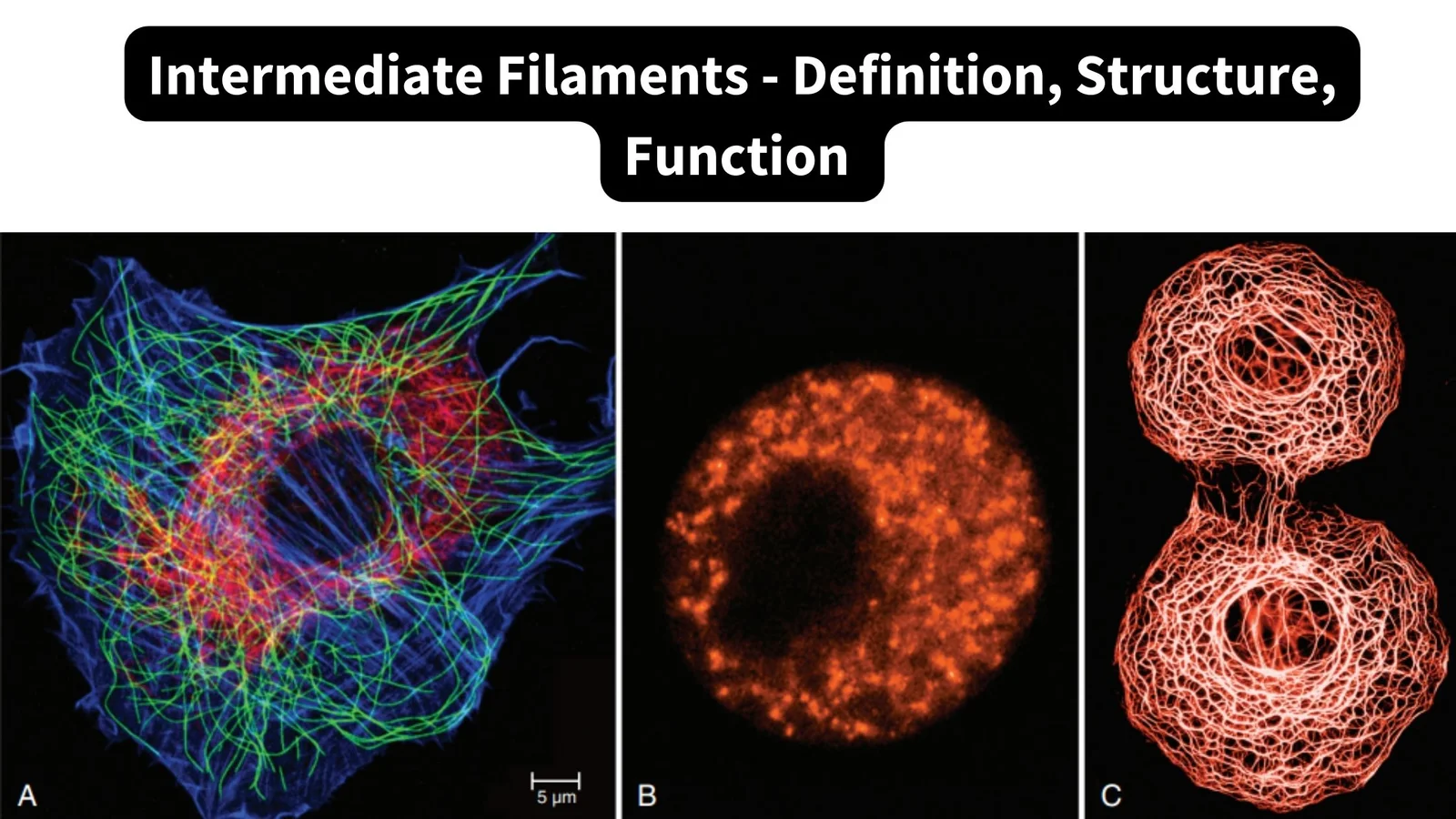
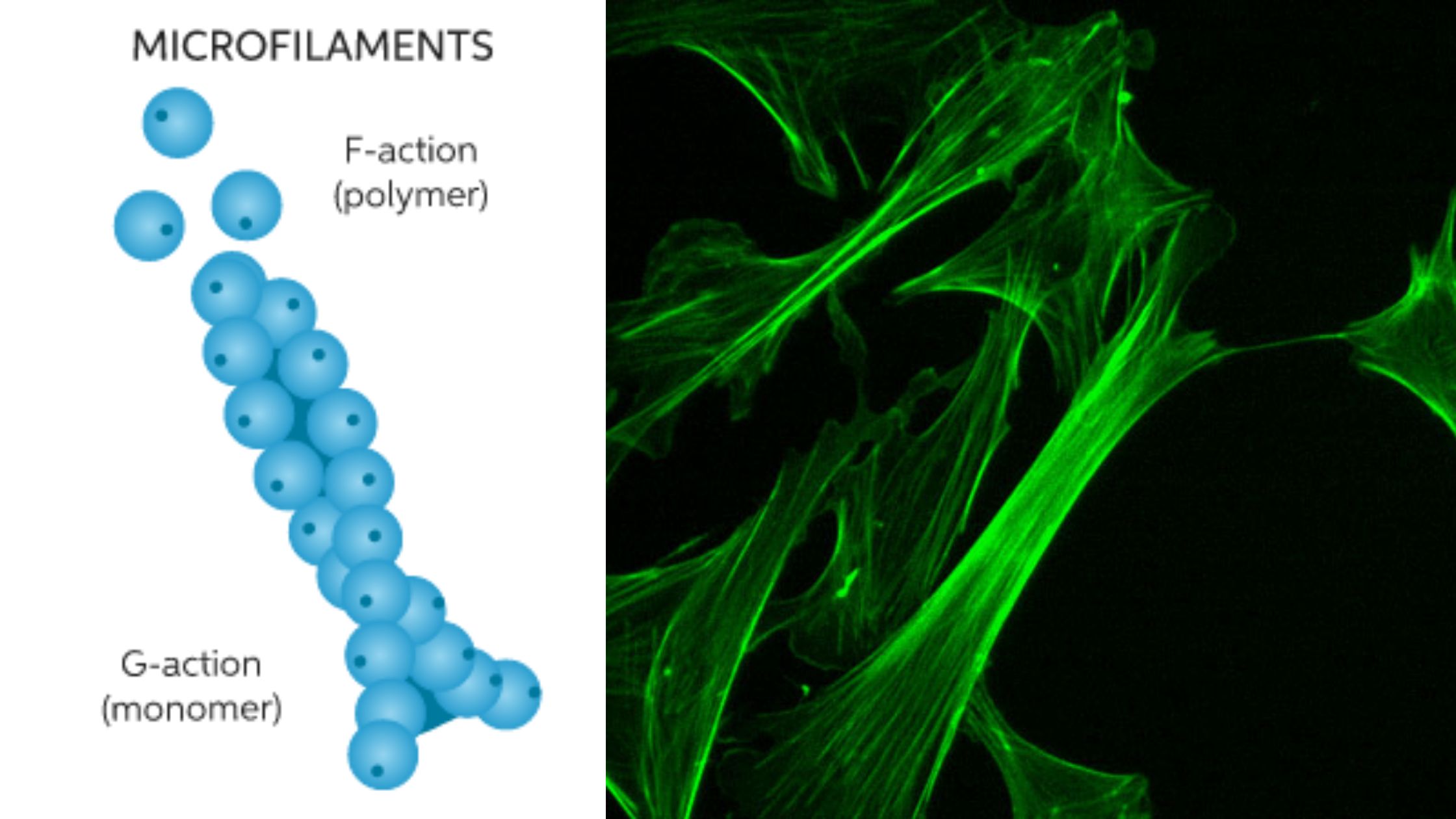
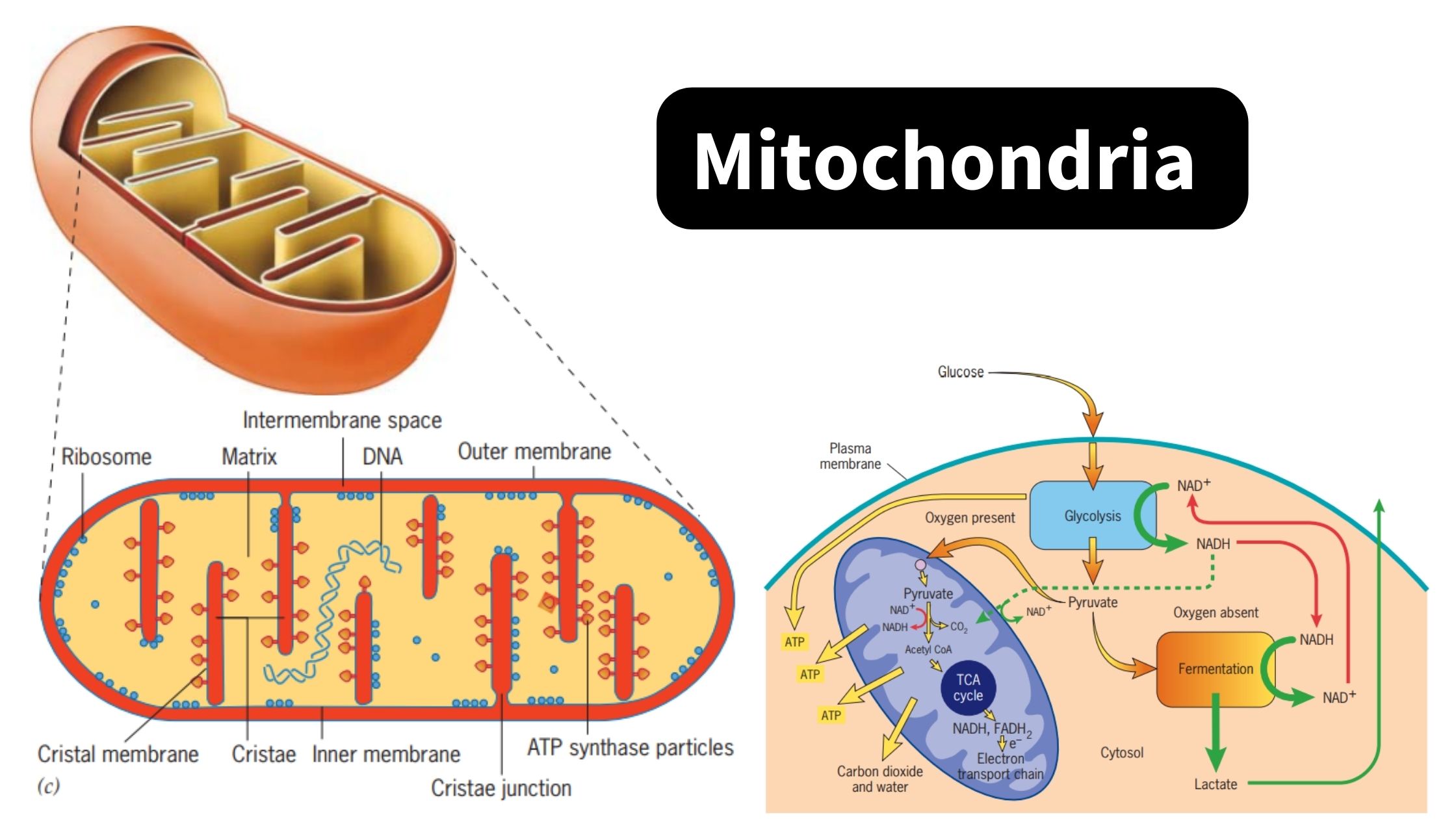
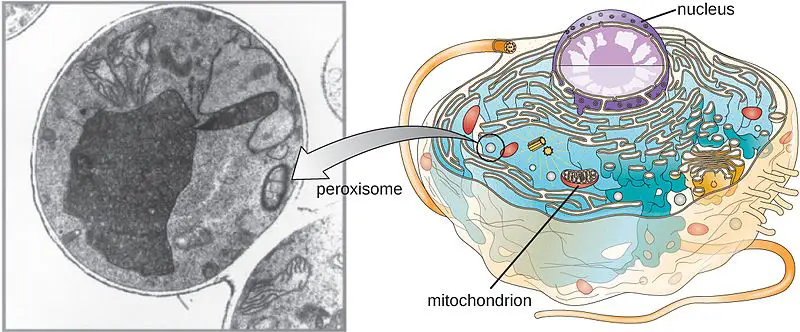
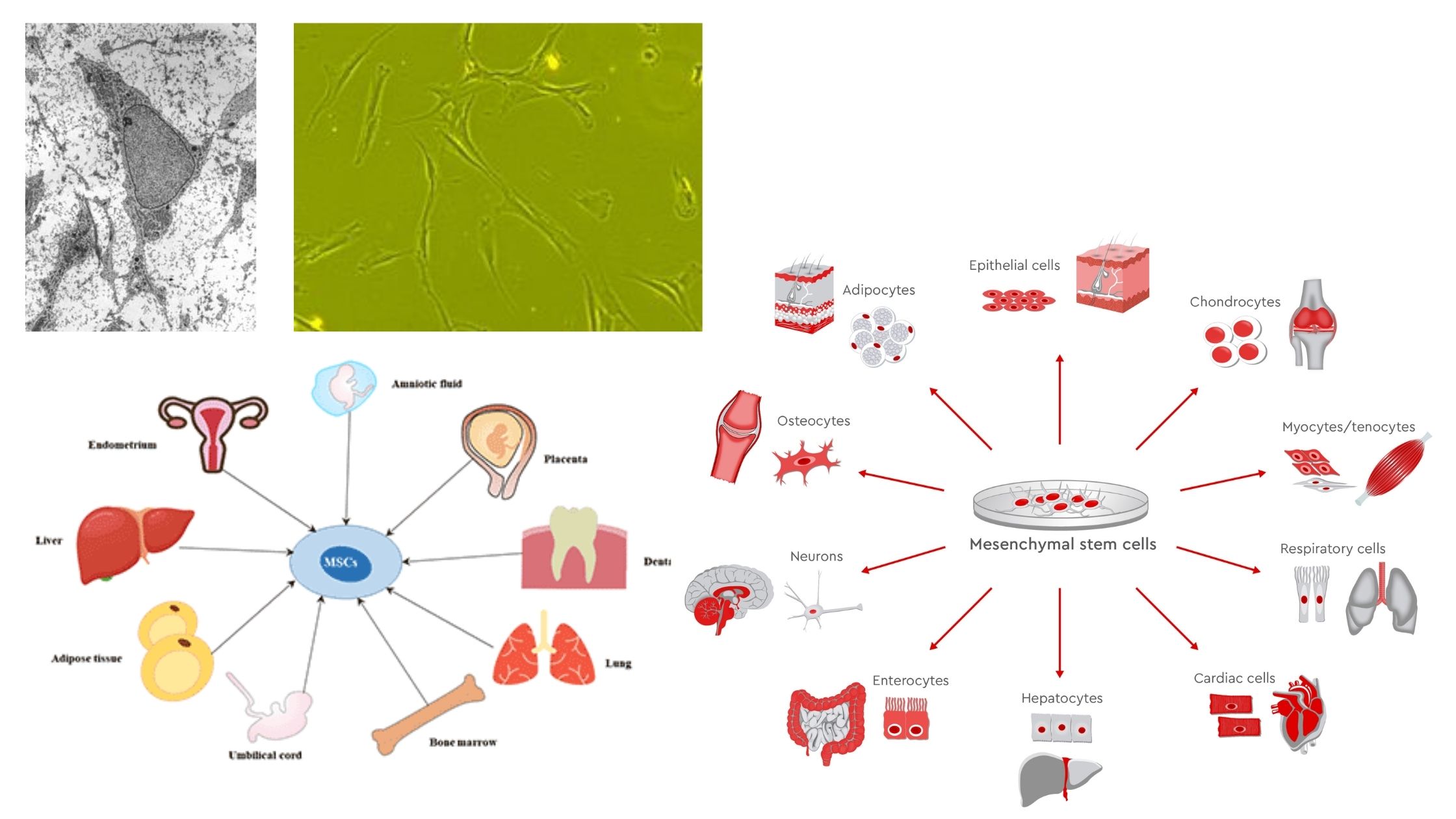
Peripheral Protein – Structure, Examples, Functions
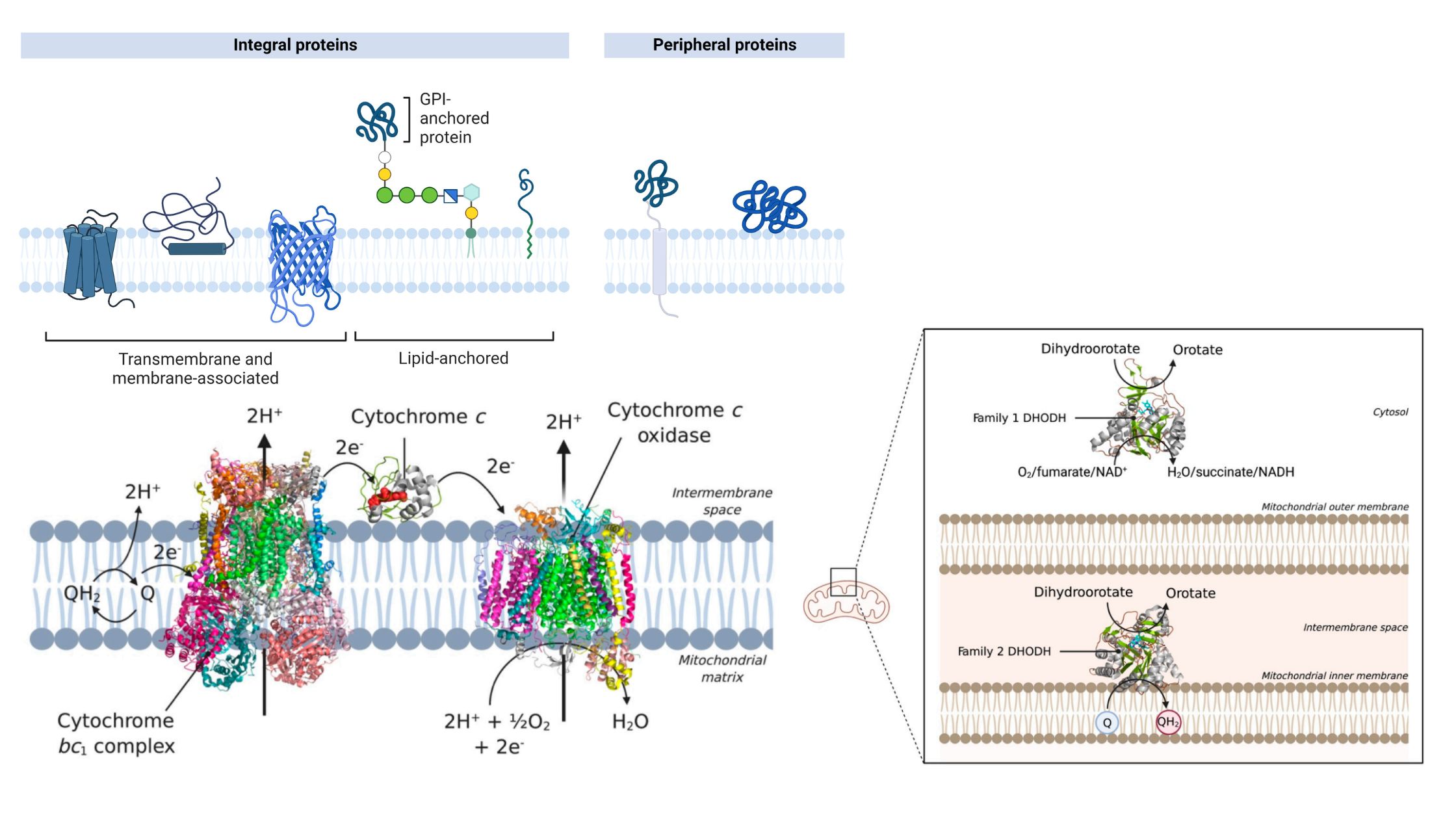
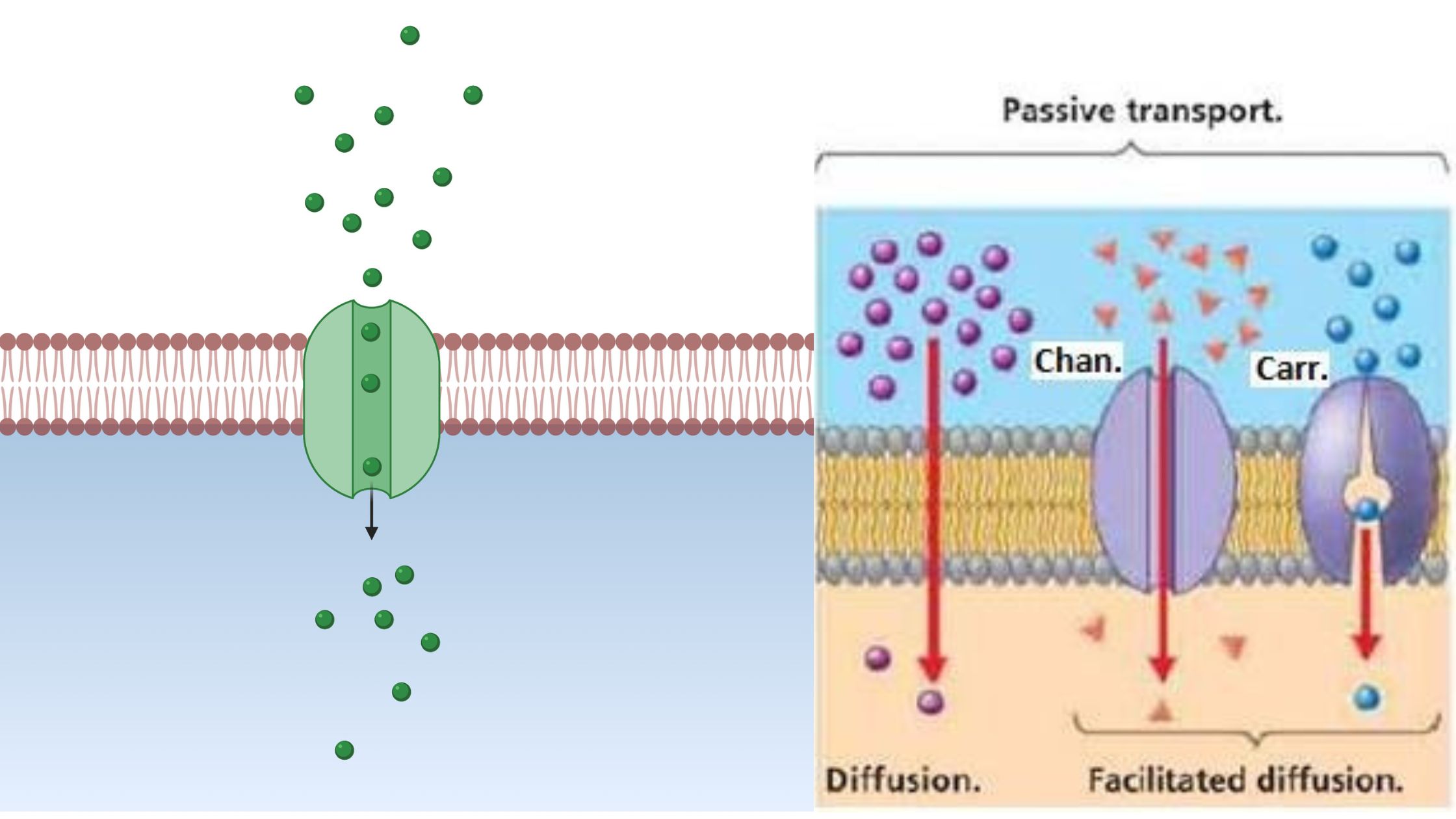
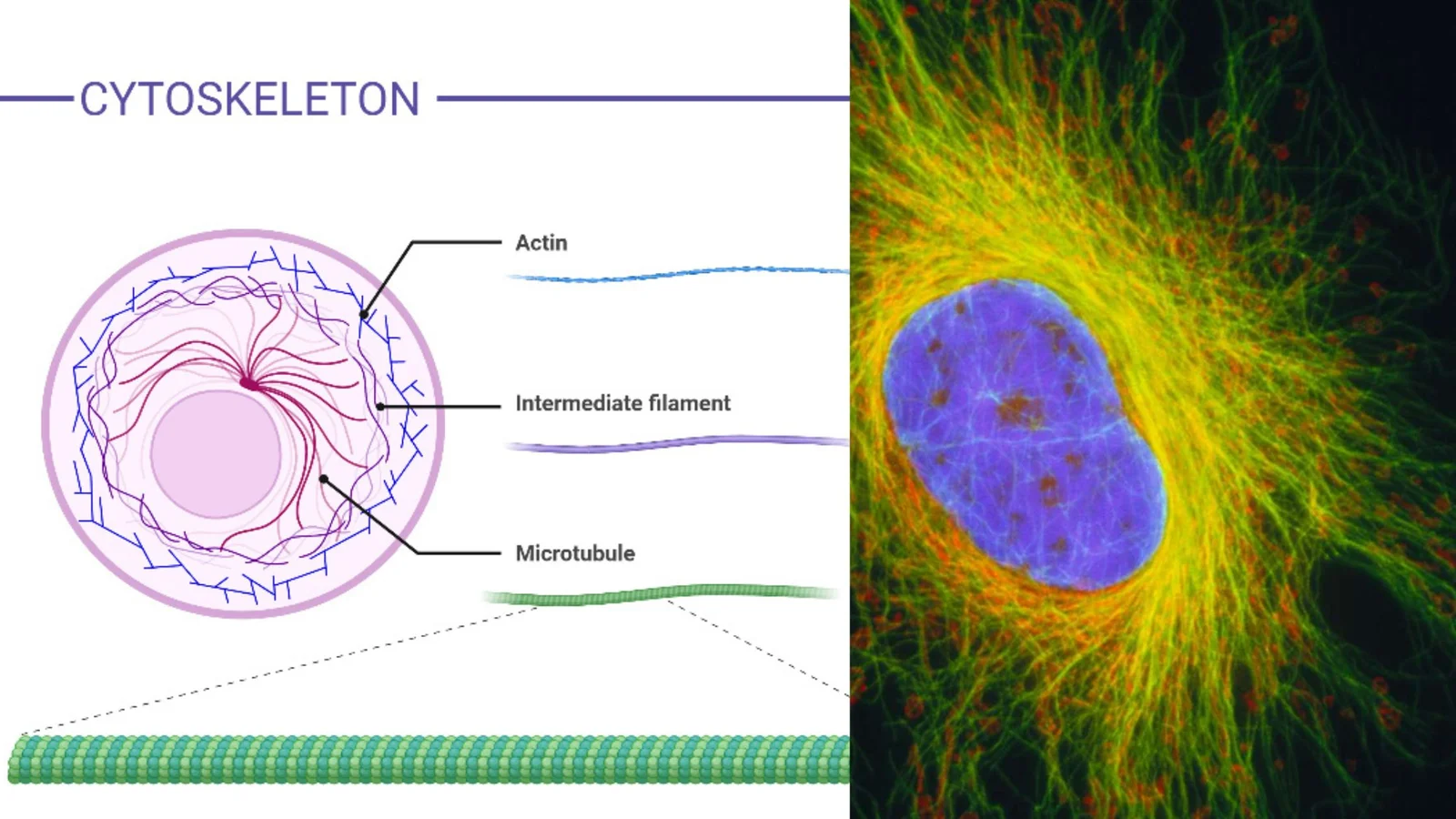
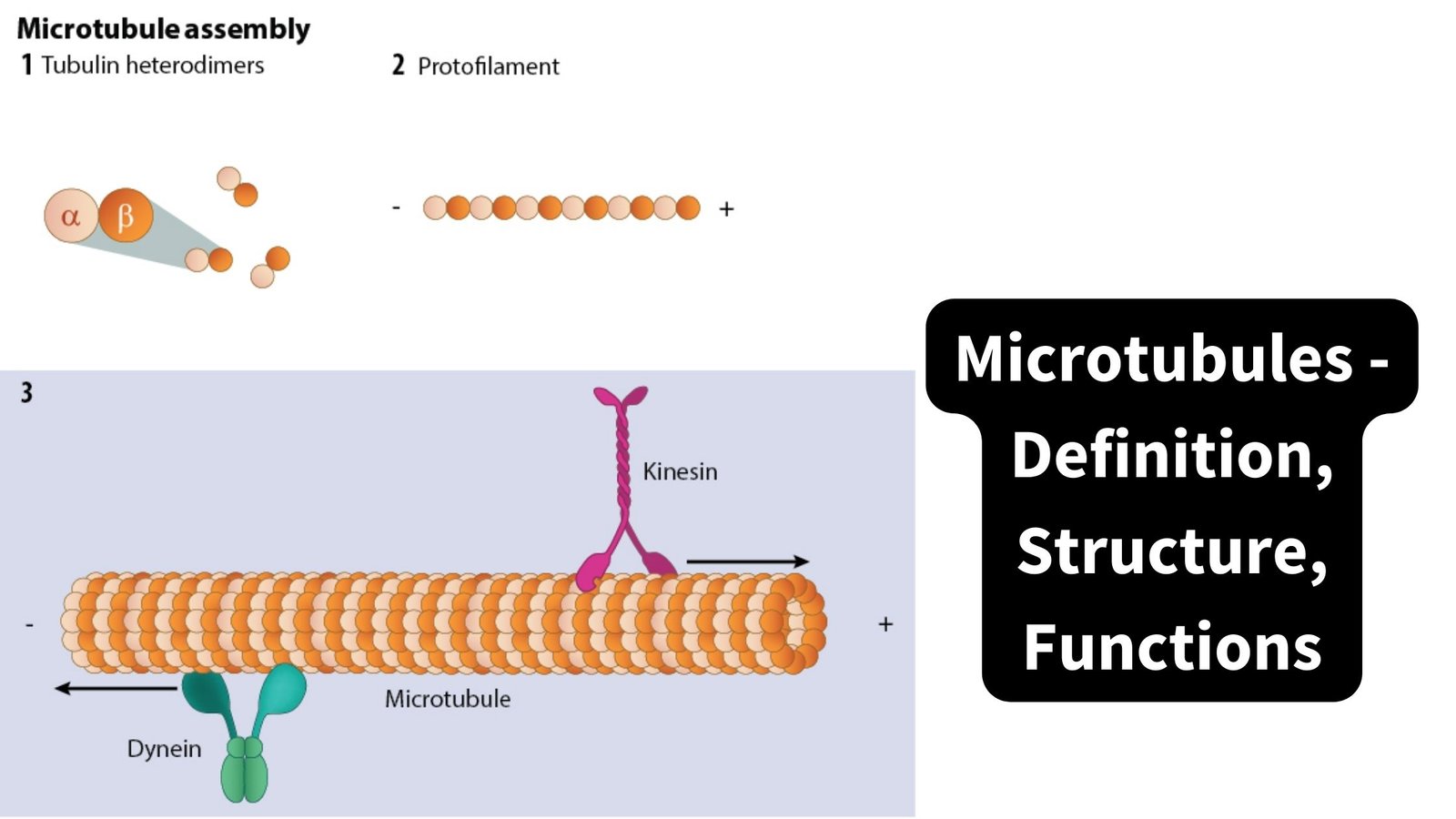
What is Peripheral Protein? Structure of Peripheral Proteins Several peripheral proteins are marked in the picture below. A peripheral protein doesn’t have a clear structure, but it does have a few important features that make it what it is. Example of Peripheral Proteins Alternative Oxidase Cytochrome c Type-II NADH Dehydrogenase Dihydroorotate Dehydrogenase Functions of Peripheral … Read more