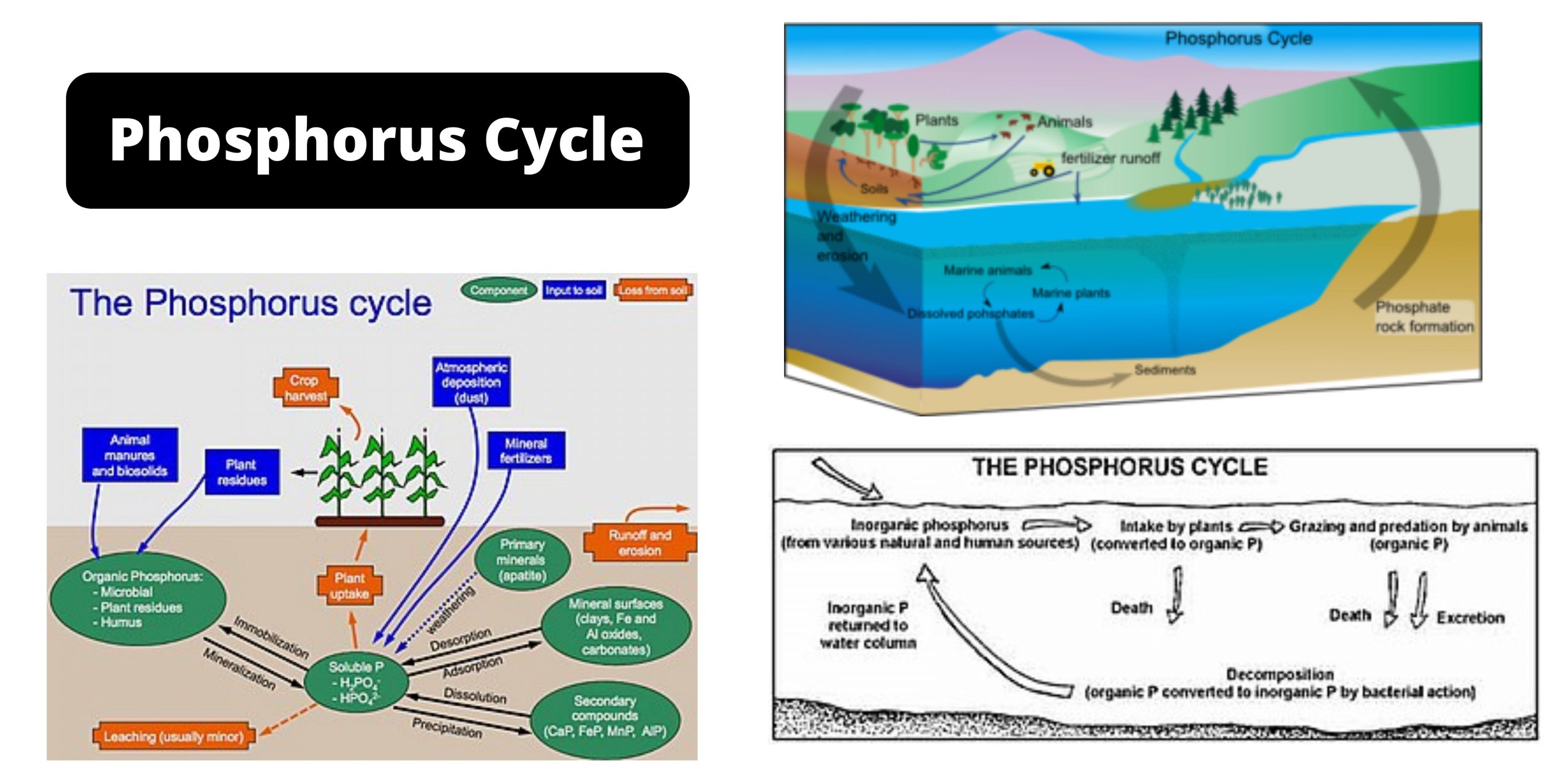
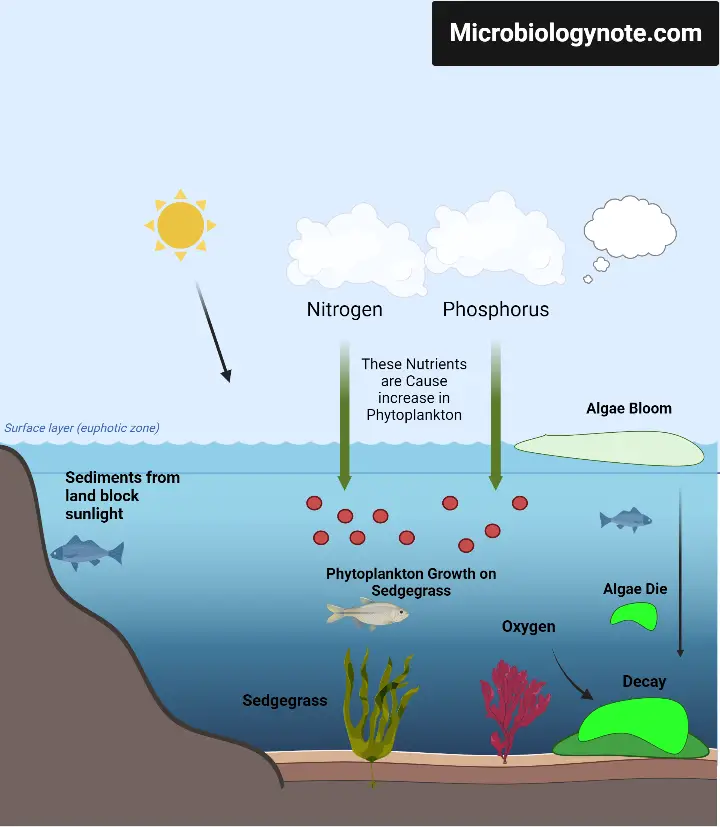
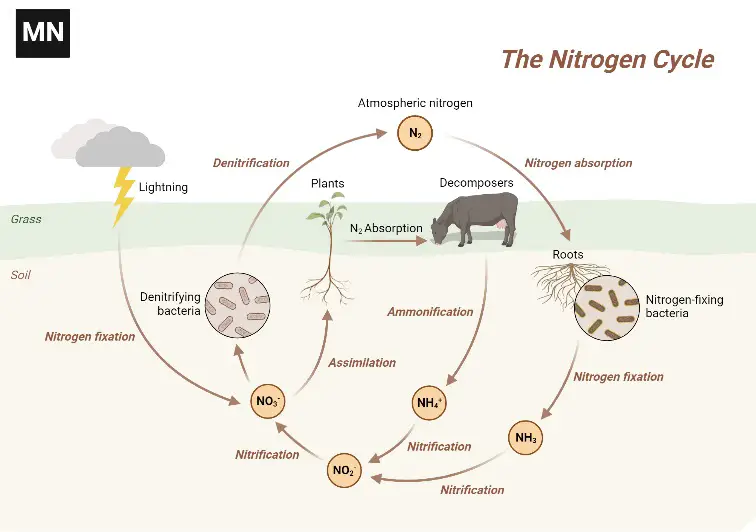
Phosphorus Cycle – Definition, Steps, Examples, Significance, and Human Impacts
Do you think phosphorus is important? This depends on whether you want DNADNAtexttextend text”D,N, End cell membranes, text or bones within your body? It’s a good bet that the likelihood is that yes!