Diatoms – Definition, Structure, Life Cycle, Importance
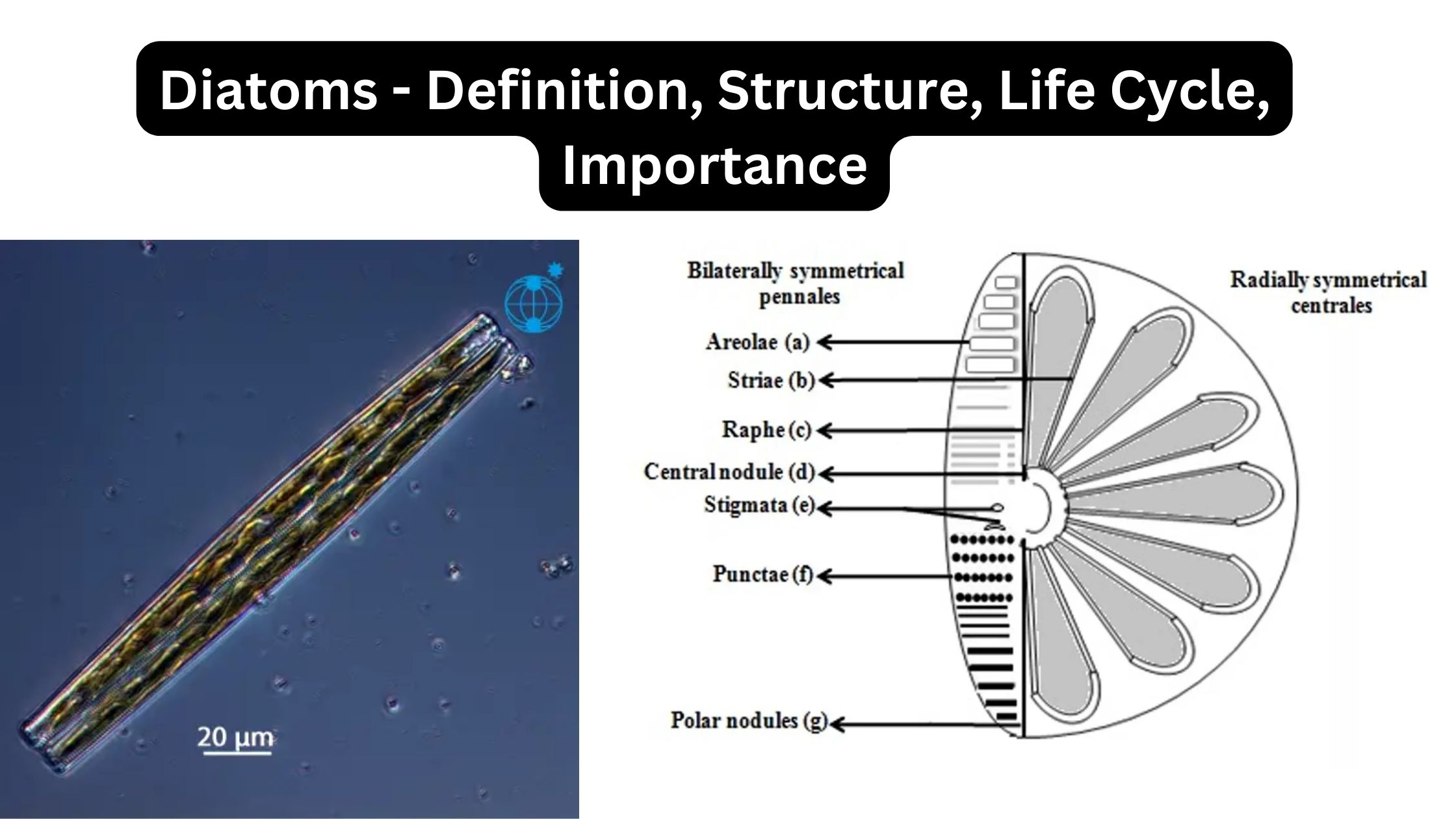
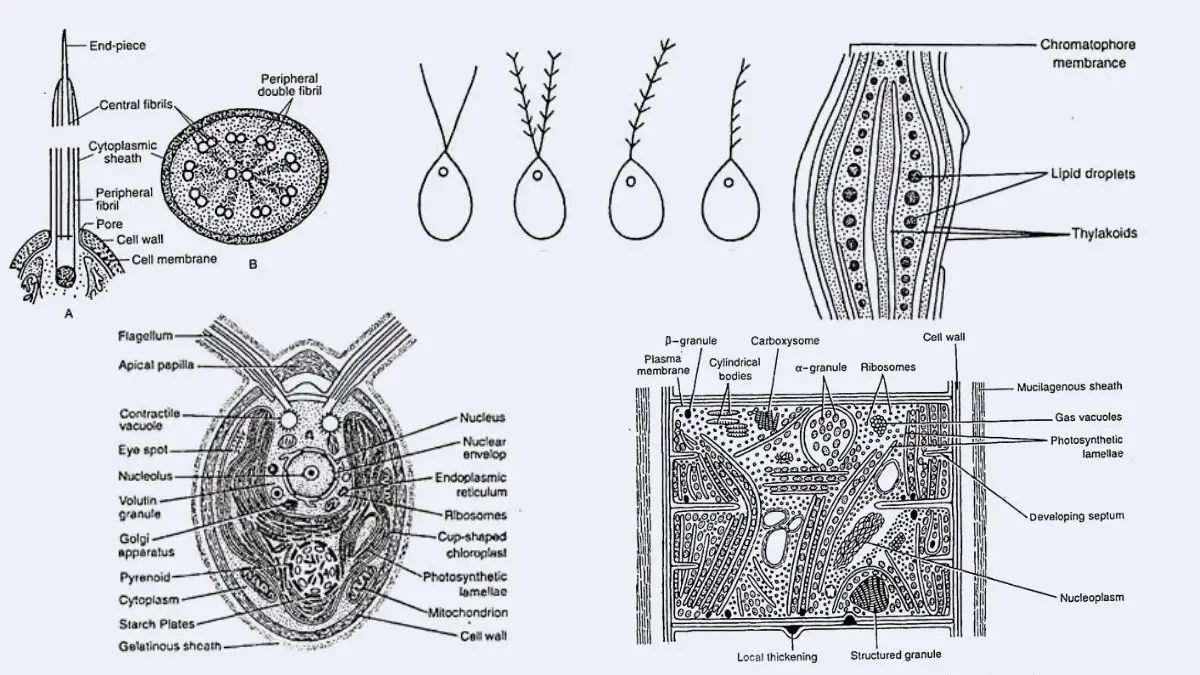
What is Diatom? Definition of Diatom A diatom is a tiny, single-celled algae with a hard shell made of silica, found in oceans, waterways, and soil. They play a crucial role in oxygen production, nutrient cycling, and the food web of aquatic ecosystems. Scientific classification of Diatom Domain: Eukaryota Clade: Diaphoretickes Clade: SAR Clade: Stramenopiles … Read more