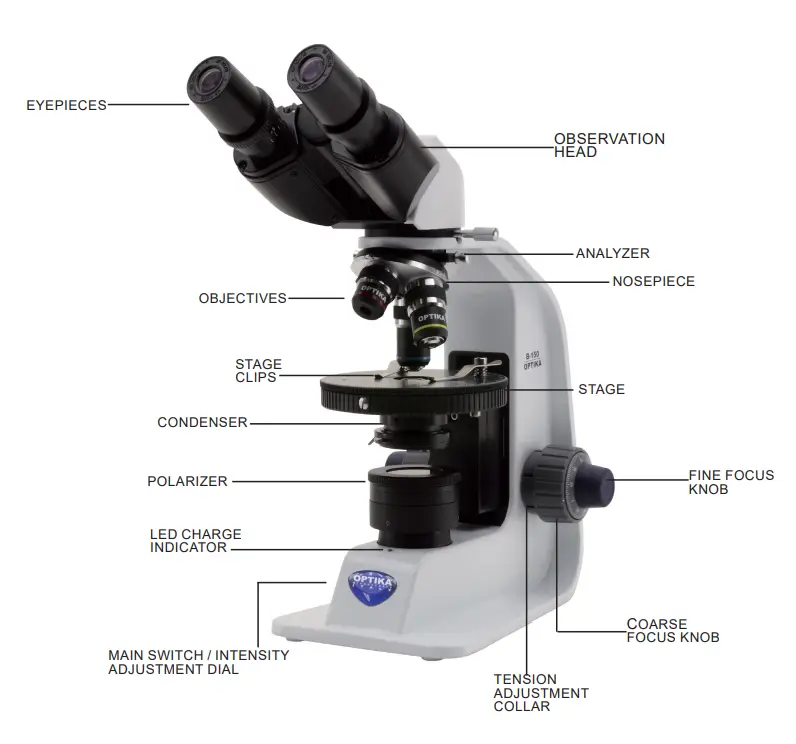
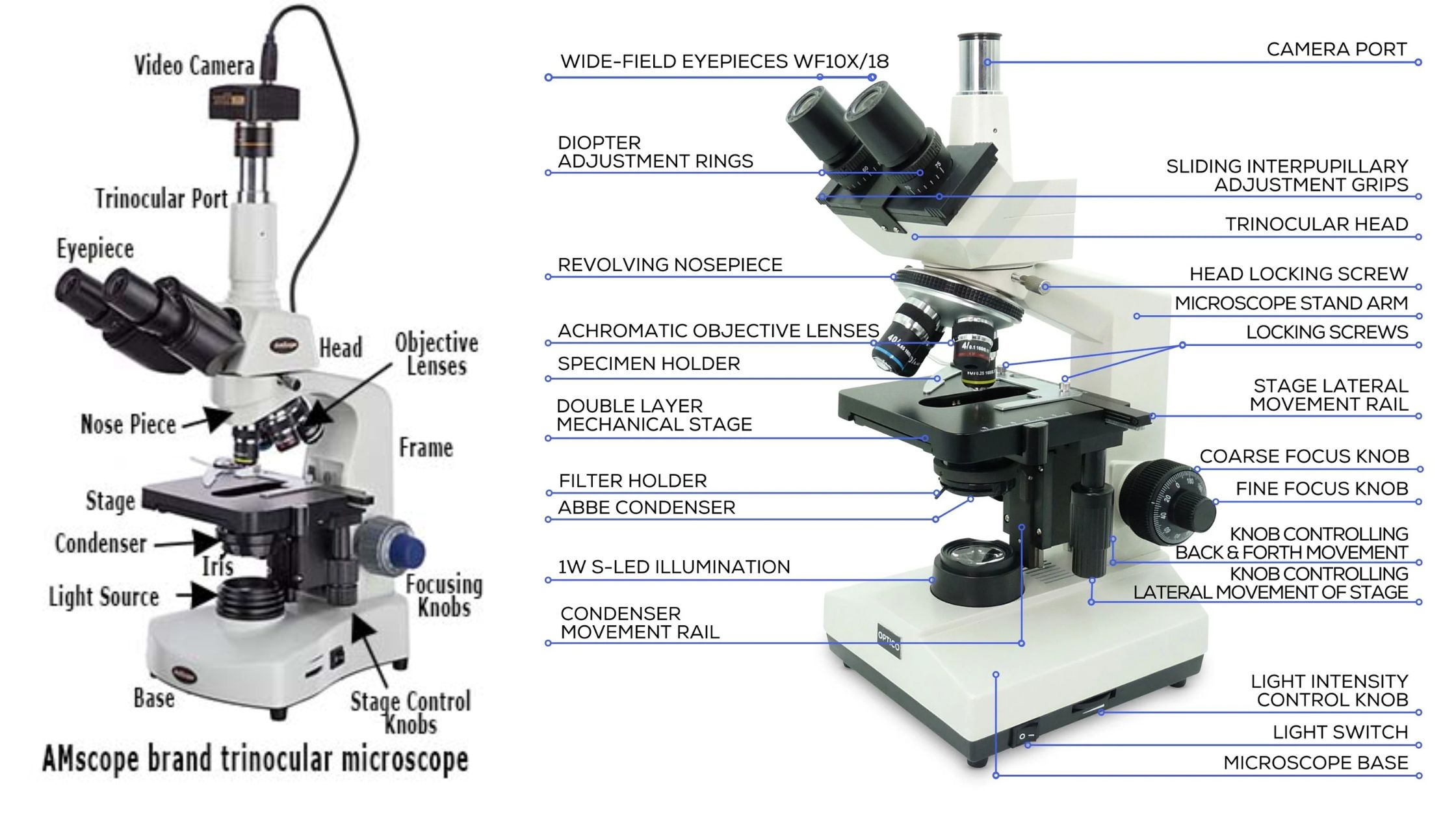
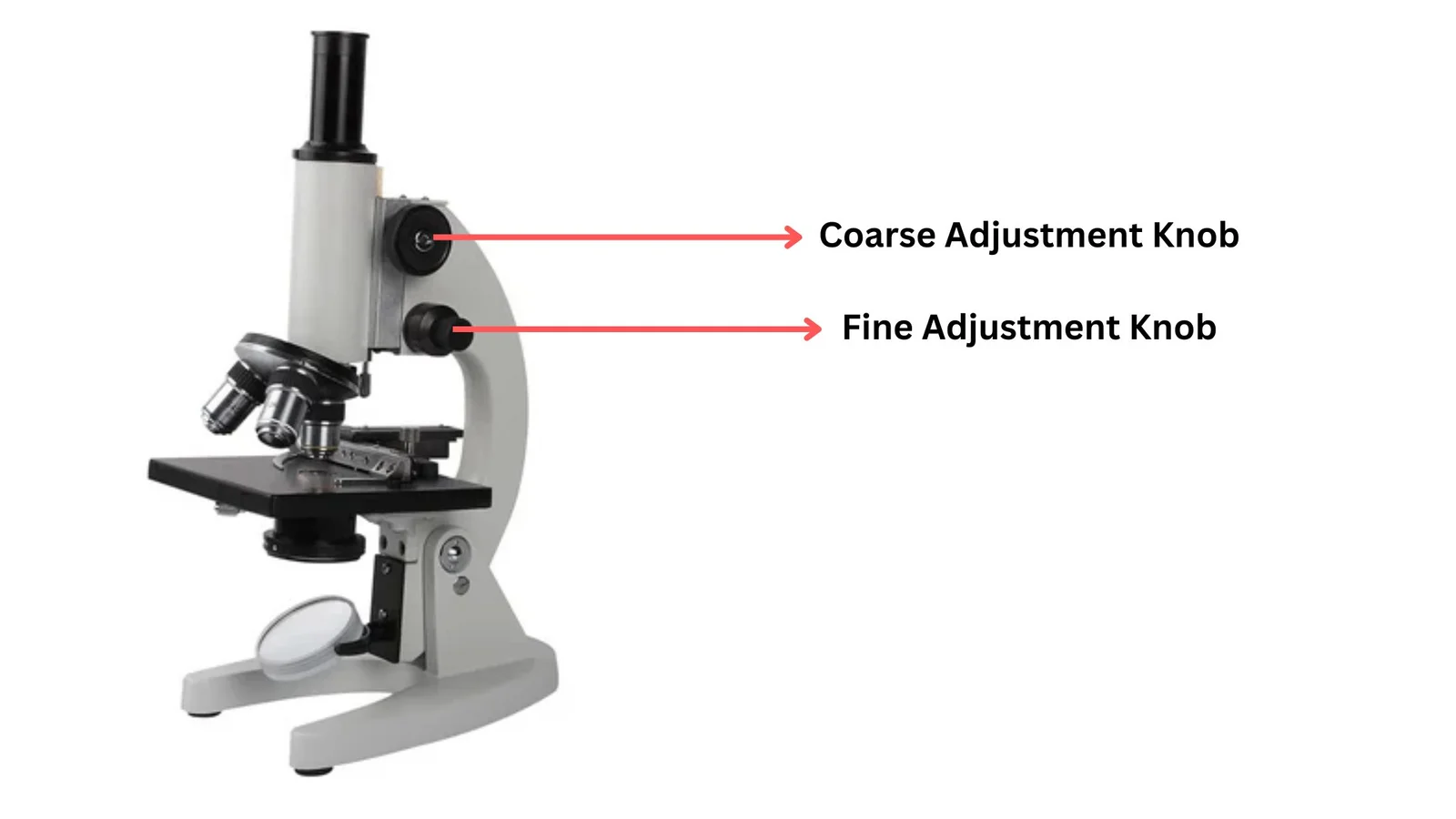
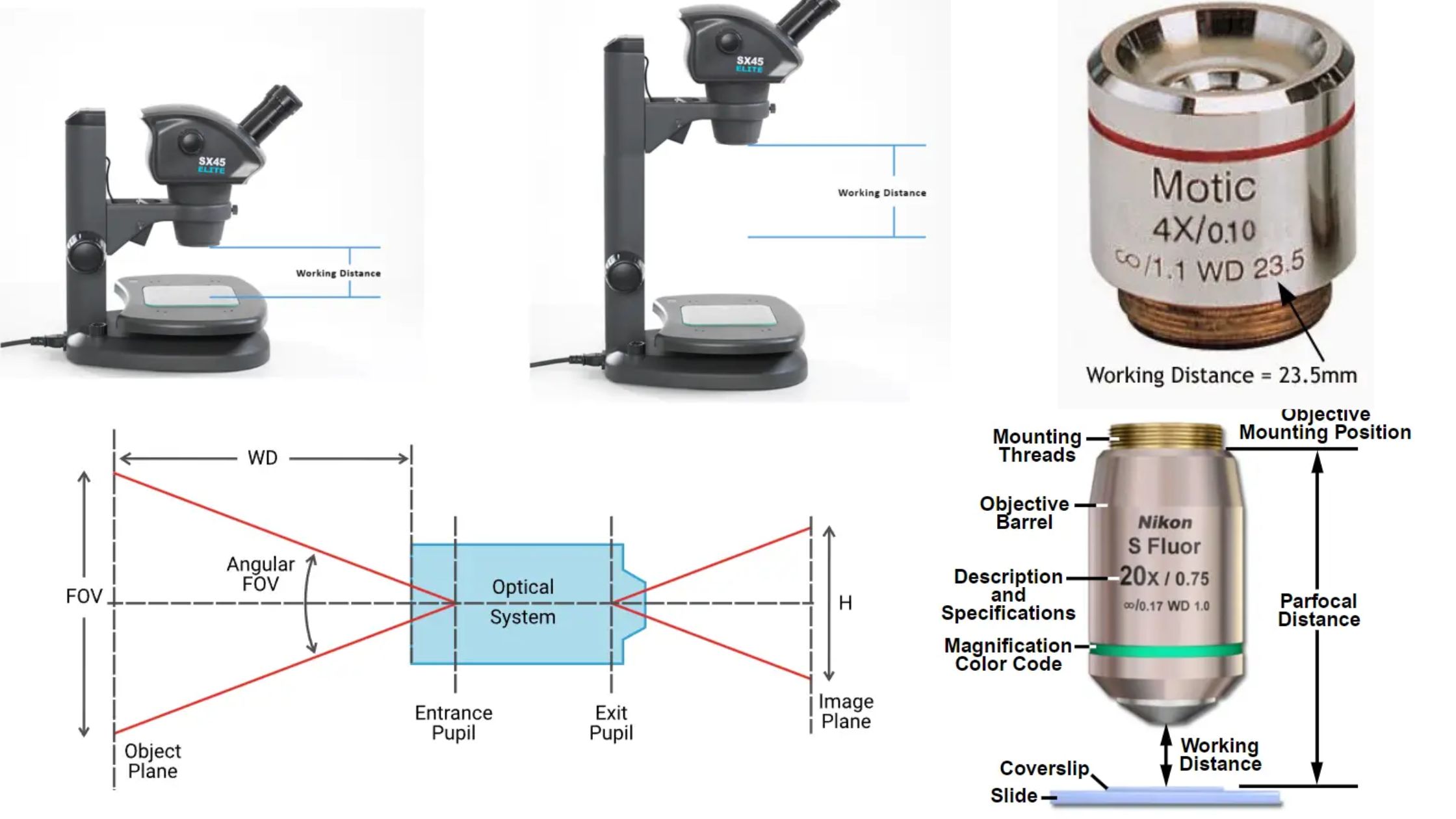
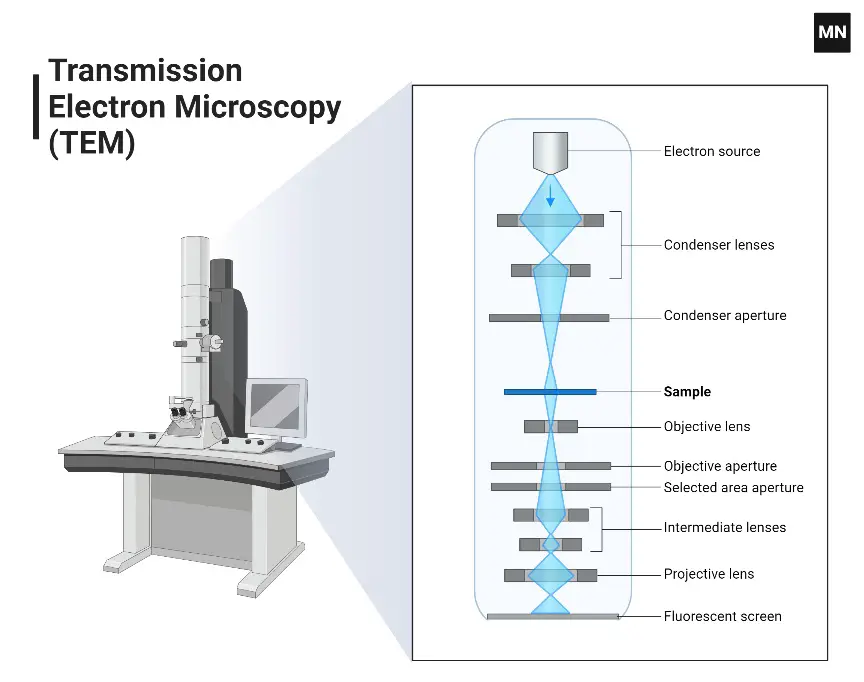
Trinocular Microscope – Definition, Principle, Parts, Protocol, Uses
What is Trinocular Microscope? Principle of Trinocular Microscope The principle of a trinocular microscope builds upon the fundamental concept of a binocular microscope, incorporating an additional third eyepiece that serves the purpose of connecting a microscope camera. The core principle involves the illumination of the specimen using light from an LED source, followed by the … Read more