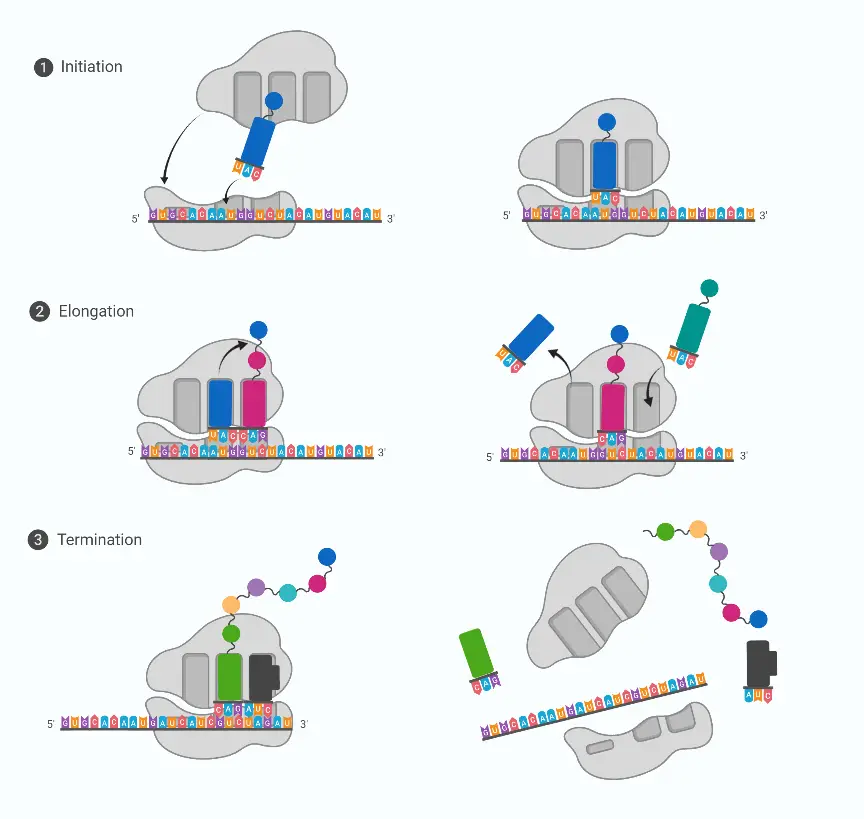
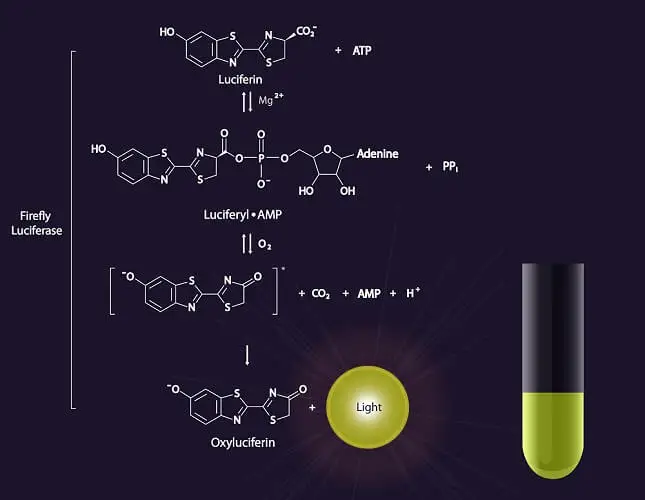
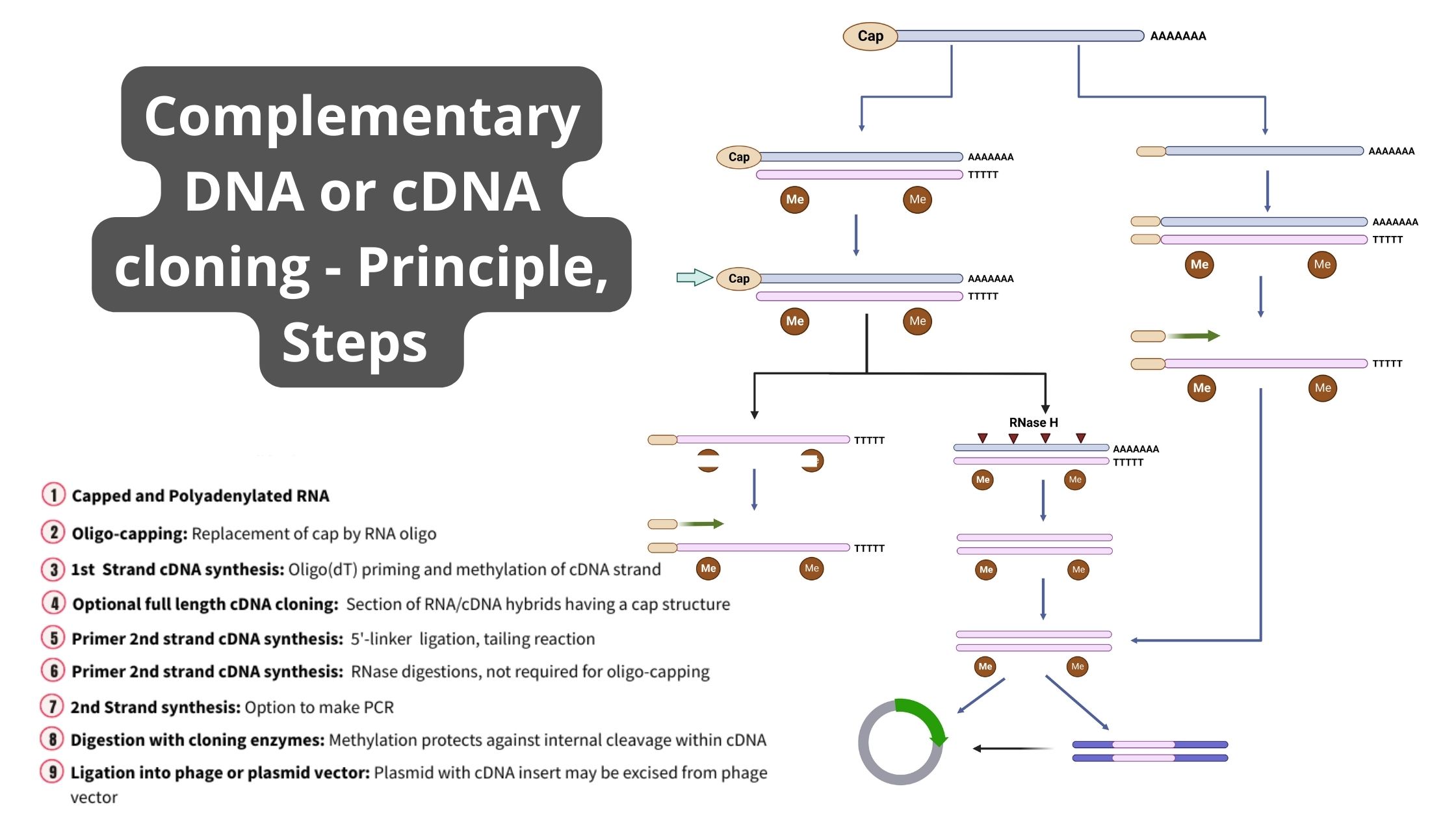
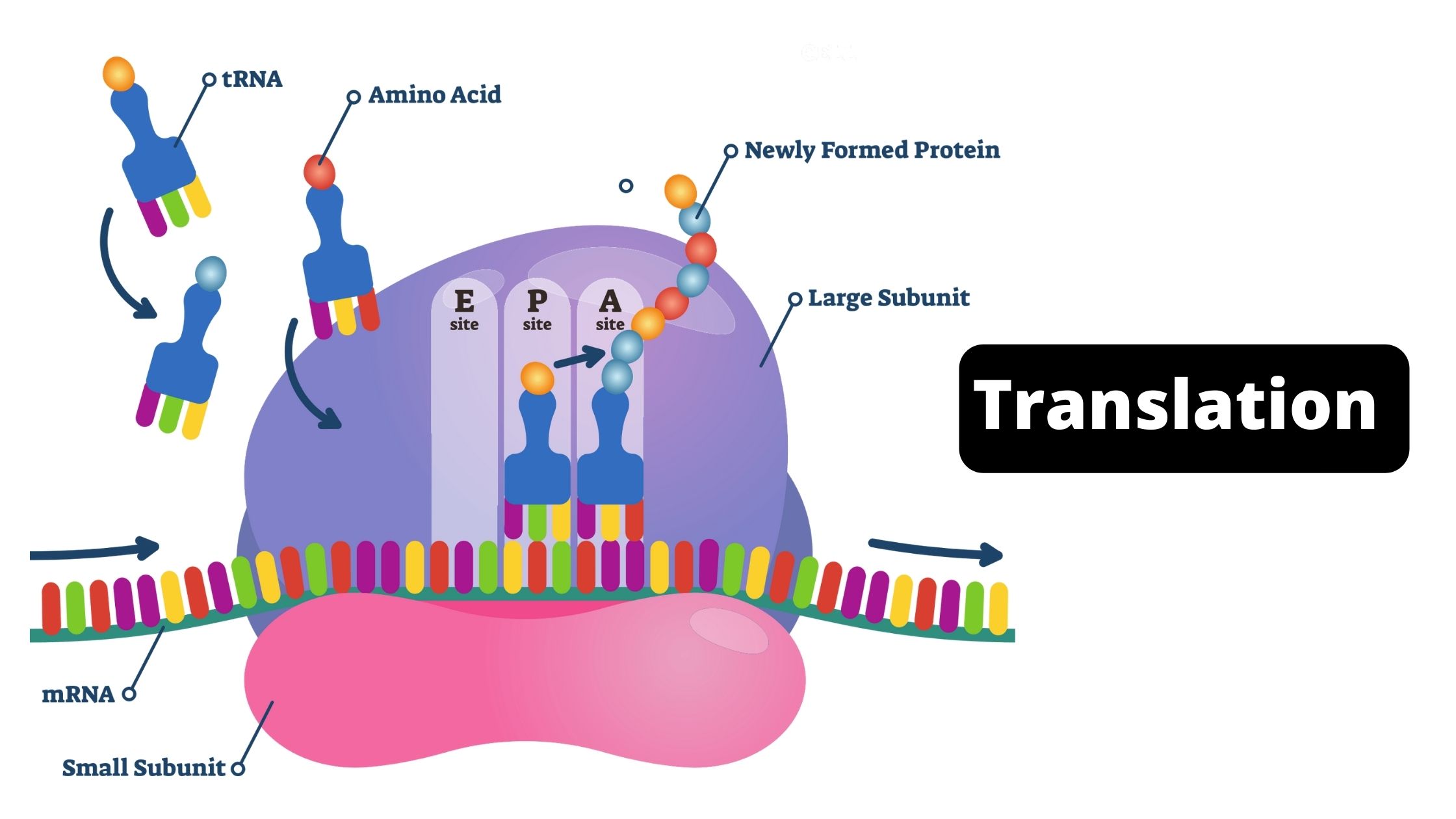
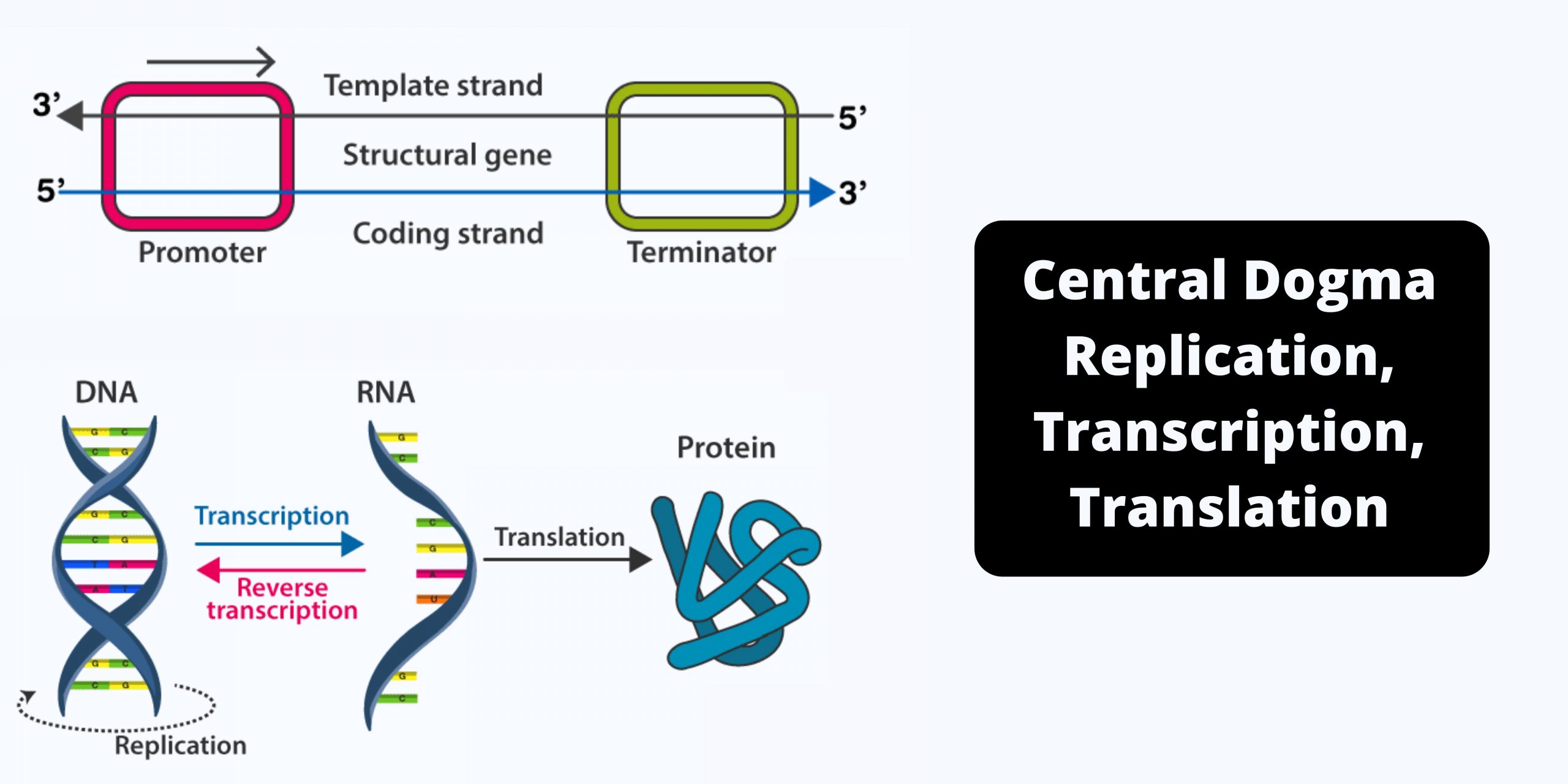
DNA Library – Types, Construction, Applications
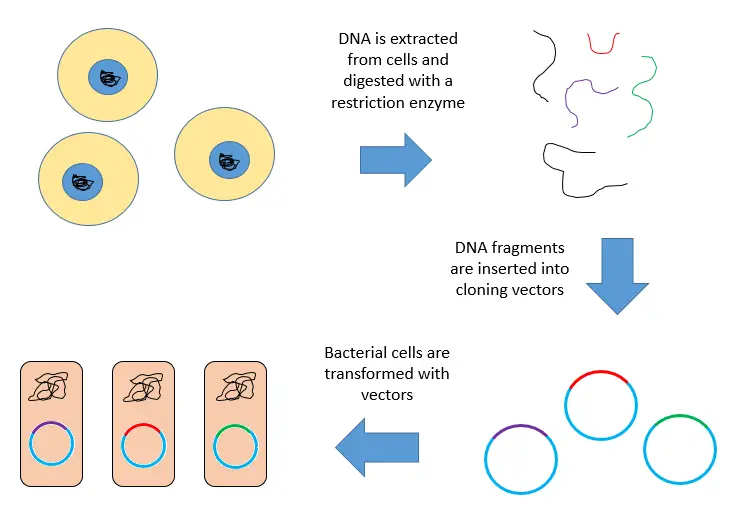
What is DNA Library (Genomic, cDNA)? Types of DNA Library There are two main types of DNA libraries: genomic libraries, and cDNA libraries. 1. Genomic Library 2. cDNA Library Genomic Library Construction Steps Genomic Library Construction Steps Creating a cDNA library begins with mRNA, which carries genetic instructions from DNA to ribosomes for protein synthesis. … Read more