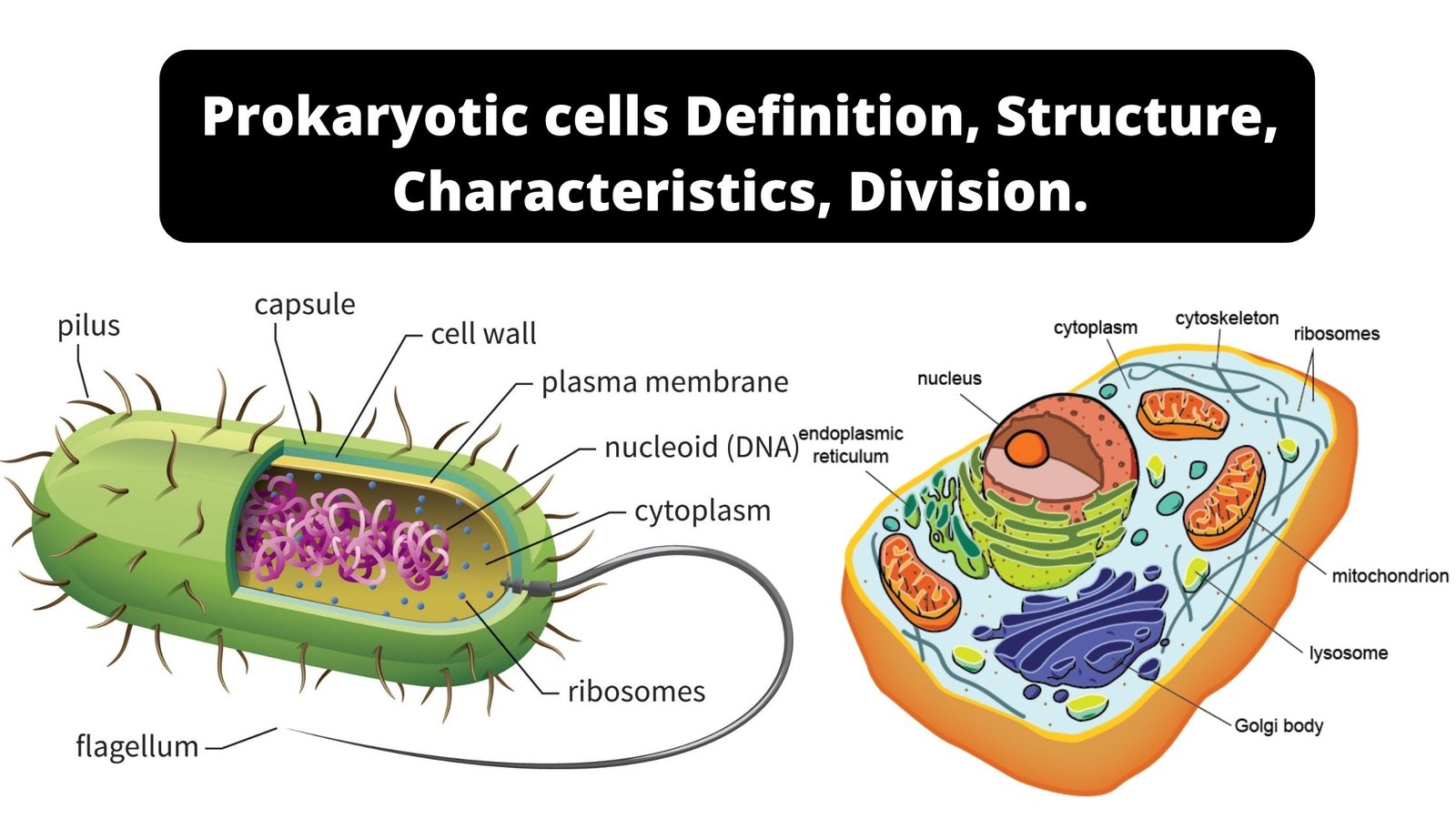
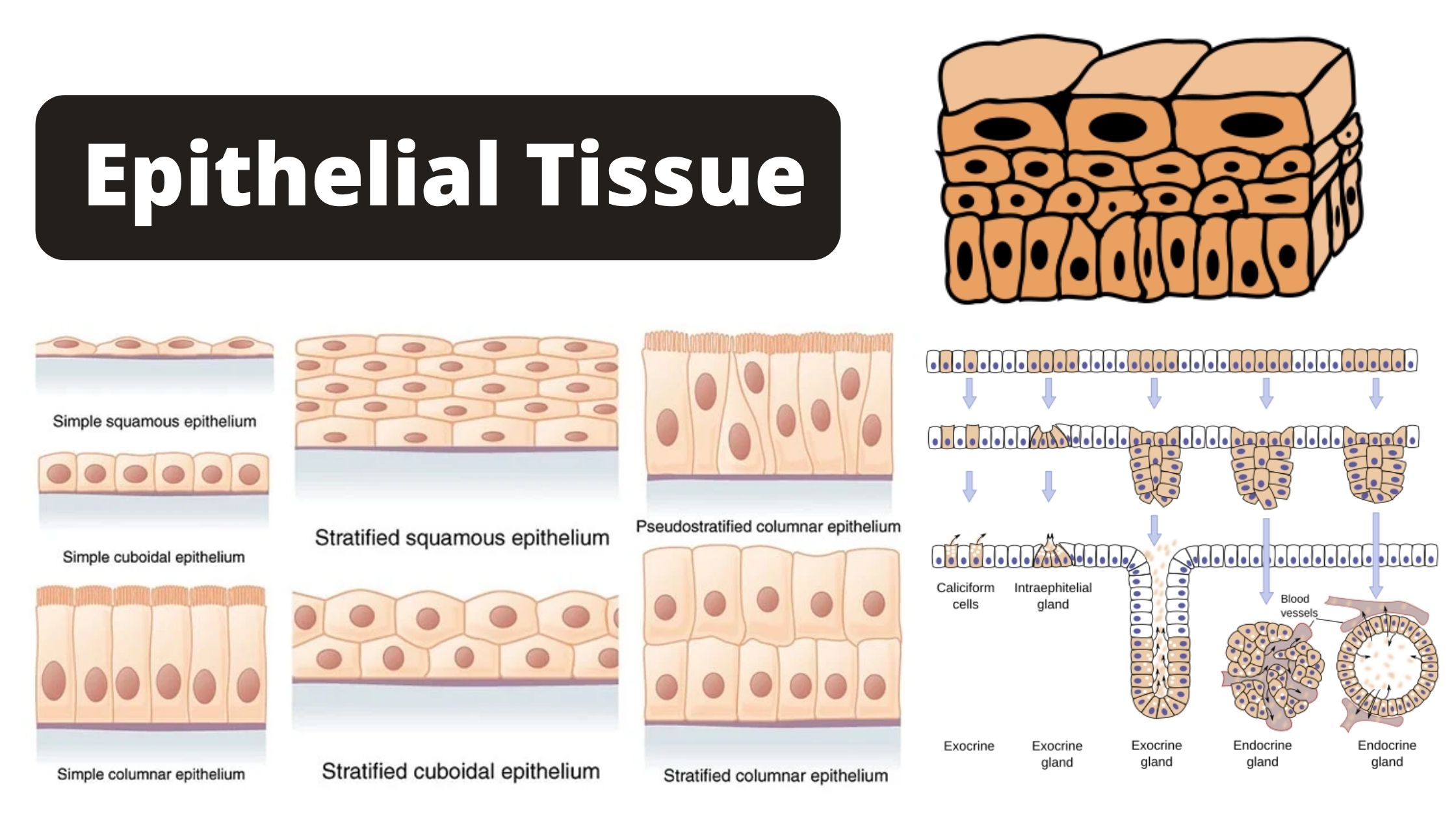
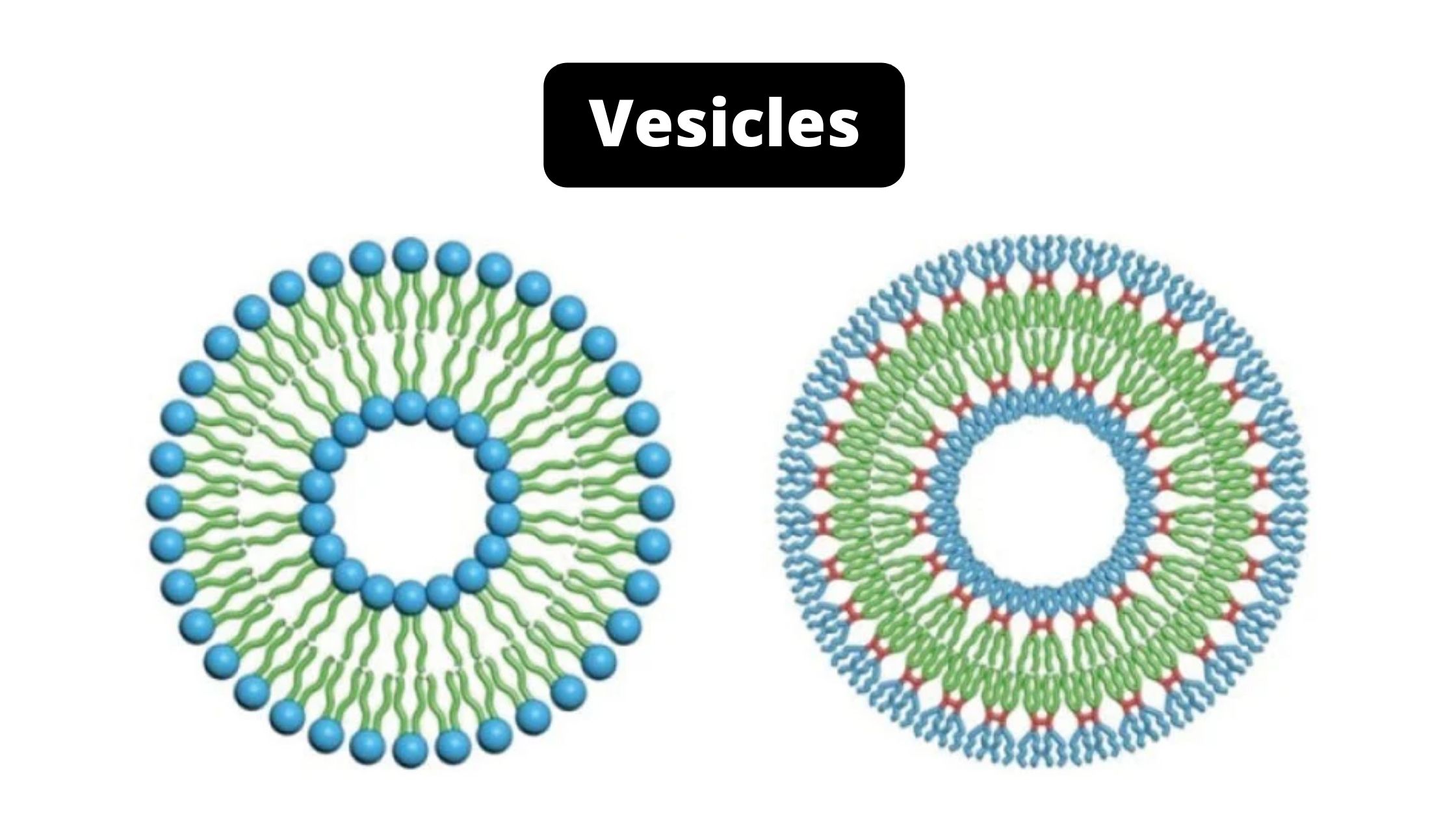
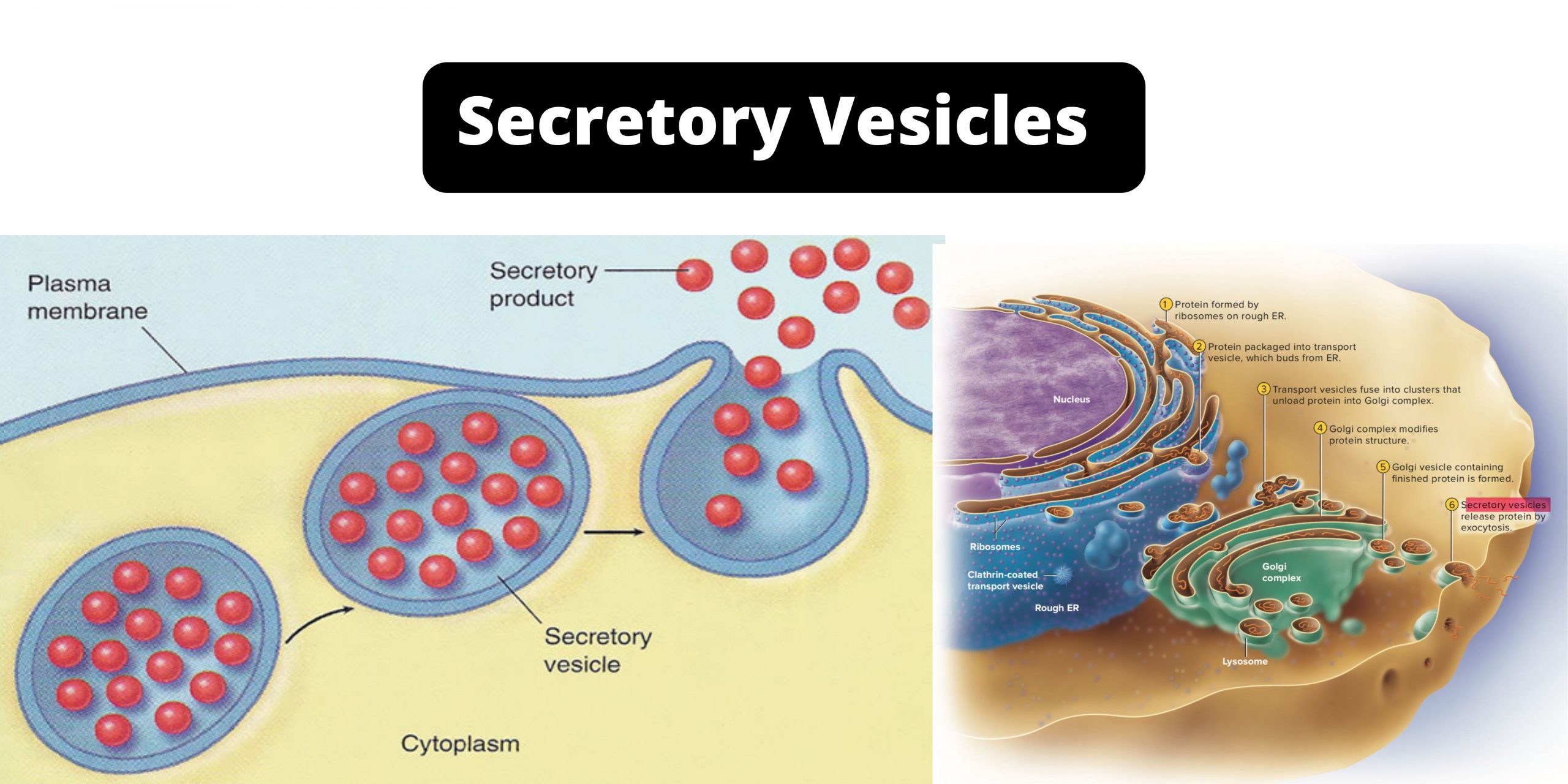
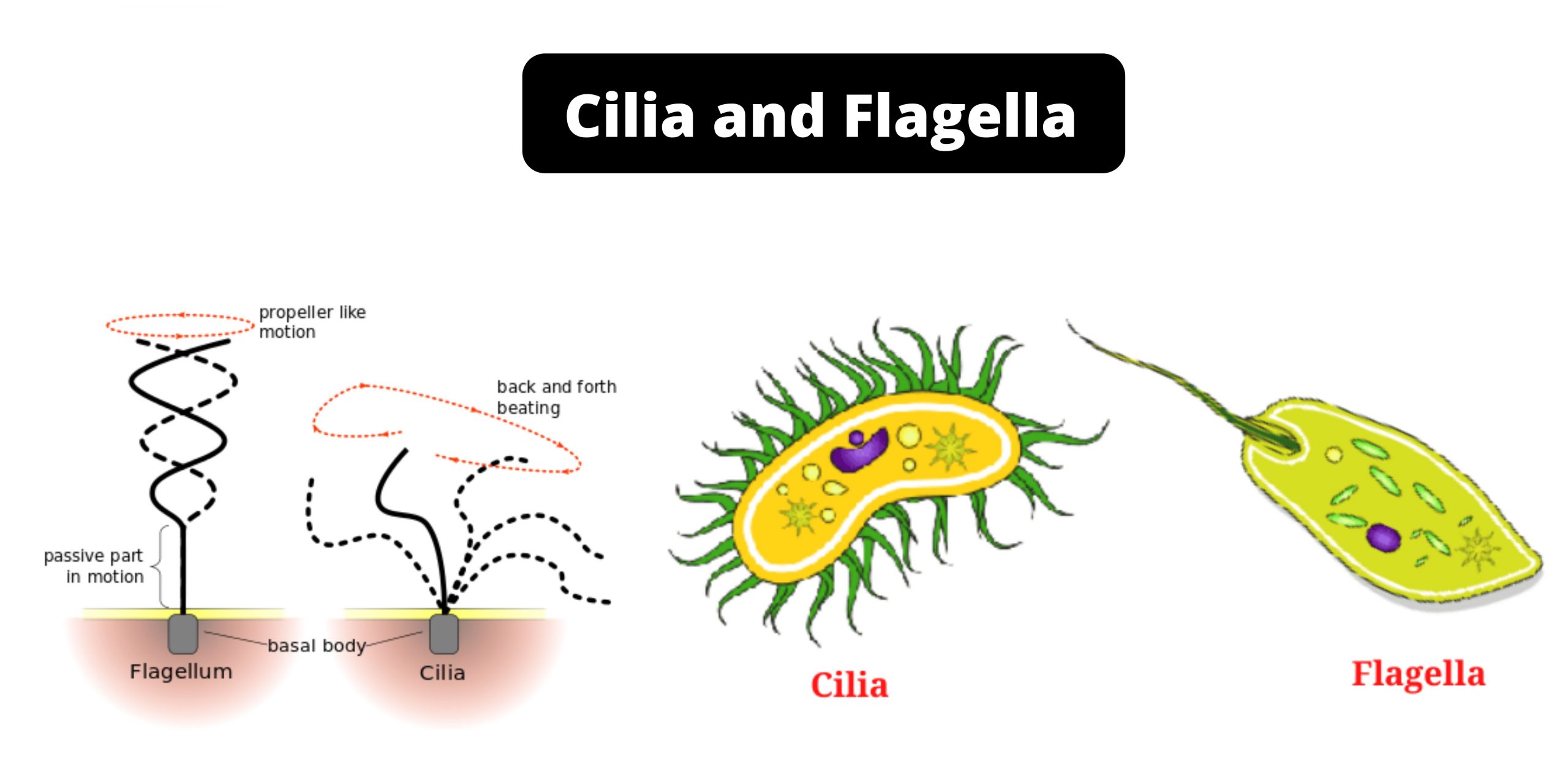
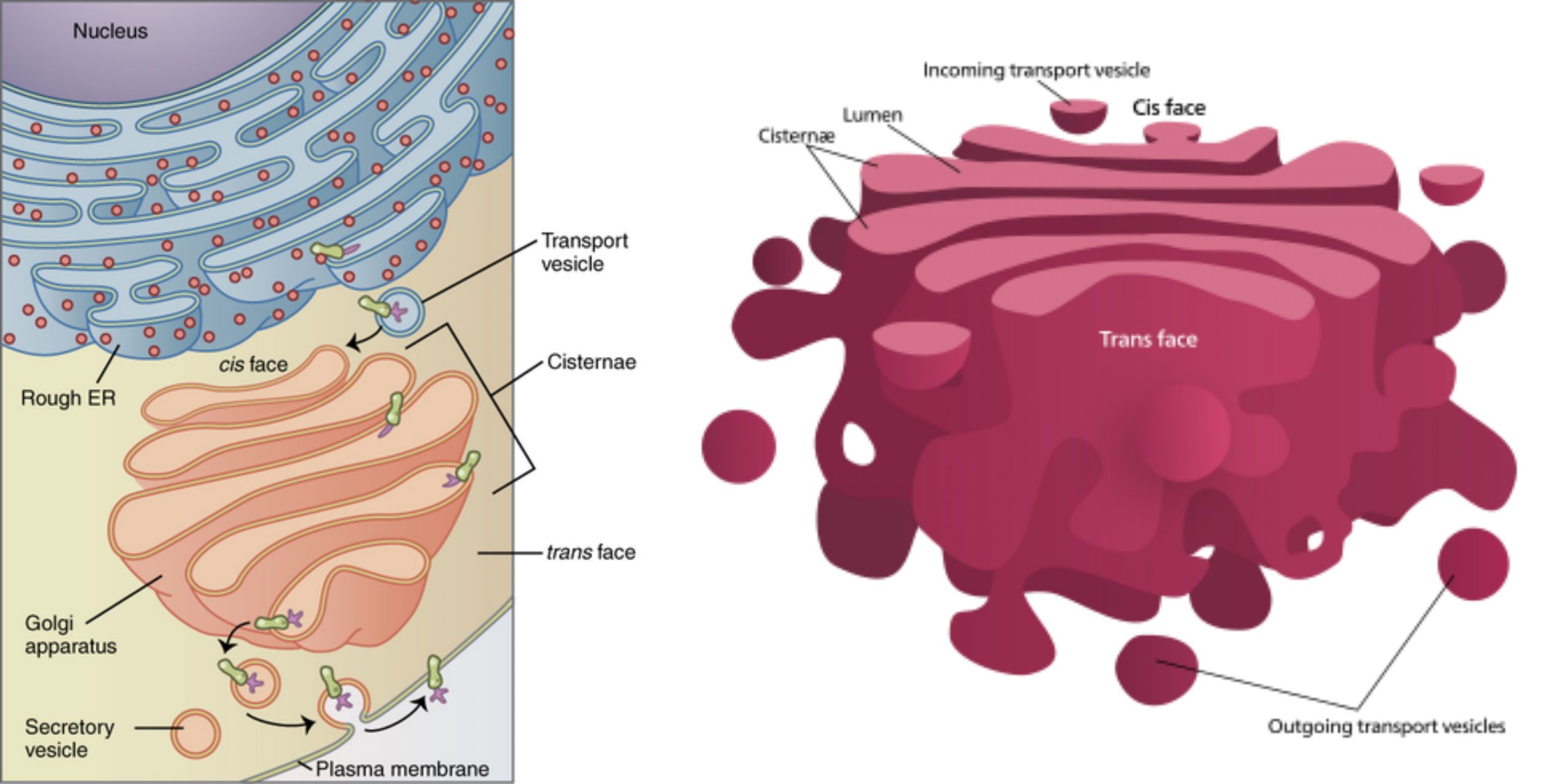
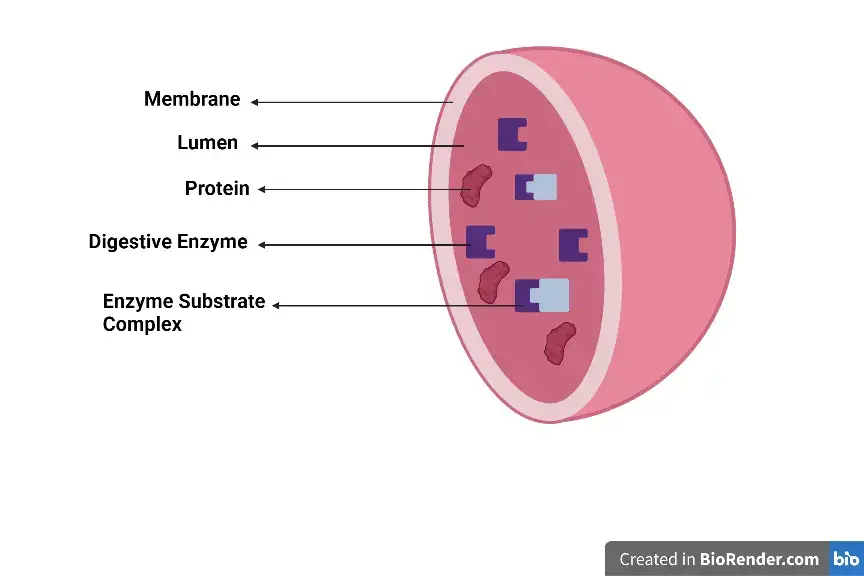
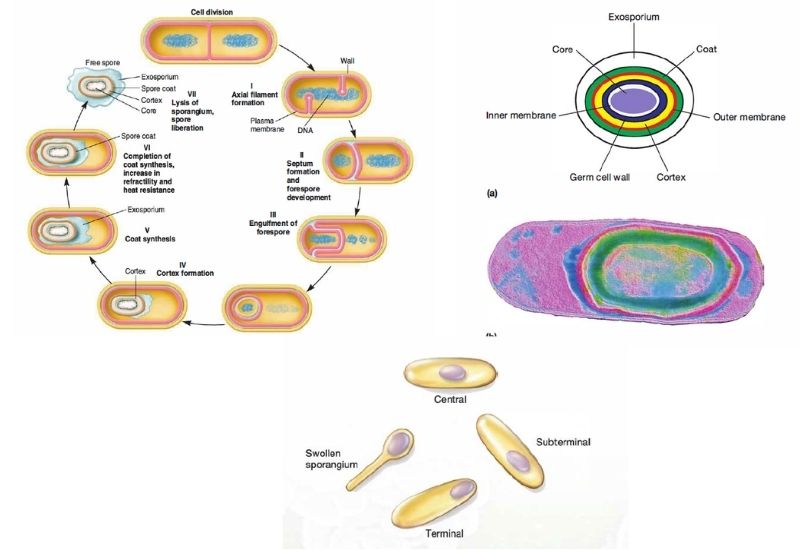
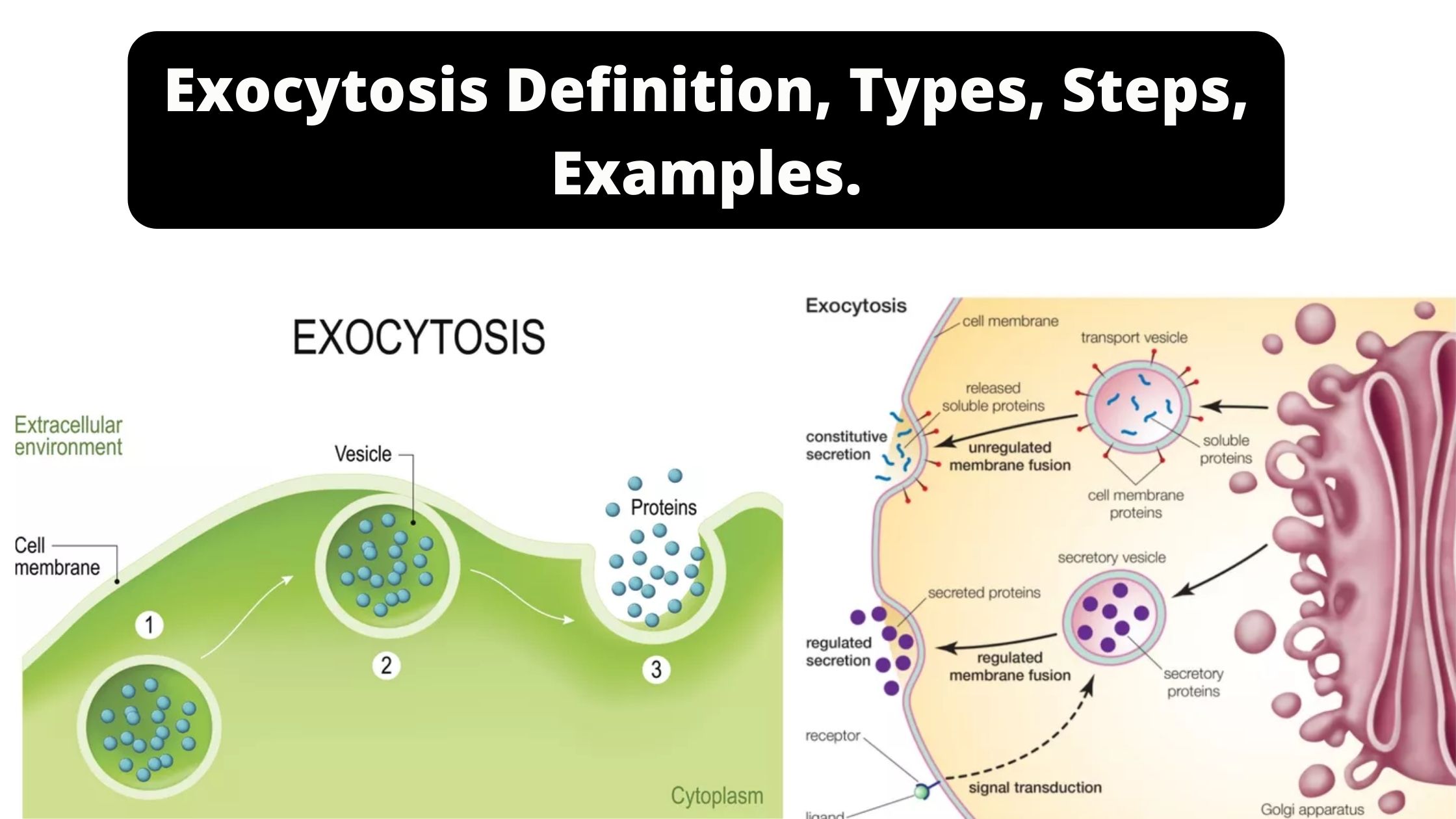
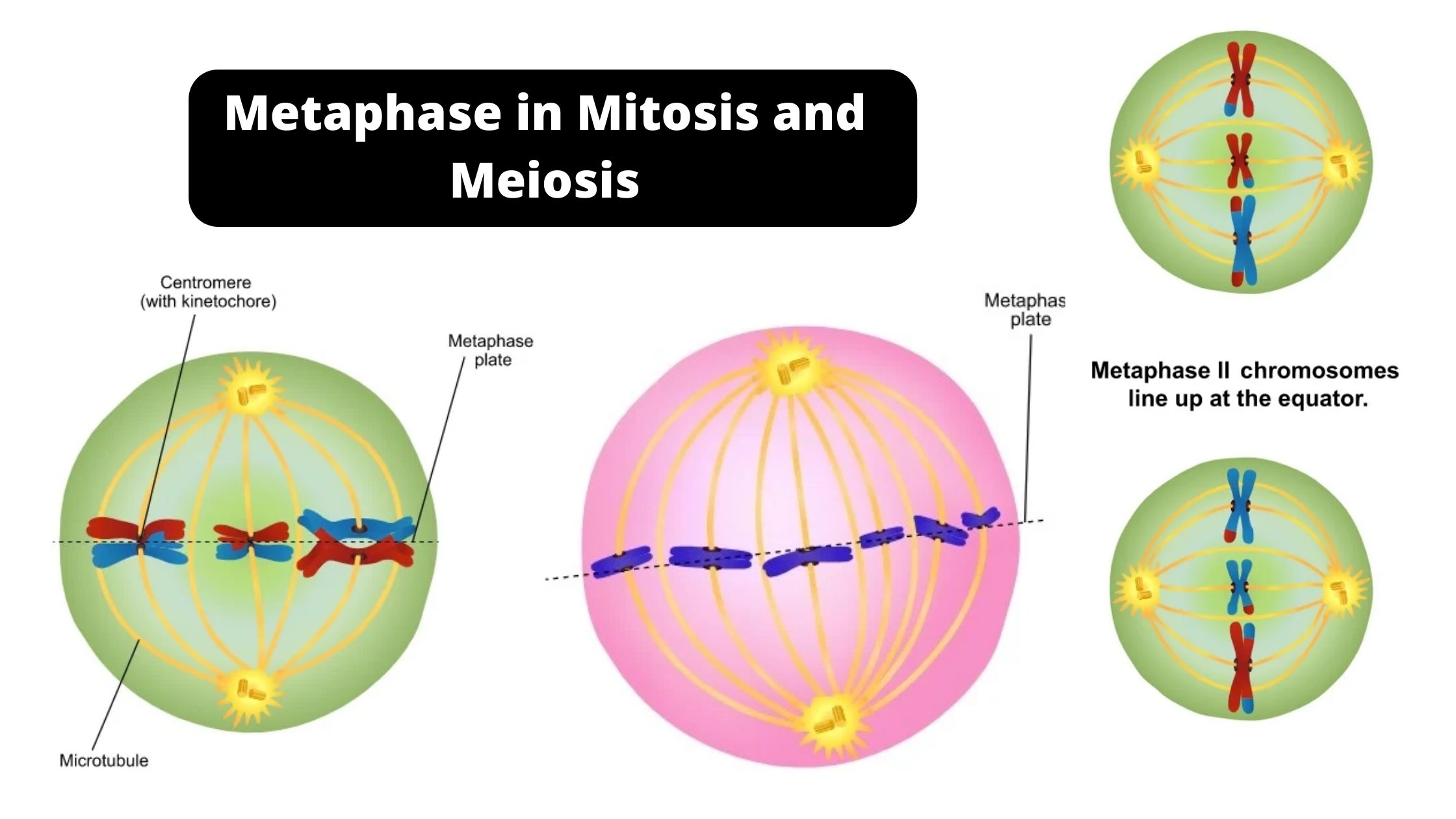
Prokaryotic cells – Definition, Structure, Characteristics, Examples
It is important to note that the distinction between prokaryotes as well as eukaryotes was clearly established by microbiologists Roger Stanier and C. B. van Niel in their 1962 paper on the concept of bacteria (though they used the words procaryote as well as eucaryot in the paper).