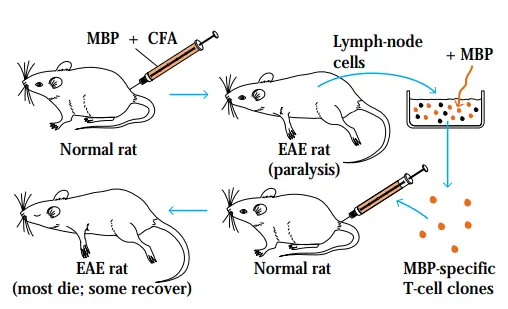
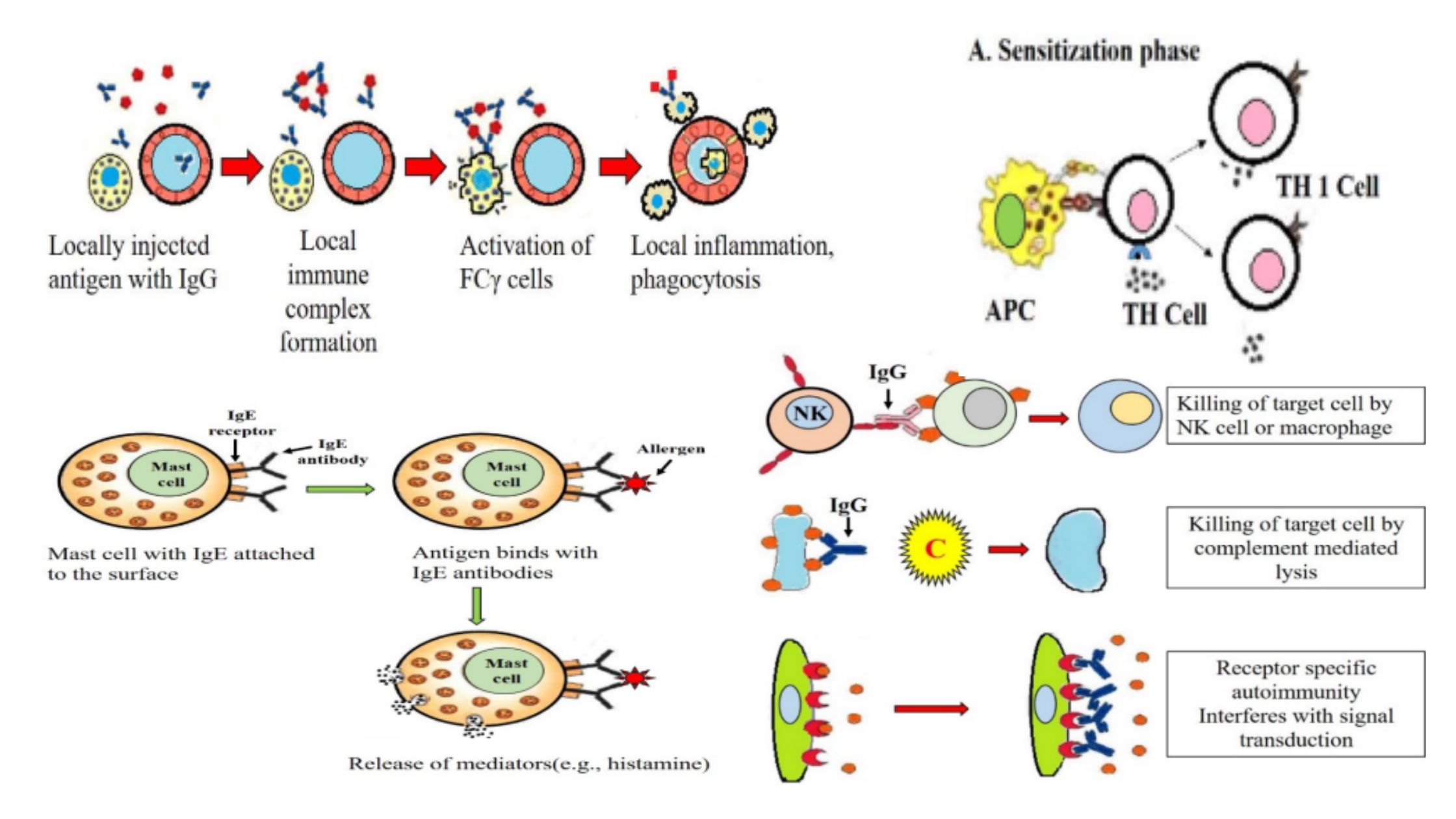
Antigen – Definition, Types, Structure, Detection, Properties
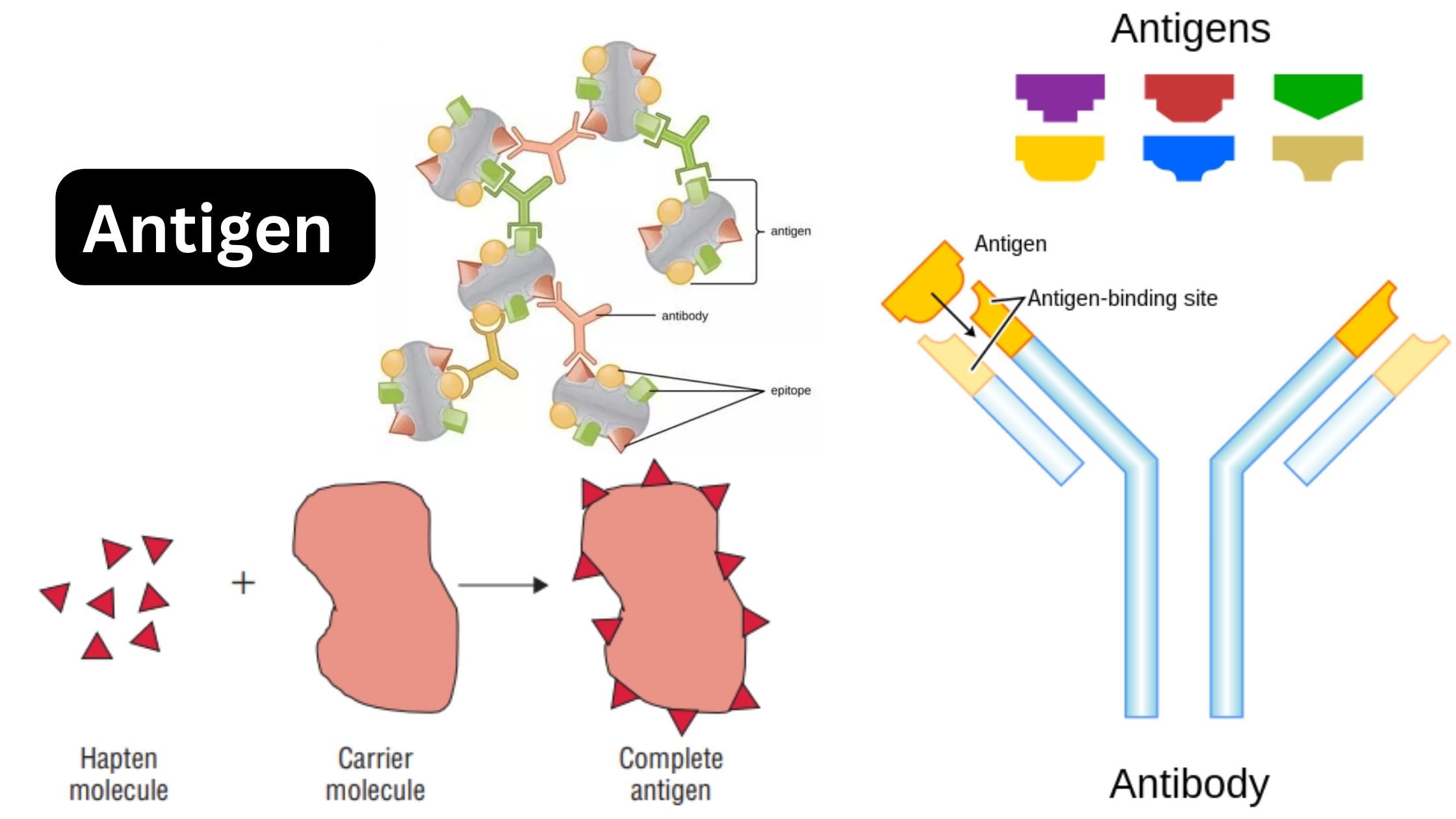
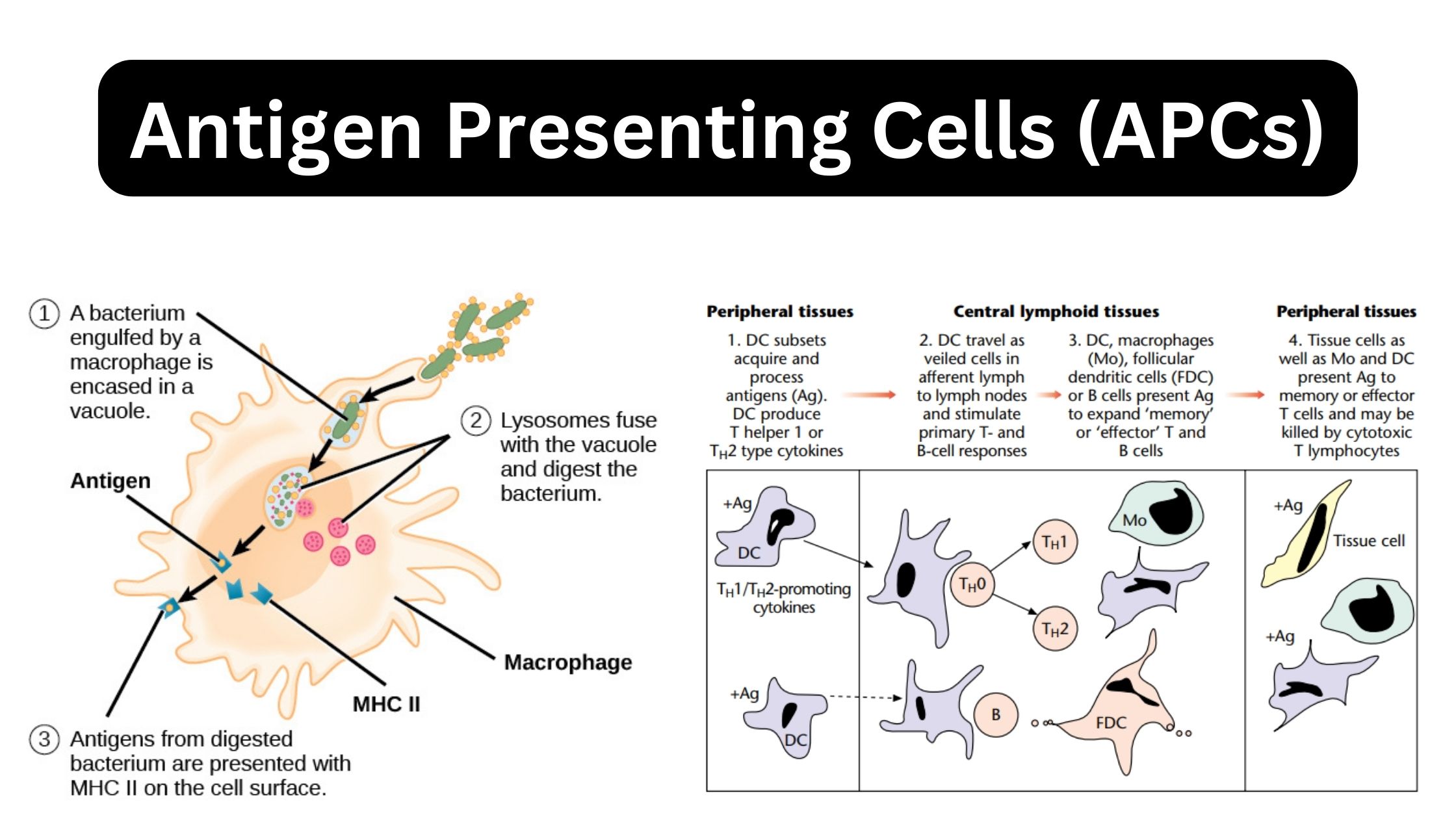
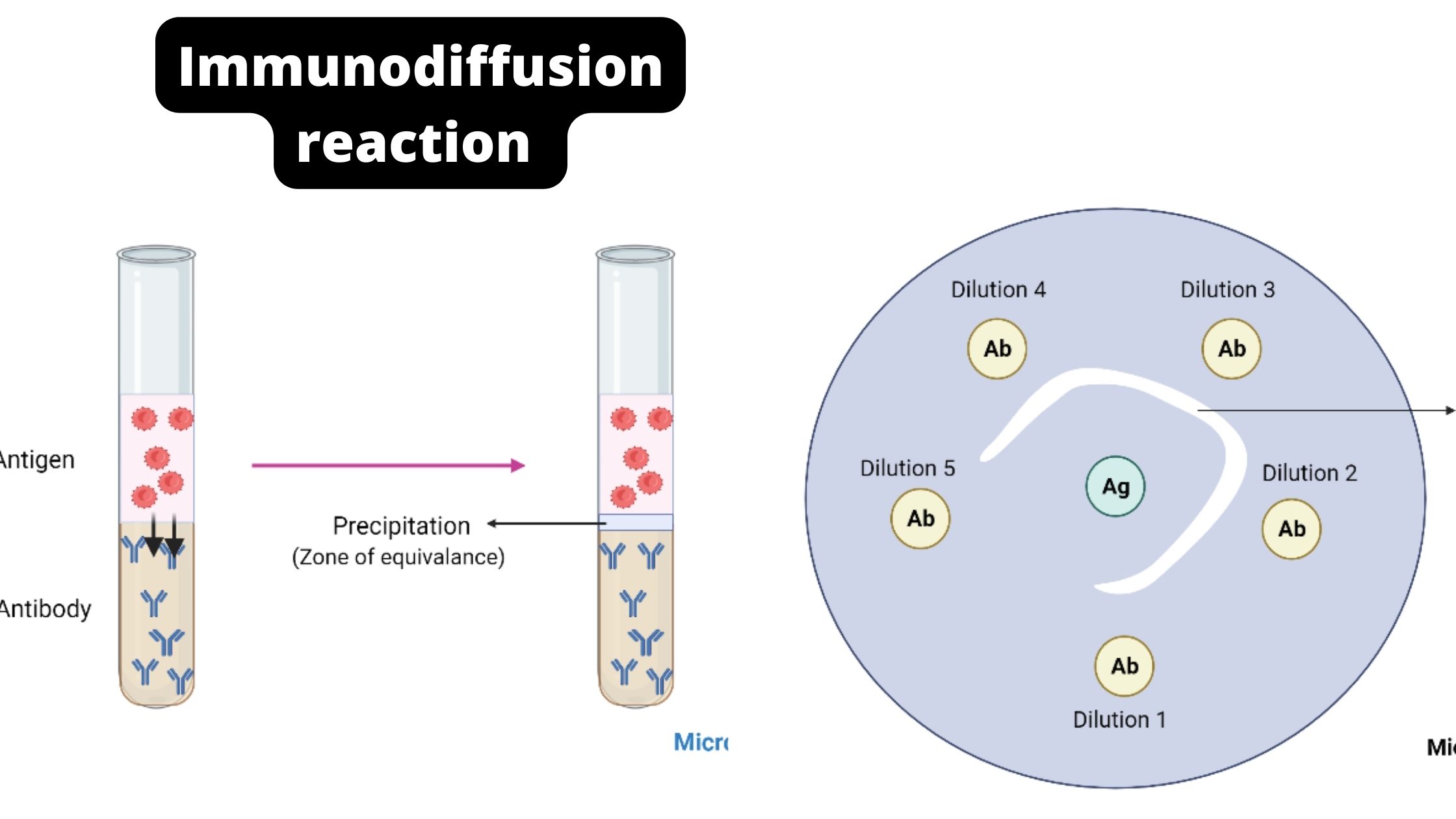
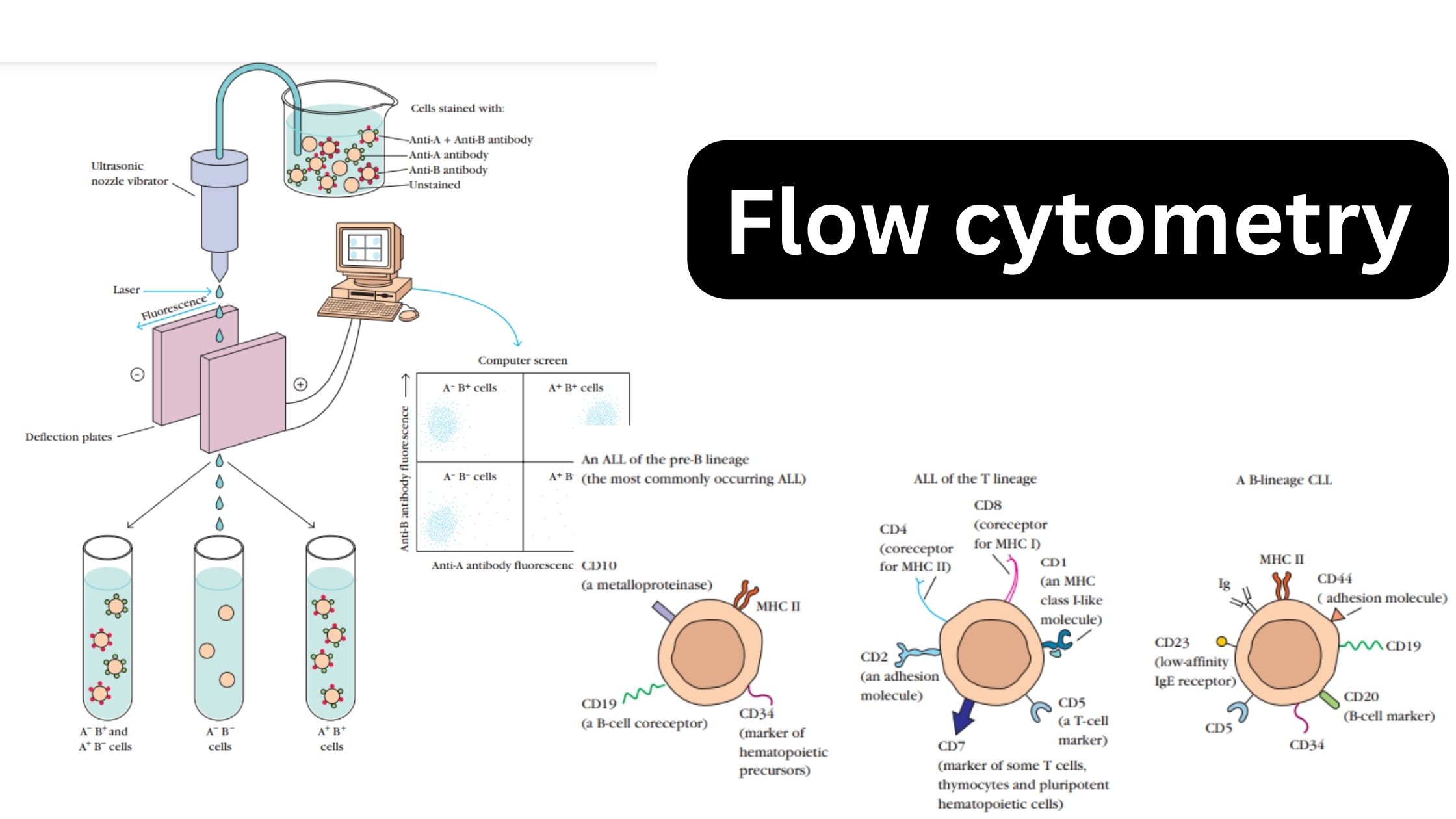
What is Antigen? Antigen Definition An antigen is a foreign molecule or substance that triggers an immune response in the body, leading to the production of antibodies. or An antigen is a substance that can stimulate an immune response in the body. It can be a molecule or a part of a molecule, such as … Read more