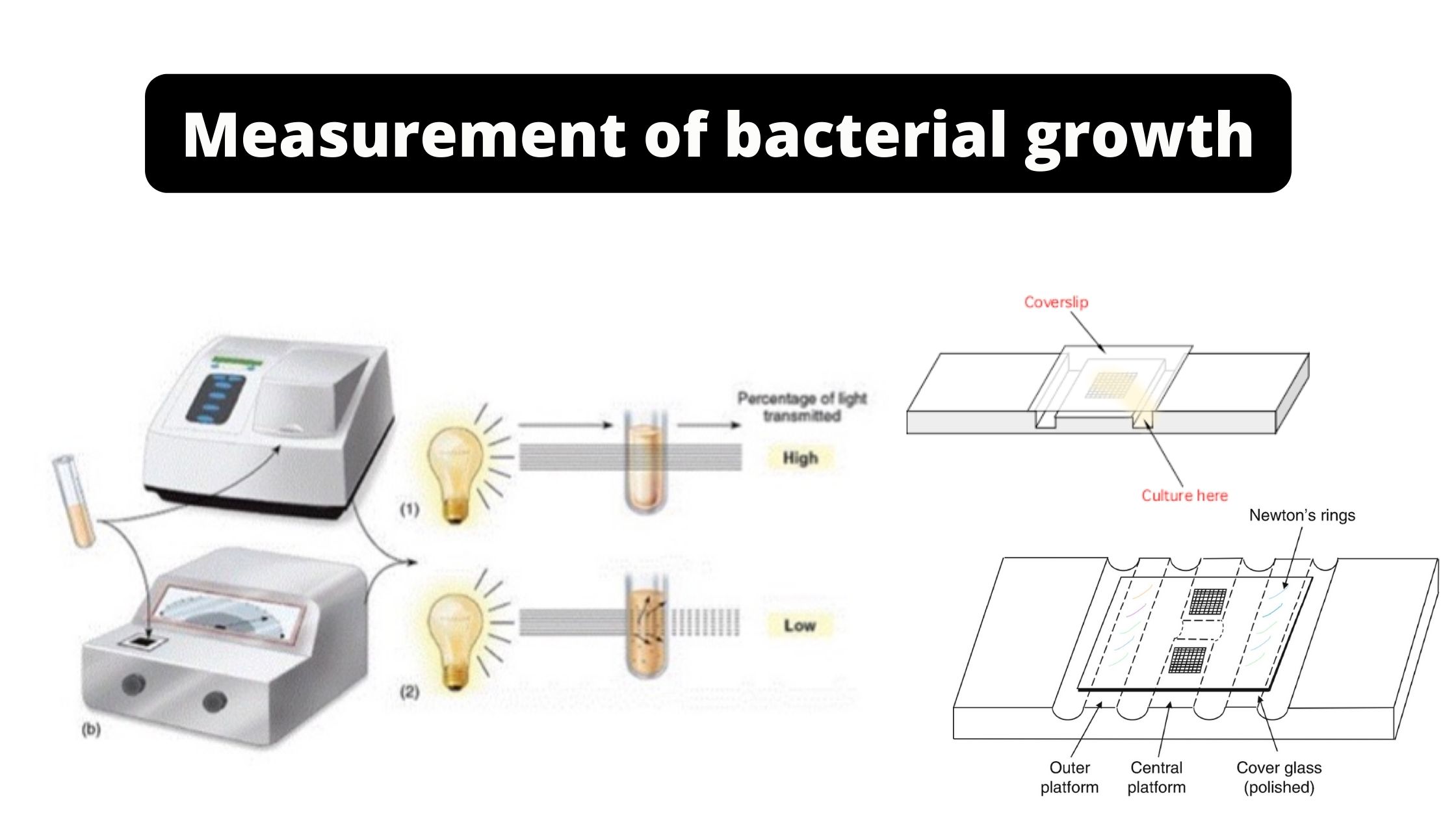
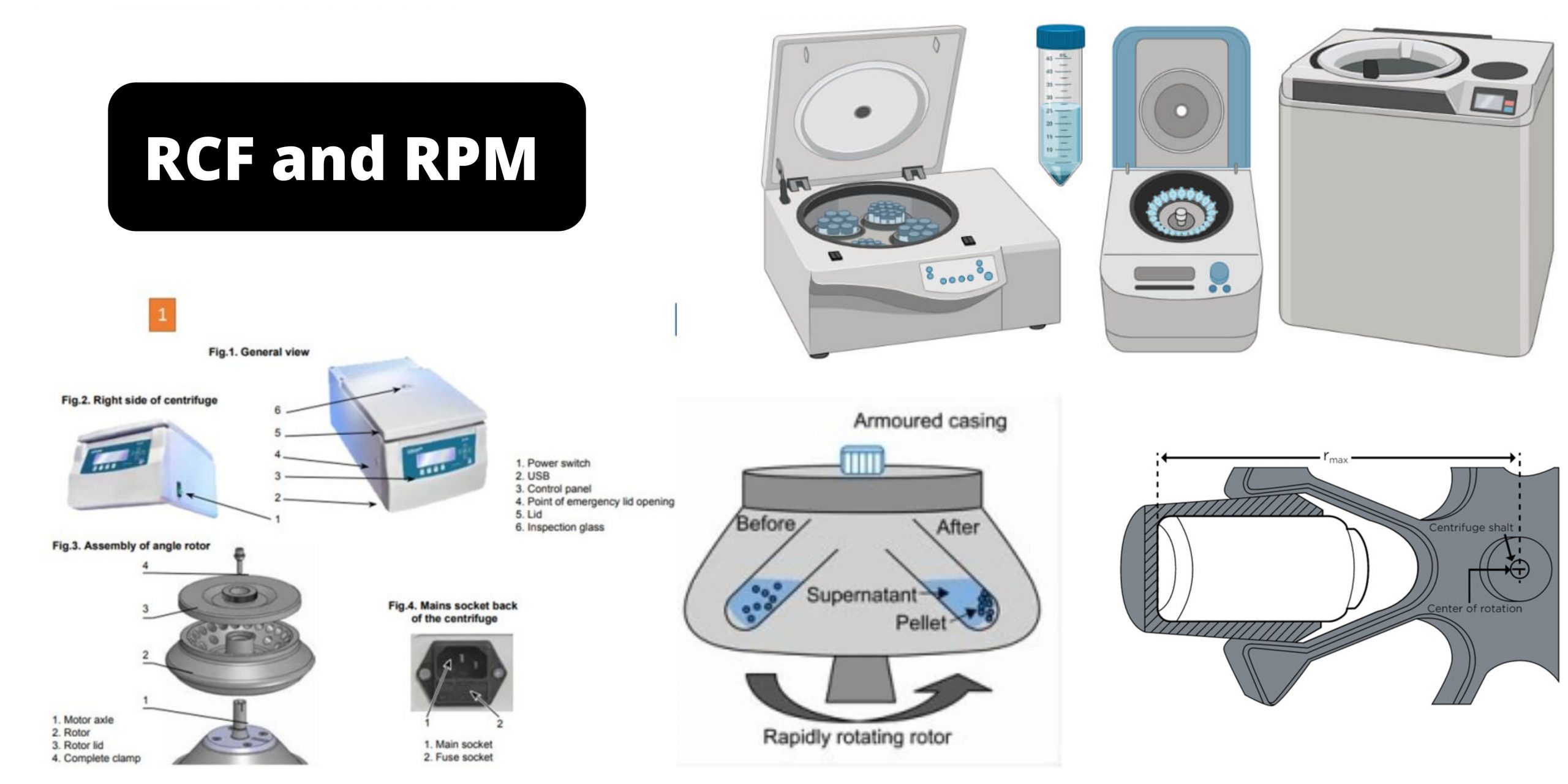
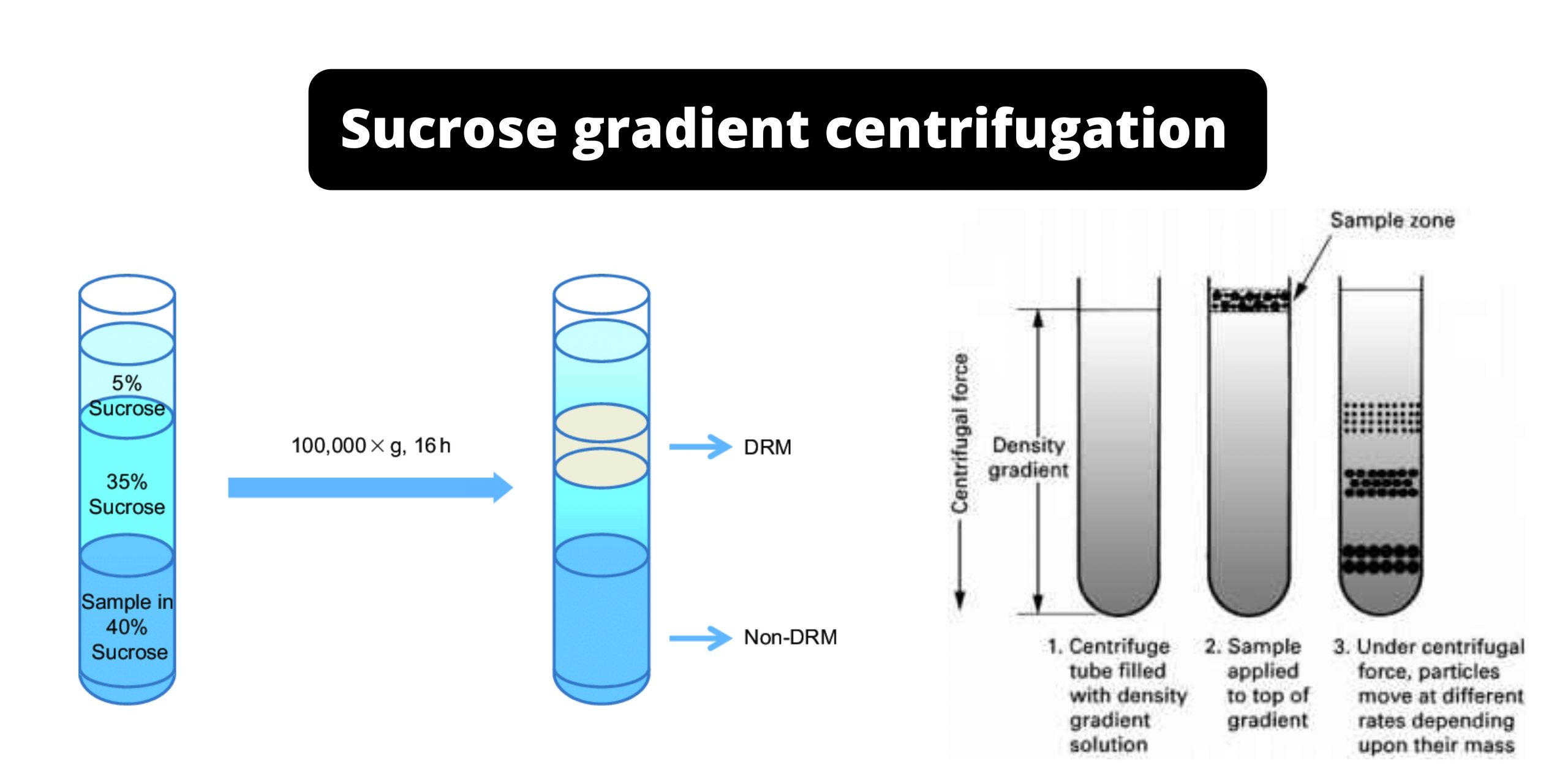
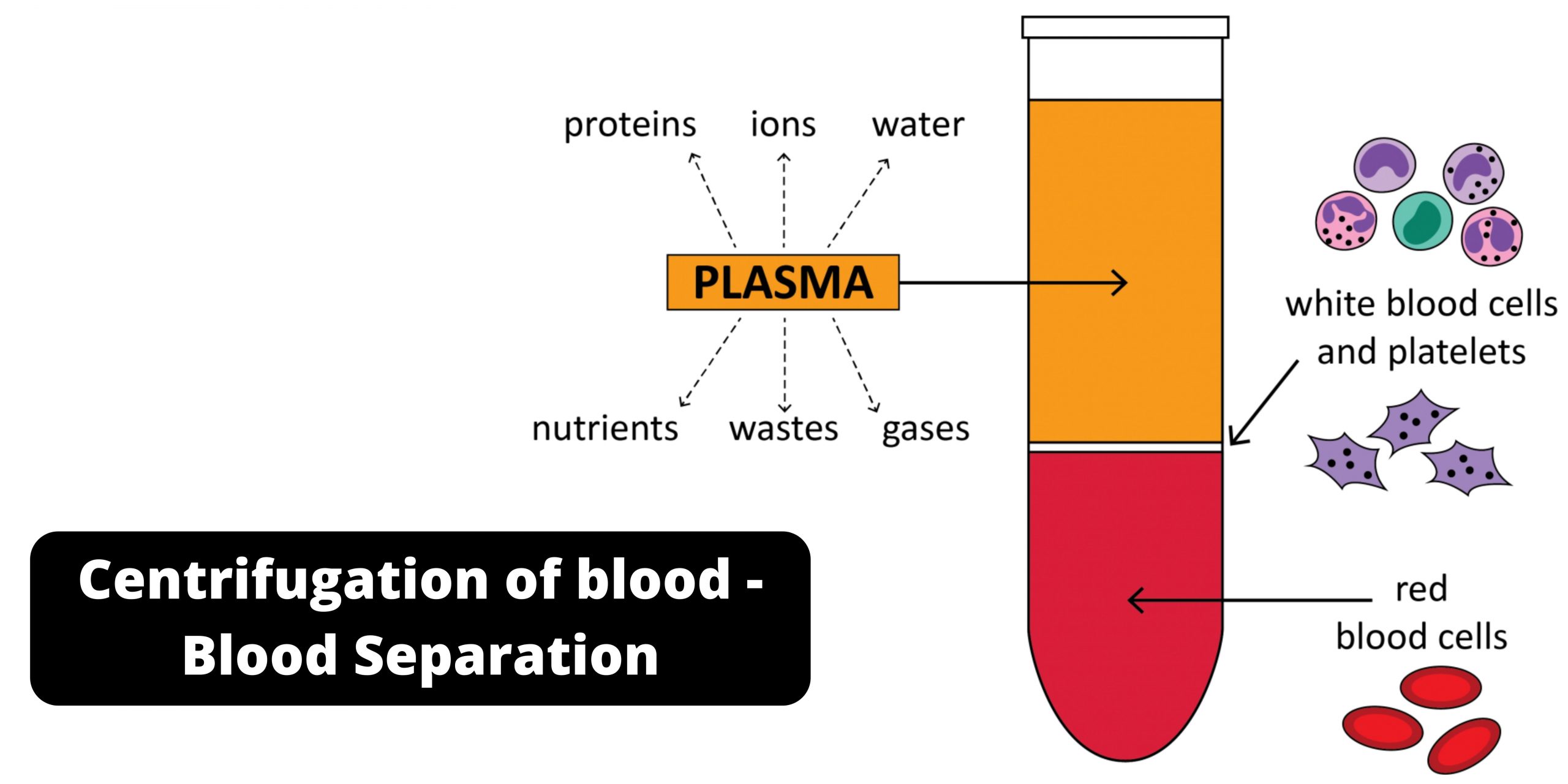
Scope of Epidemiology
Definition of Epidemiology Overview of Epidemiology Scope of Epidemiology/Objective of Epidemiology The objectives of epidemiology are to: Major Areas of Discussion in Epidemiology The Major Areas of Discussion in Epidemiology are; Population Disease frequency Disease Distribution Disease Determinants Disease Control Fields of Epidemiology