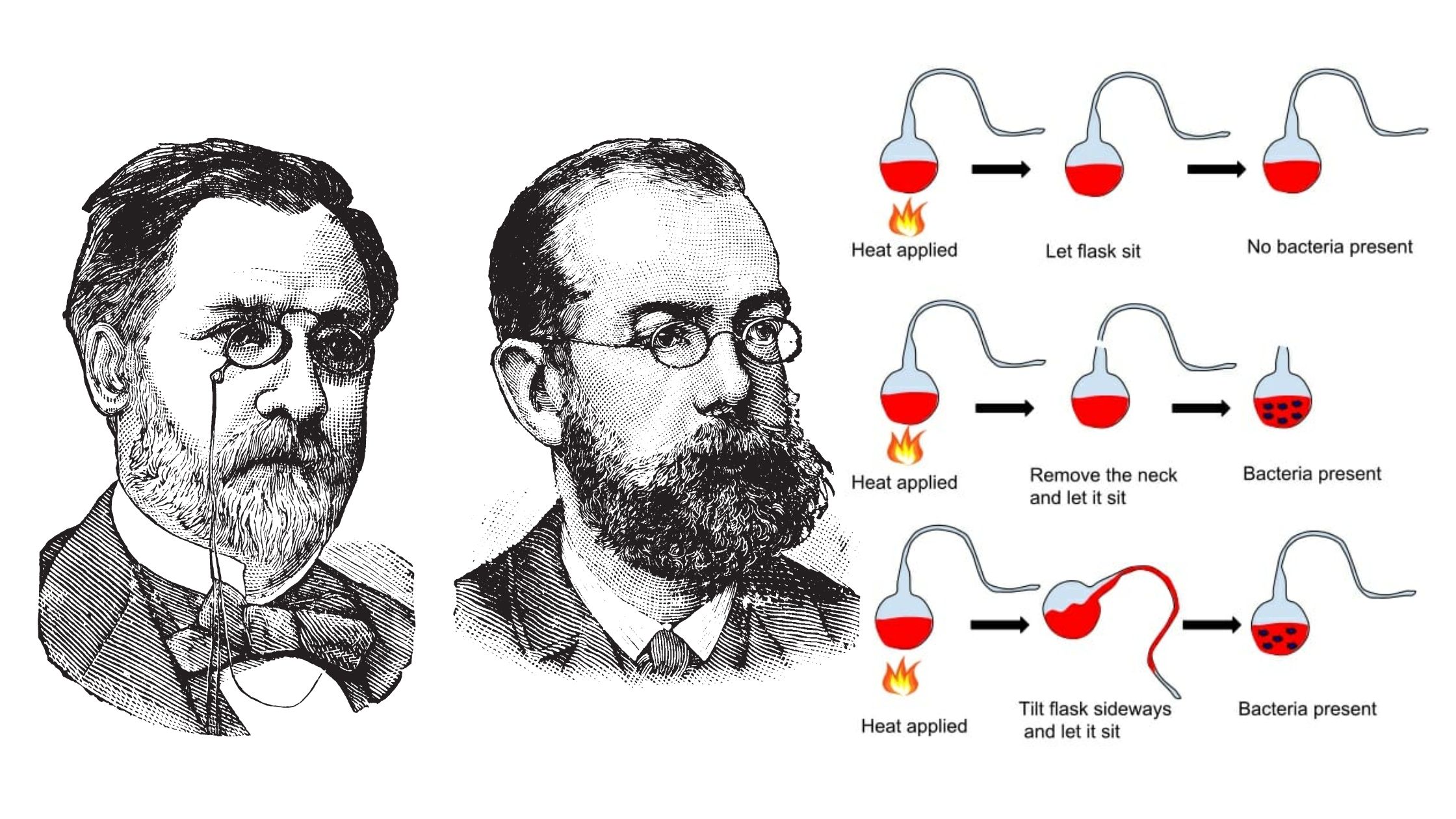
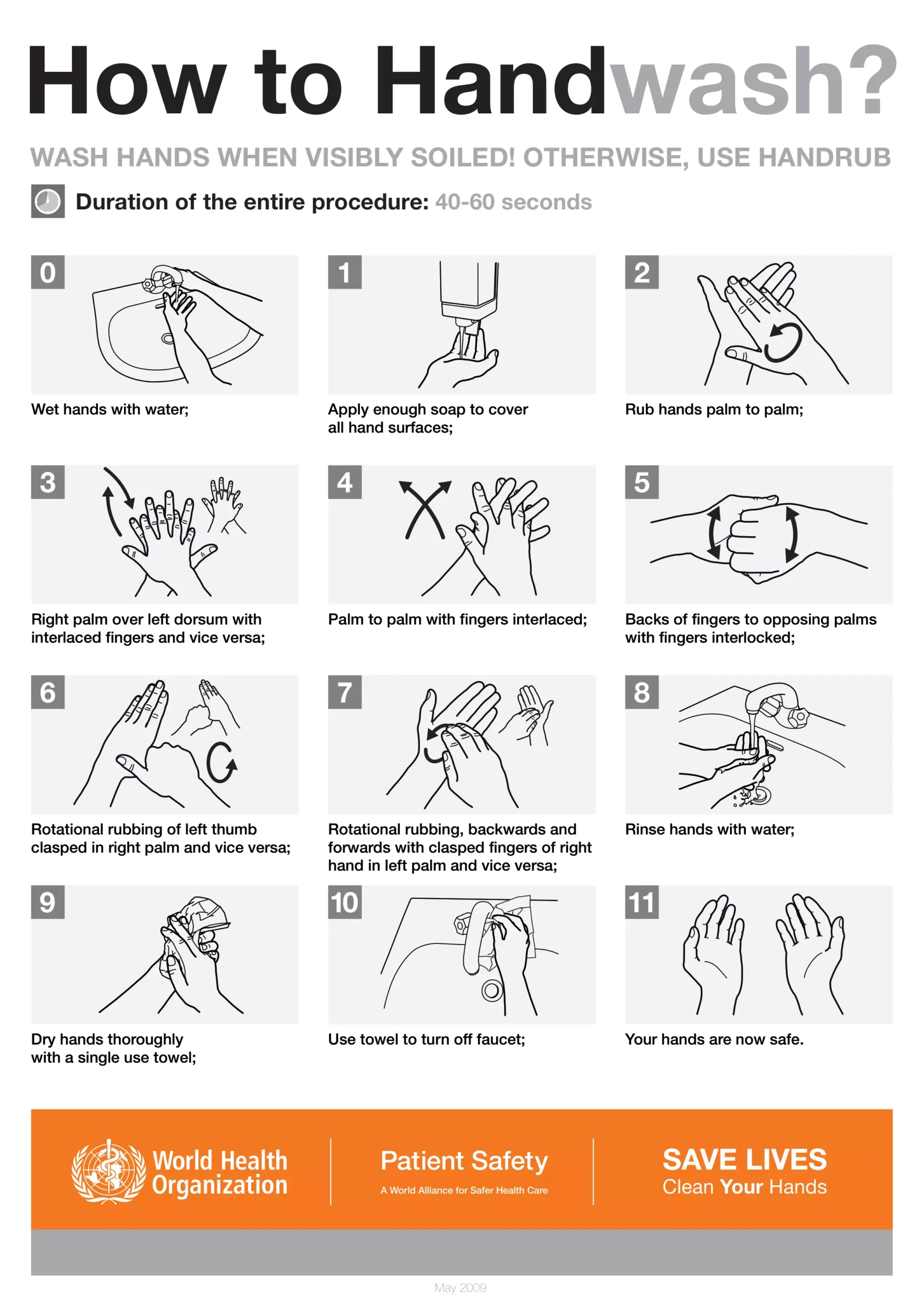
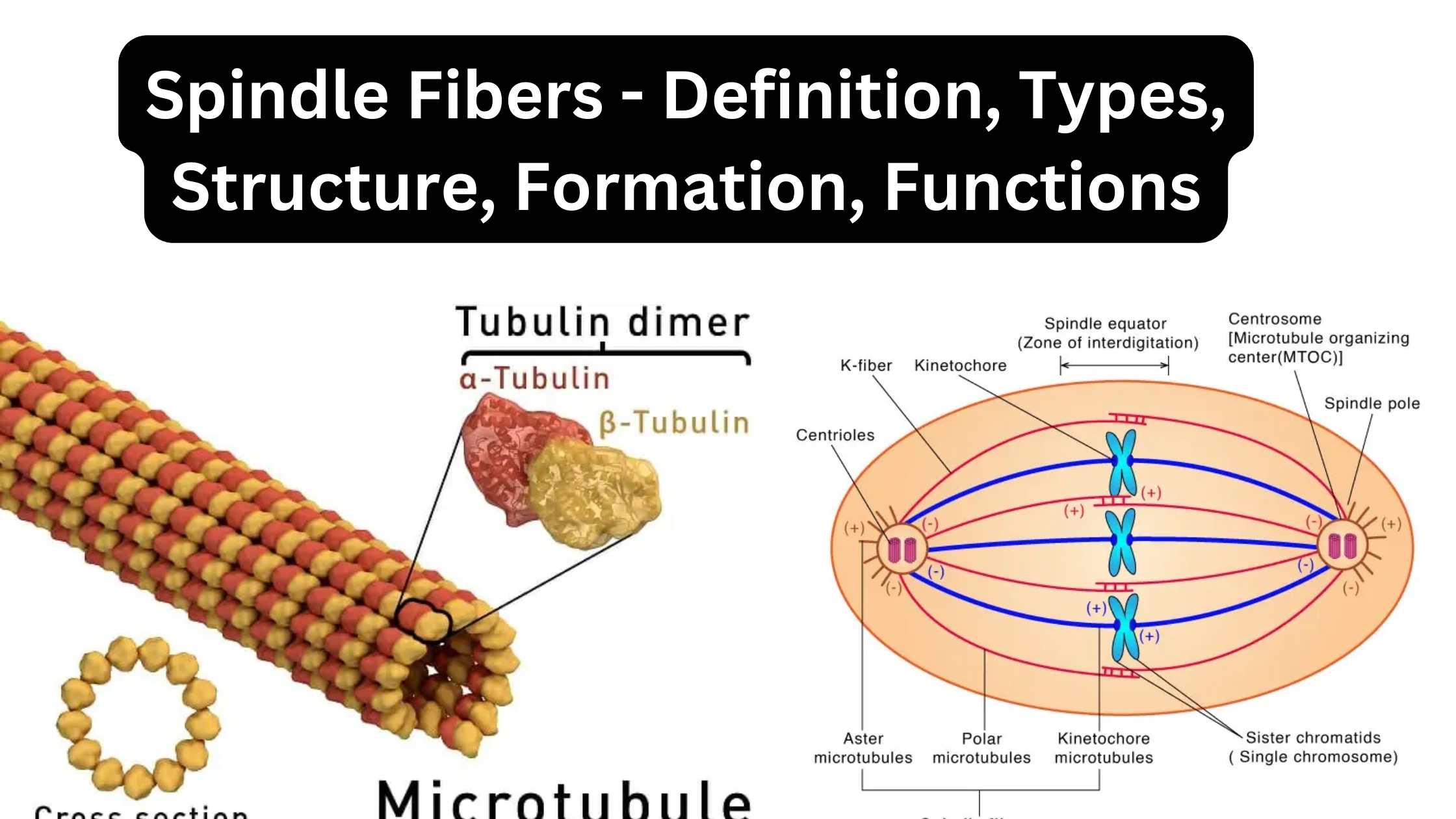
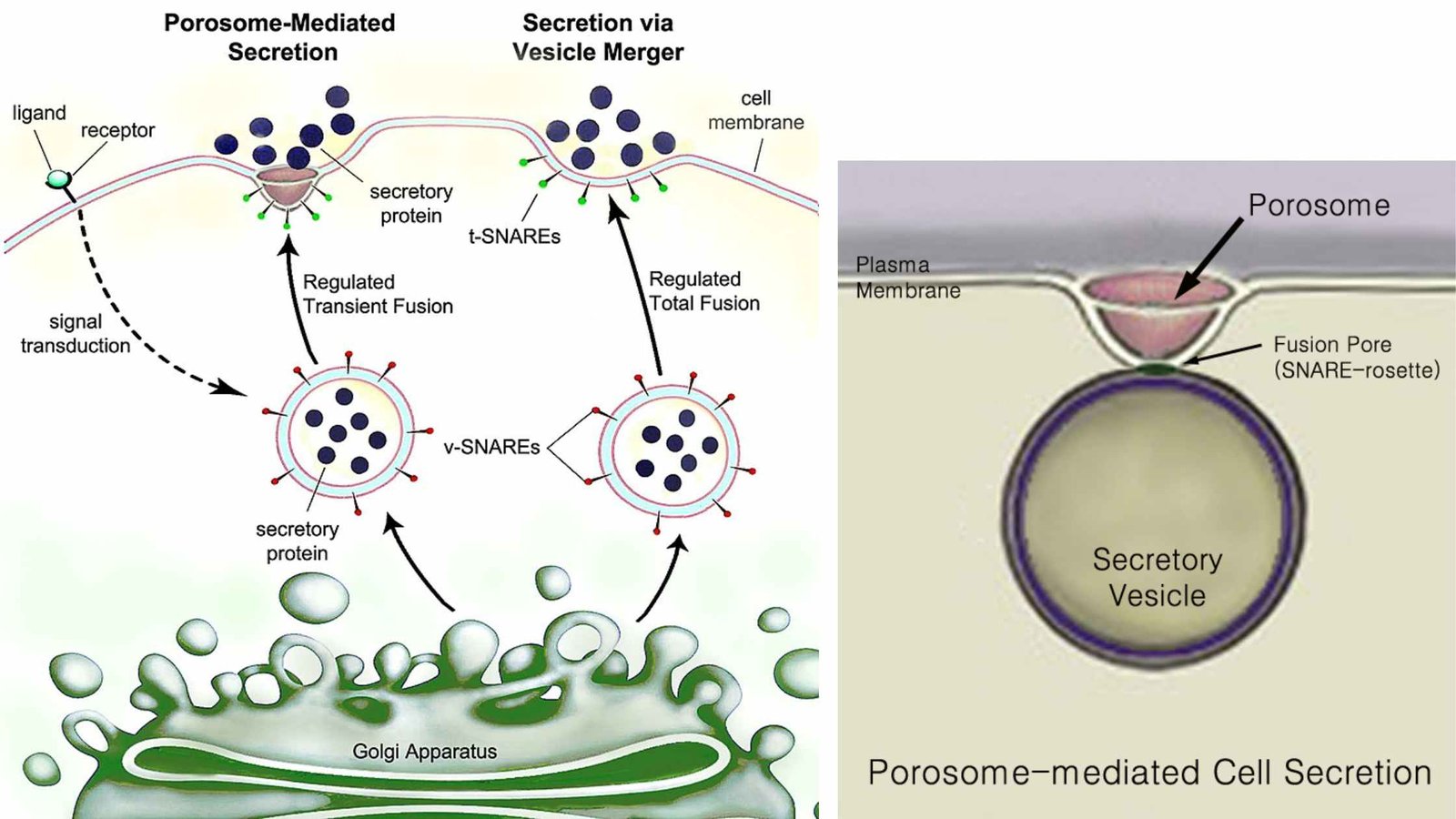
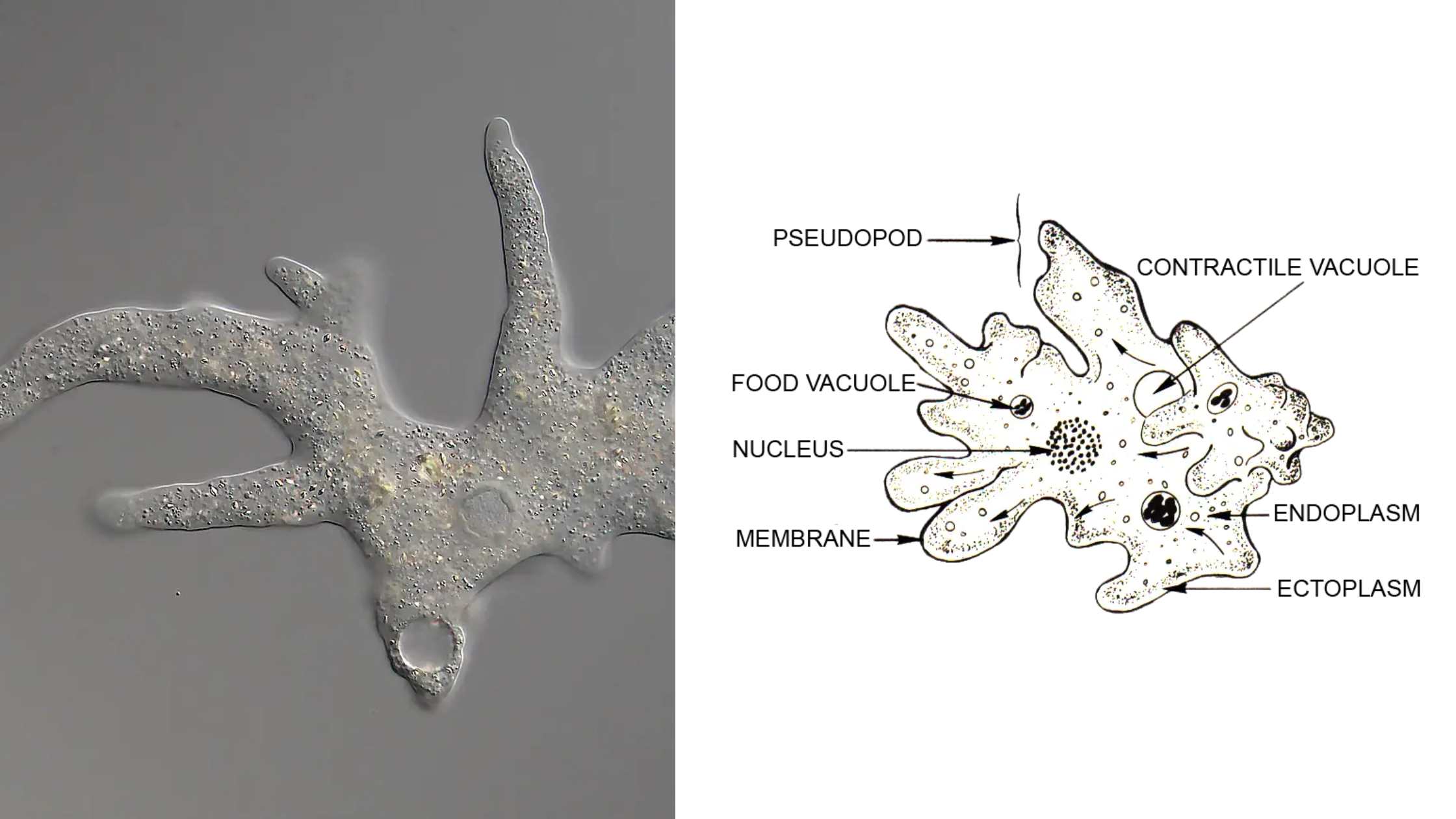
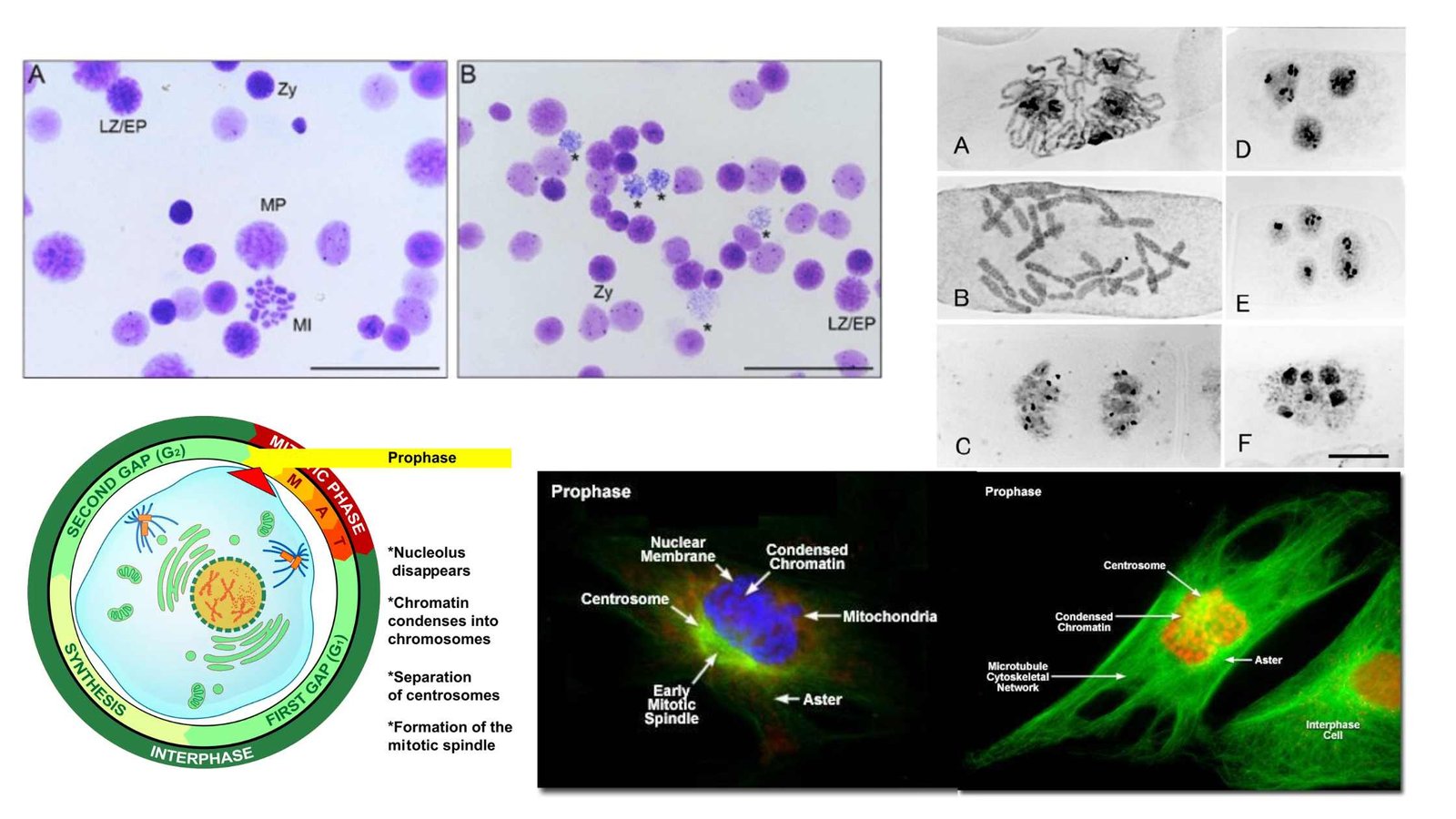
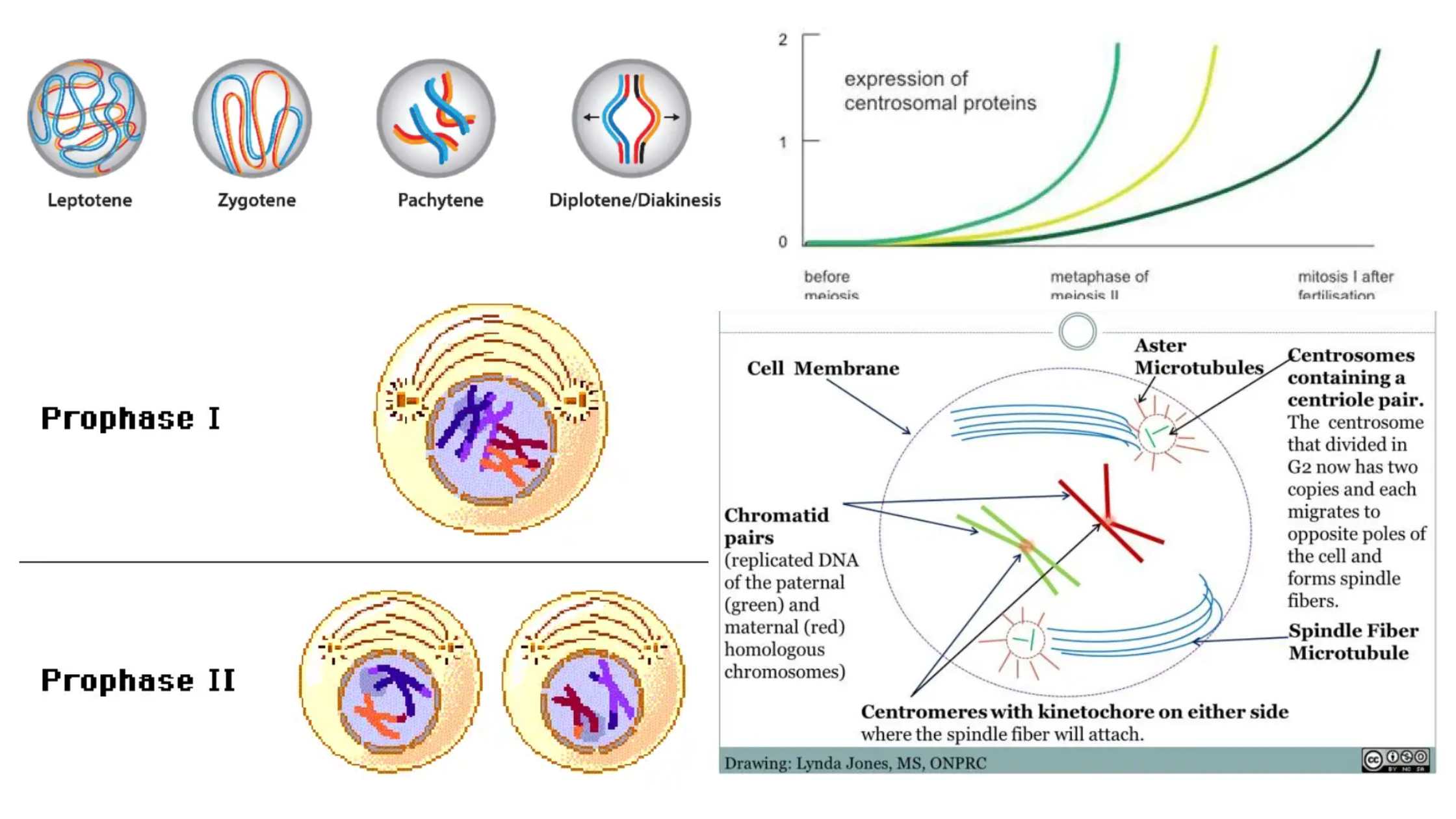
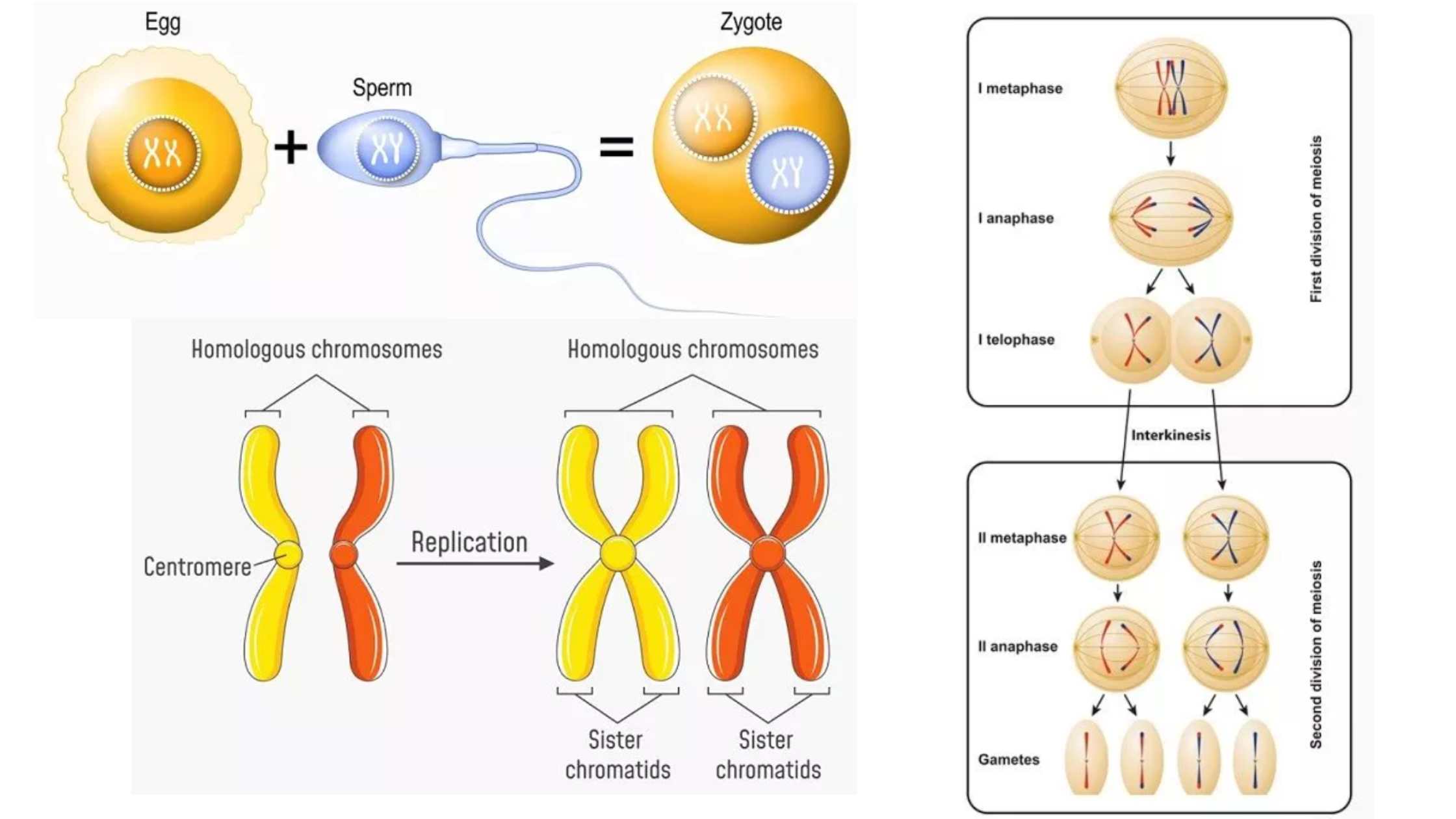
Germ Theory of Disease
What is Germ Theory of Disease? Key principles of the germ theory of disease The key principles of the germ theory of disease can be summarized as follows: These principles collectively form the foundation of the germ theory of disease, guiding our understanding of the causes, transmission, prevention, and treatment of infectious diseases. Germ theory … Read more