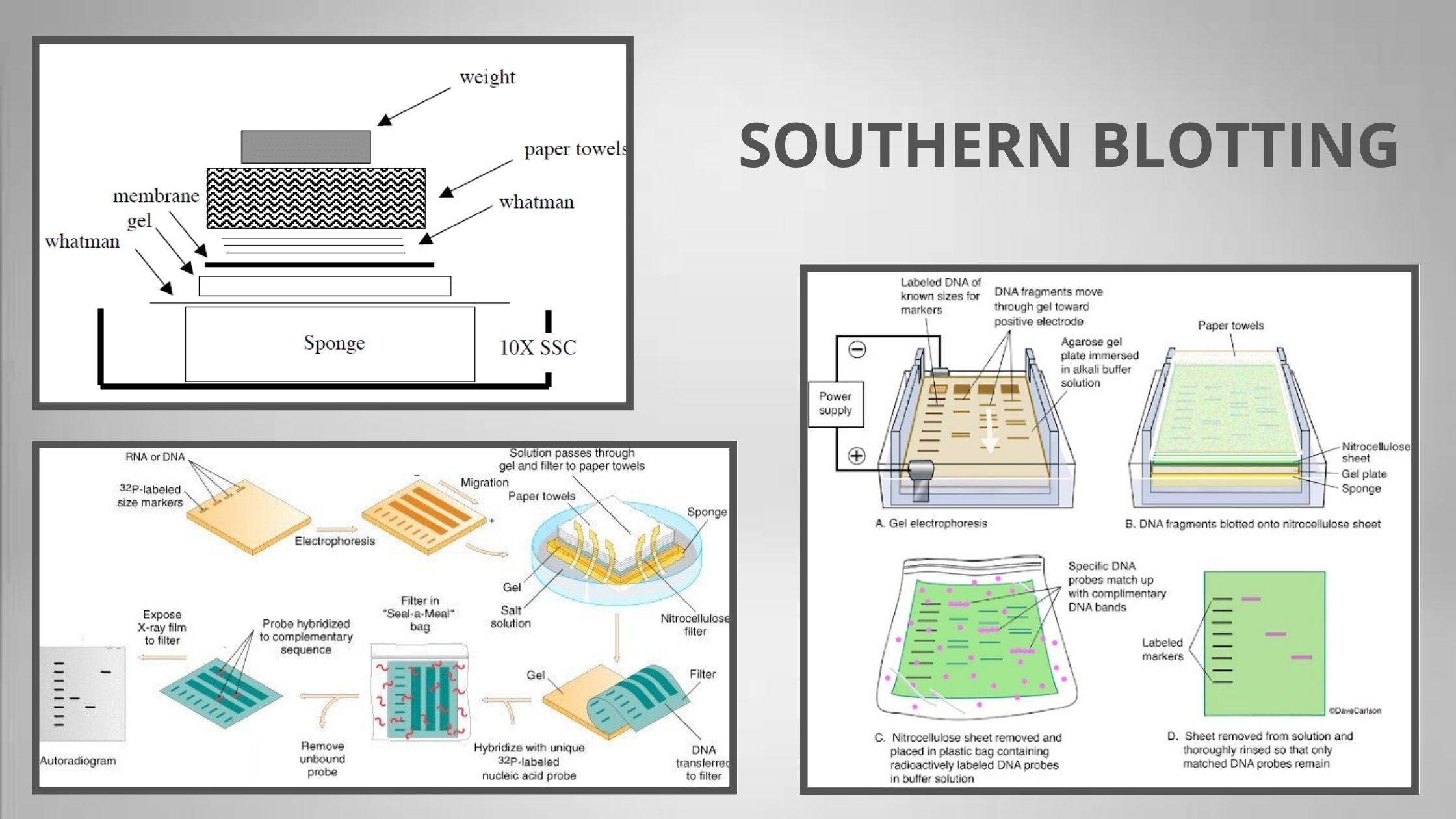
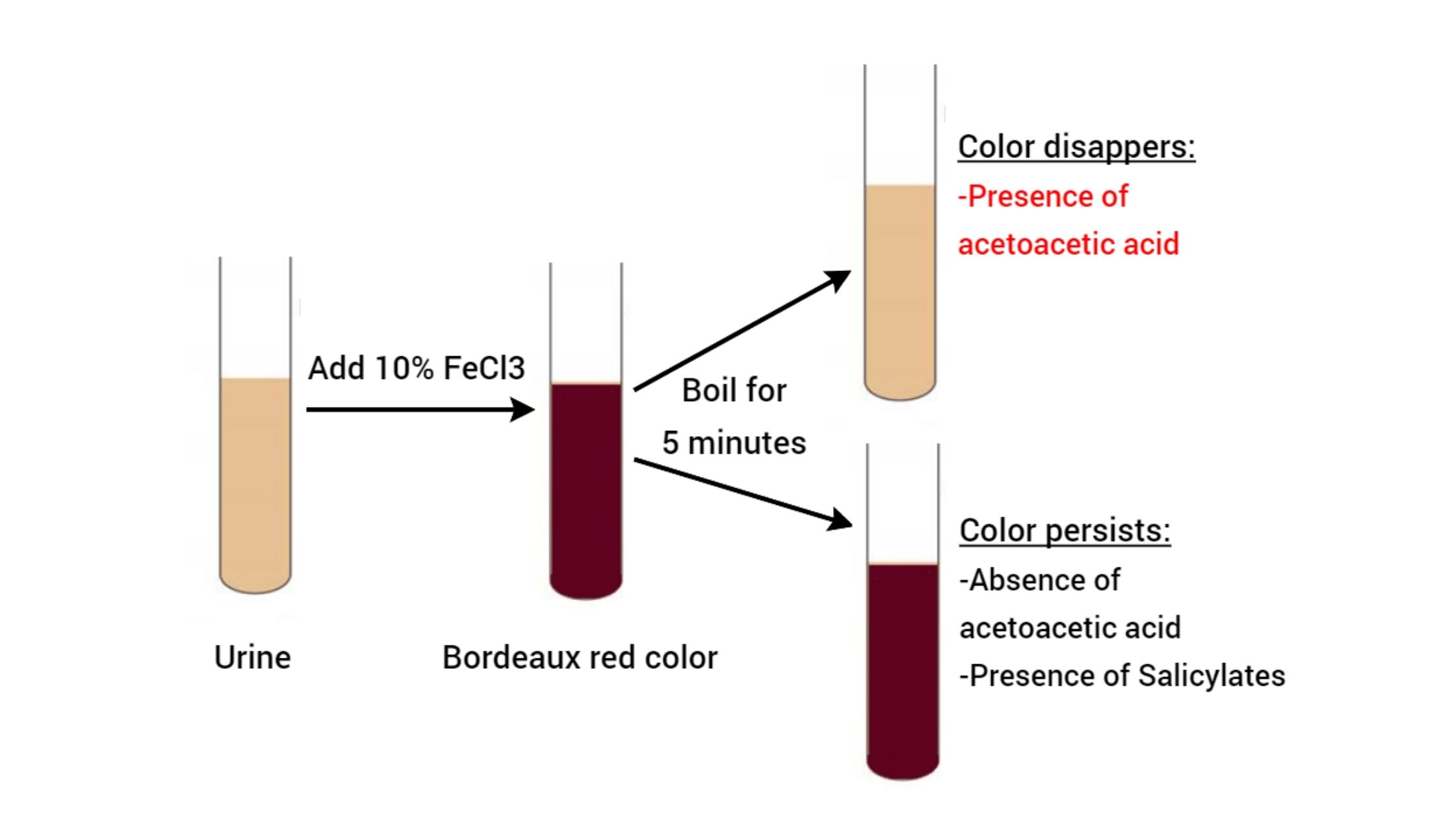
Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells – Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells
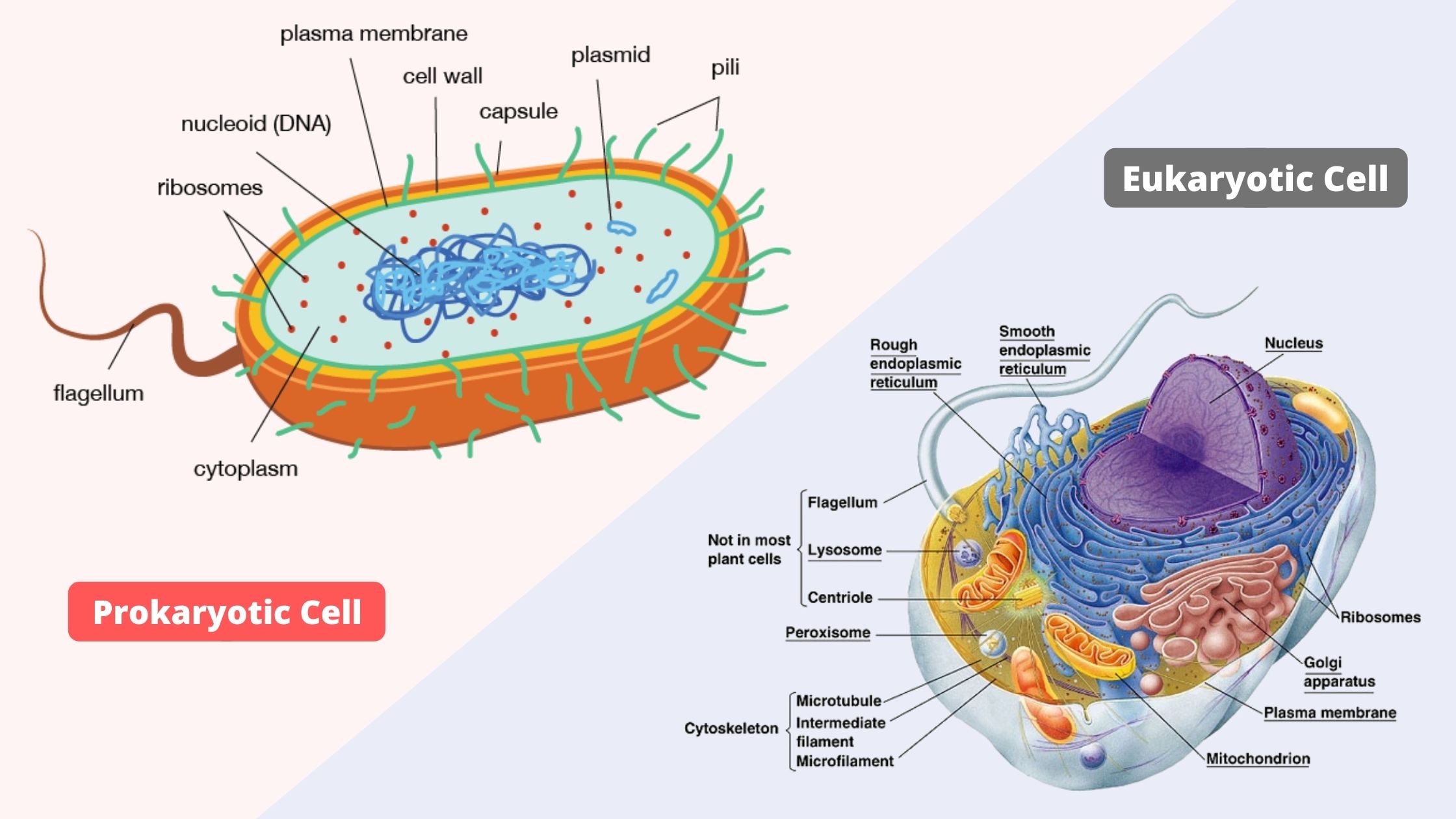
What is Prokaryotic Cell? What is Eukaryotic Cell? Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Feature Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Nucleus Absent; genetic material located in a nucleoid region. Present; genetic material enclosed within a nuclear envelope. Membrane-bound organelles Generally absent (e.g., mitochondria, chloroplasts, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus). Present (e.g., mitochondria, chloroplasts in photosynthetic cells, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi … Read more