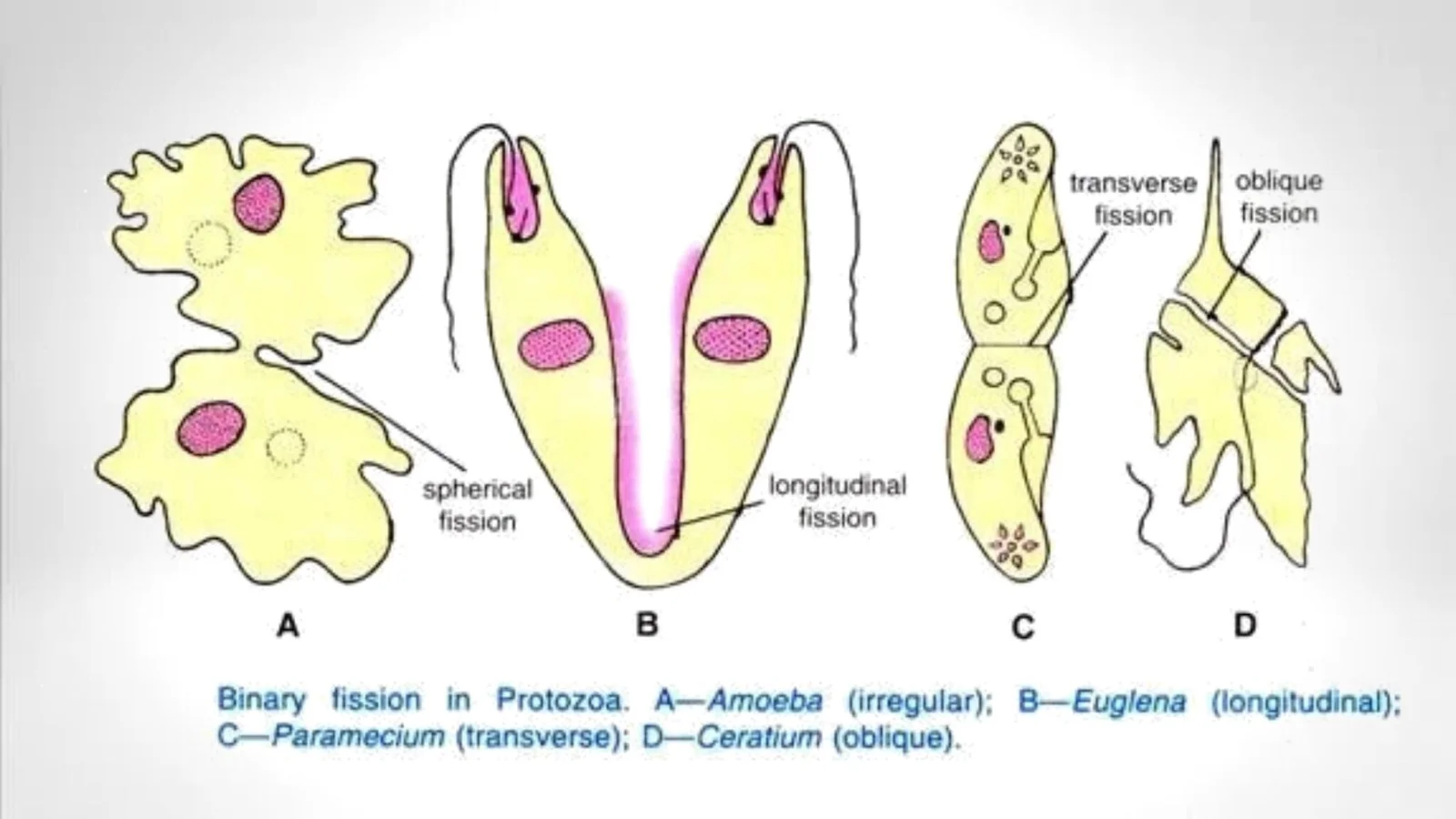
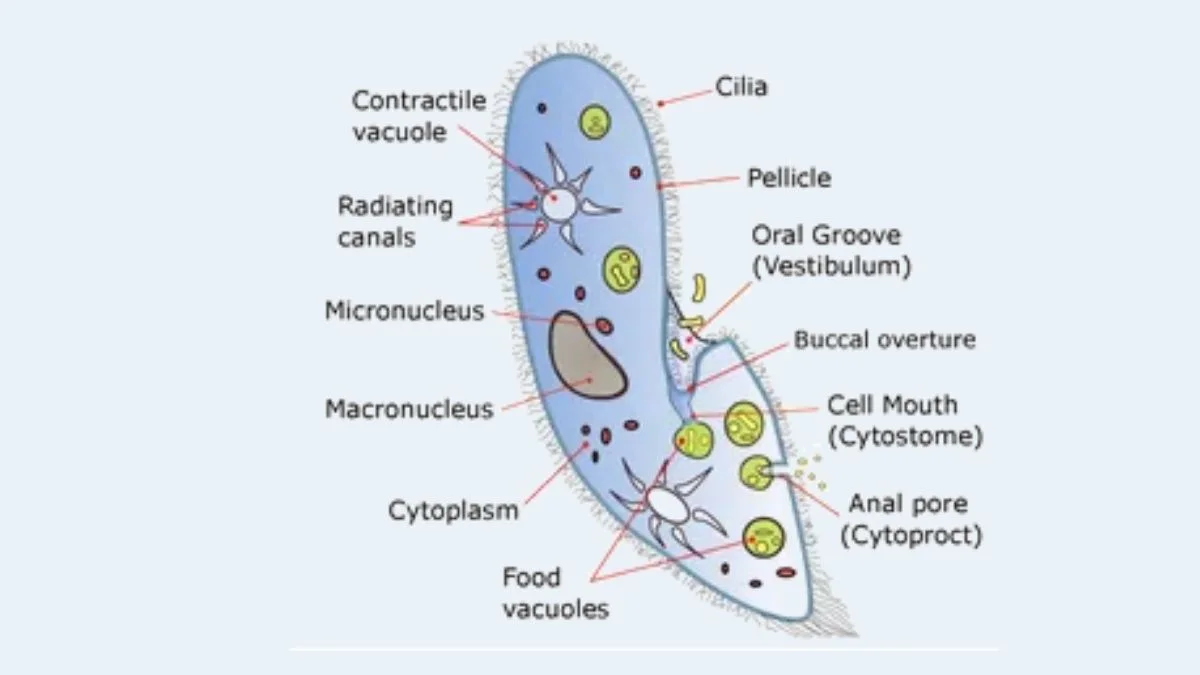
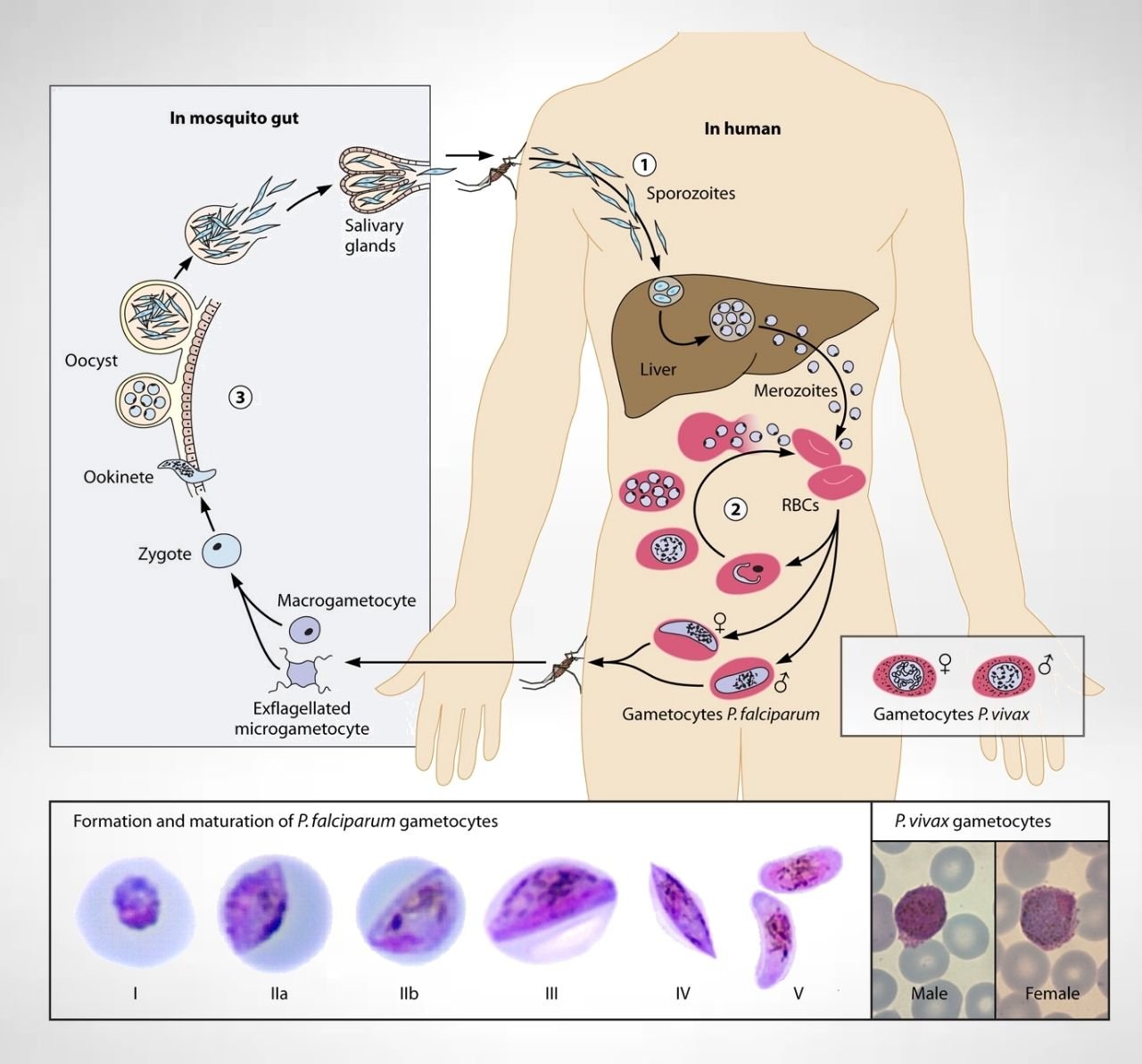
Reproduction in Protozoa – Sexual reproduction, Asexual reproduction
Protozoa carried out their reproduction by asexual and sexual mode of reproduction. The higher group of protozoa follow mainly sexual reproduction. Some protozoa carried out both asexual and sexual reproduction based on the types of the host cells.