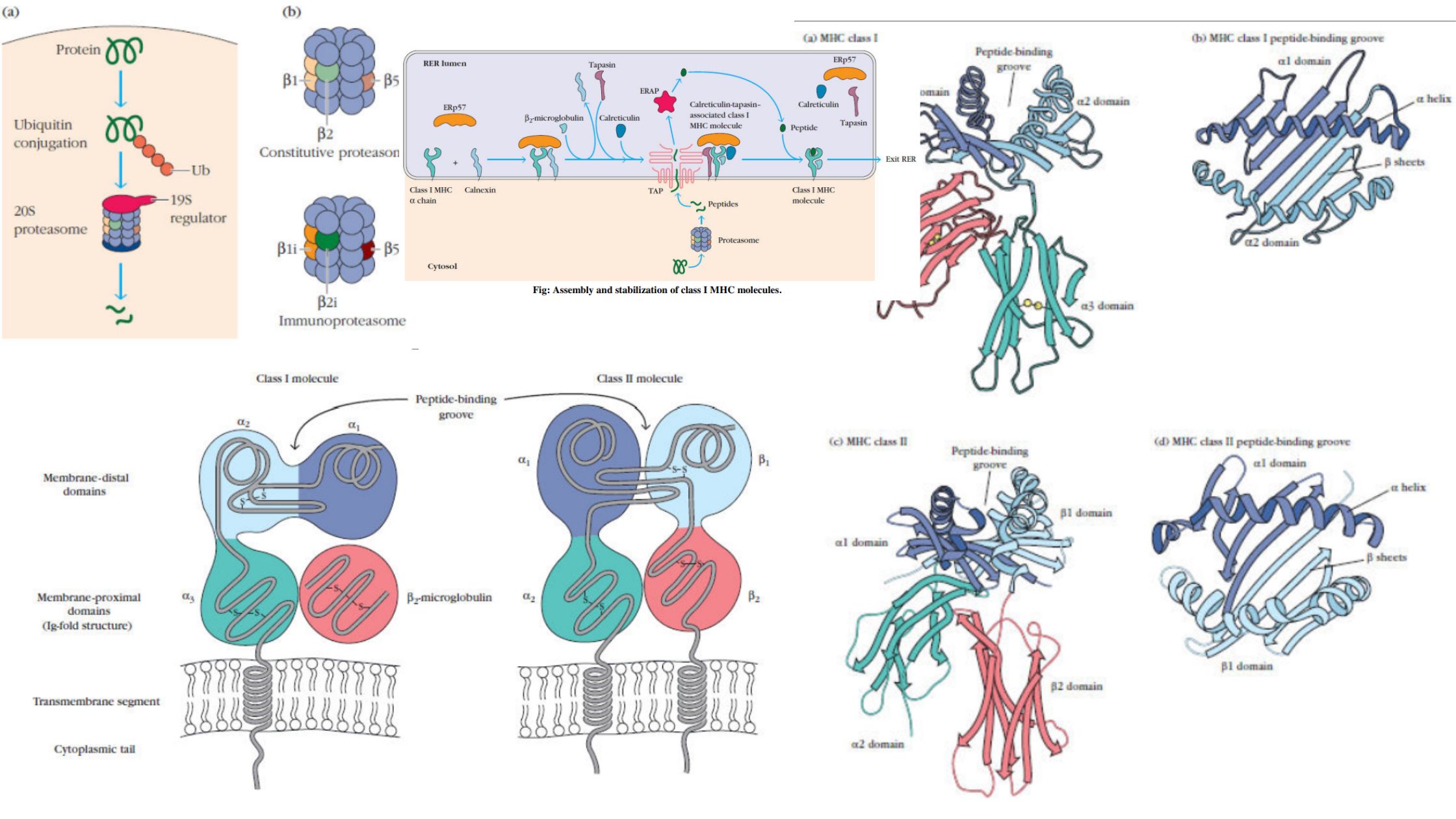
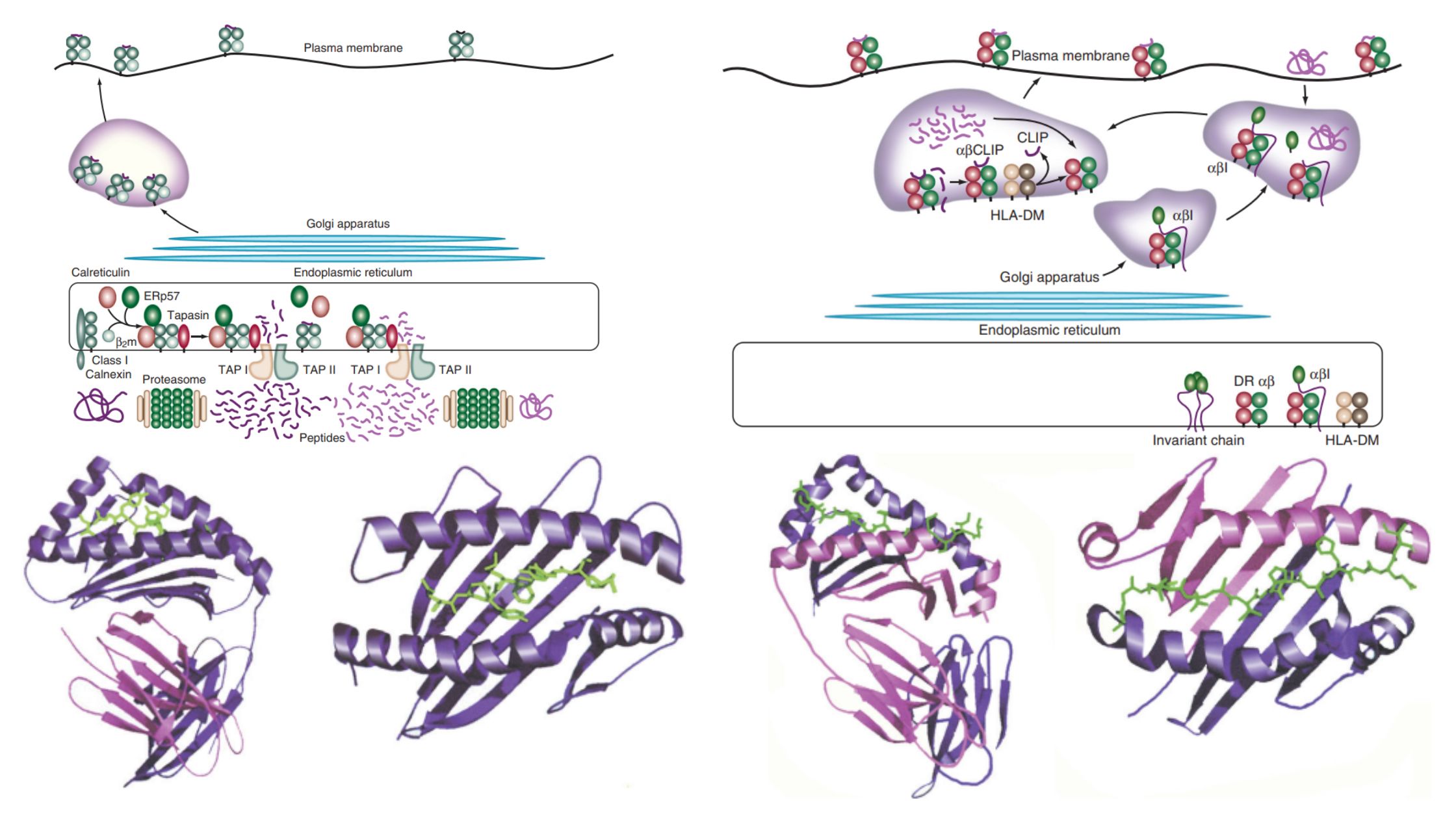
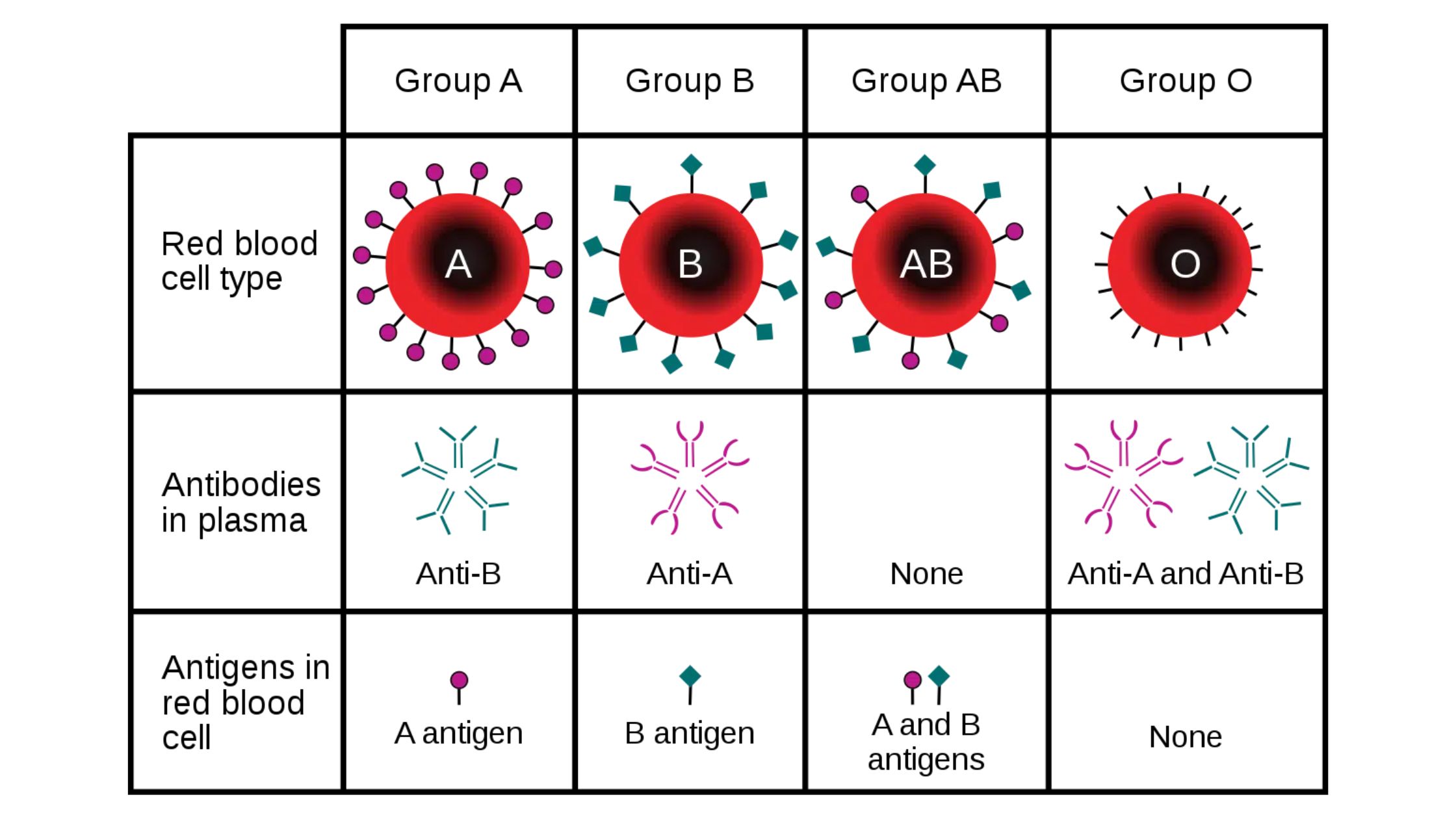
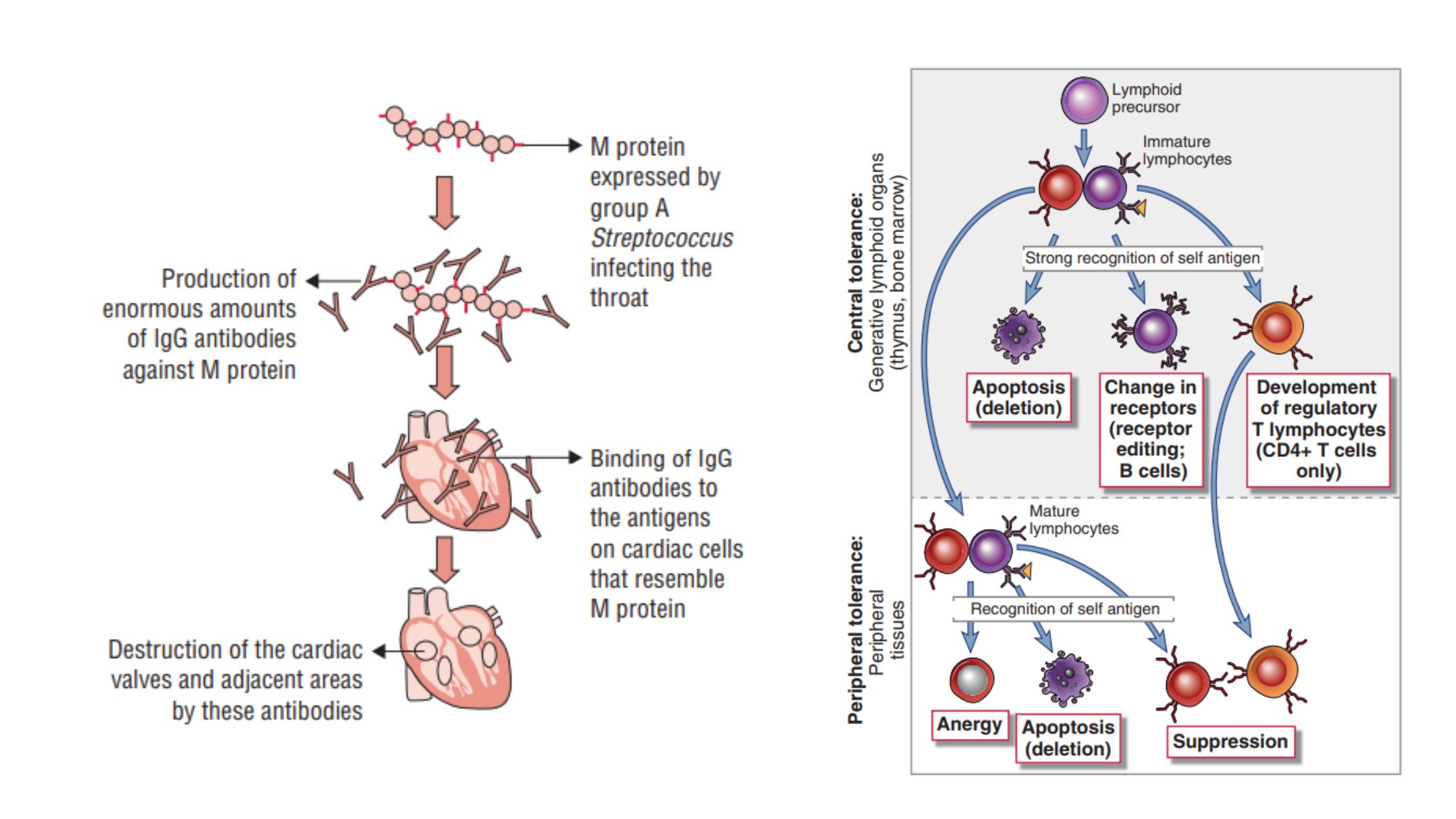
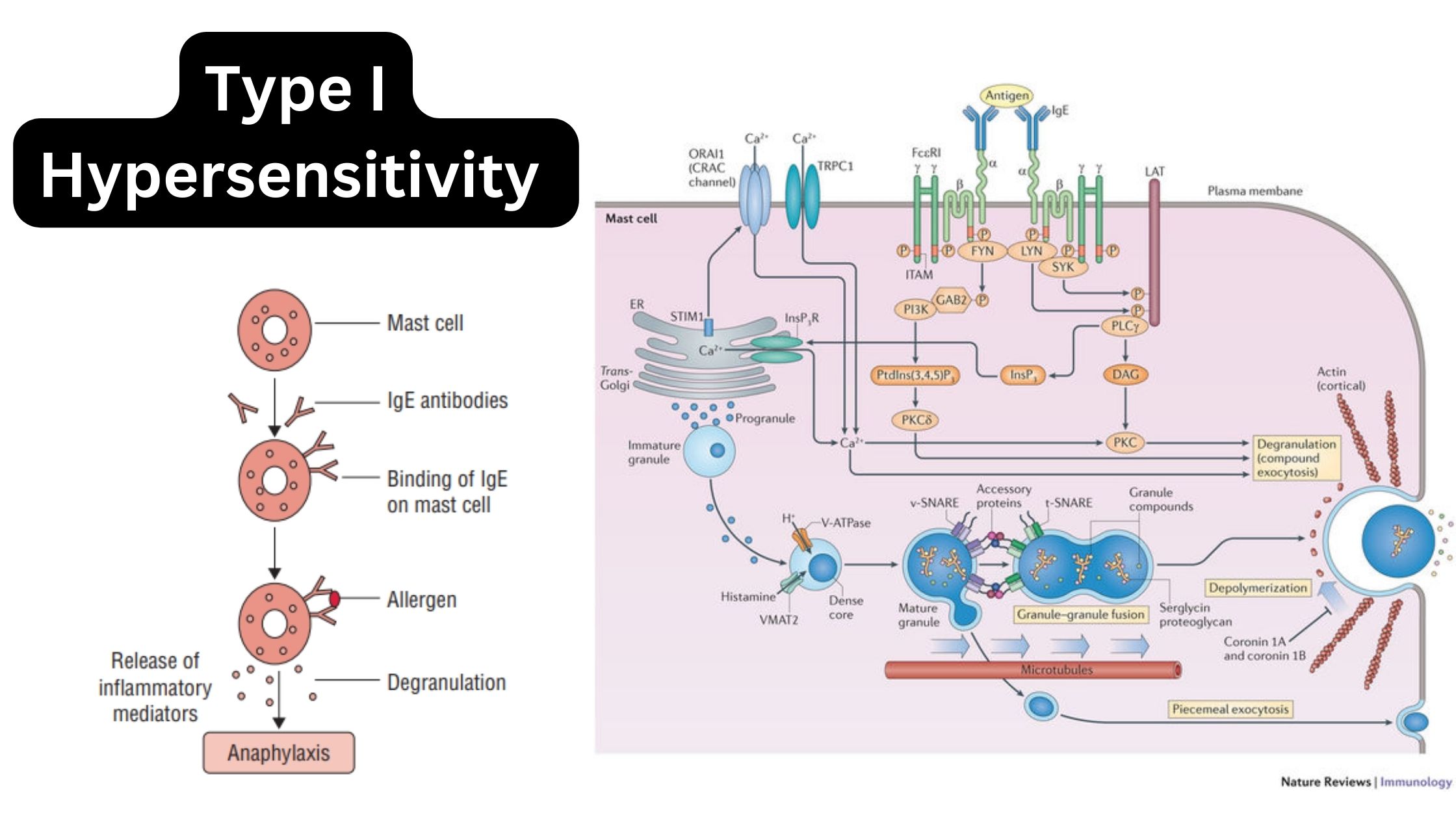
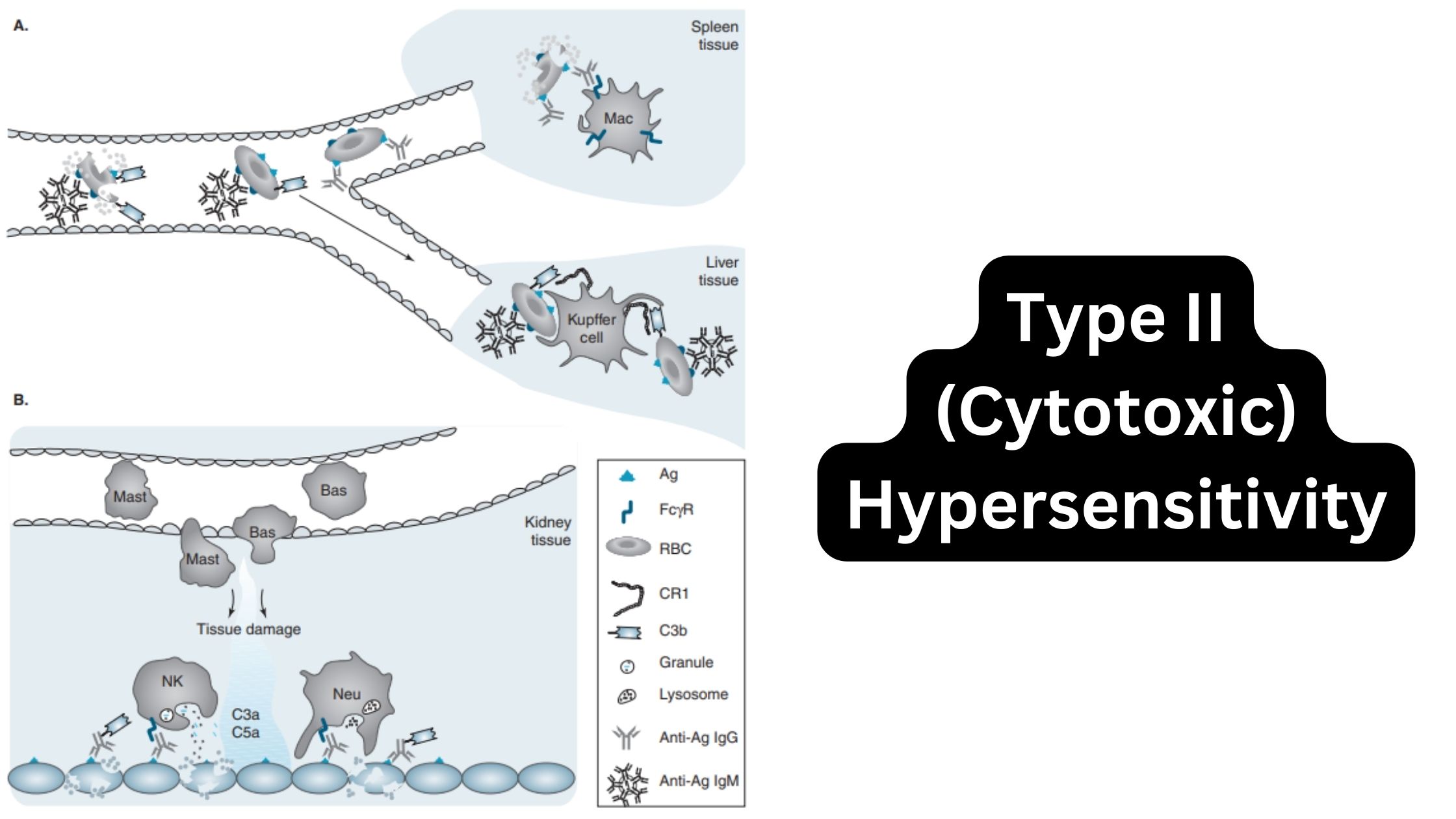
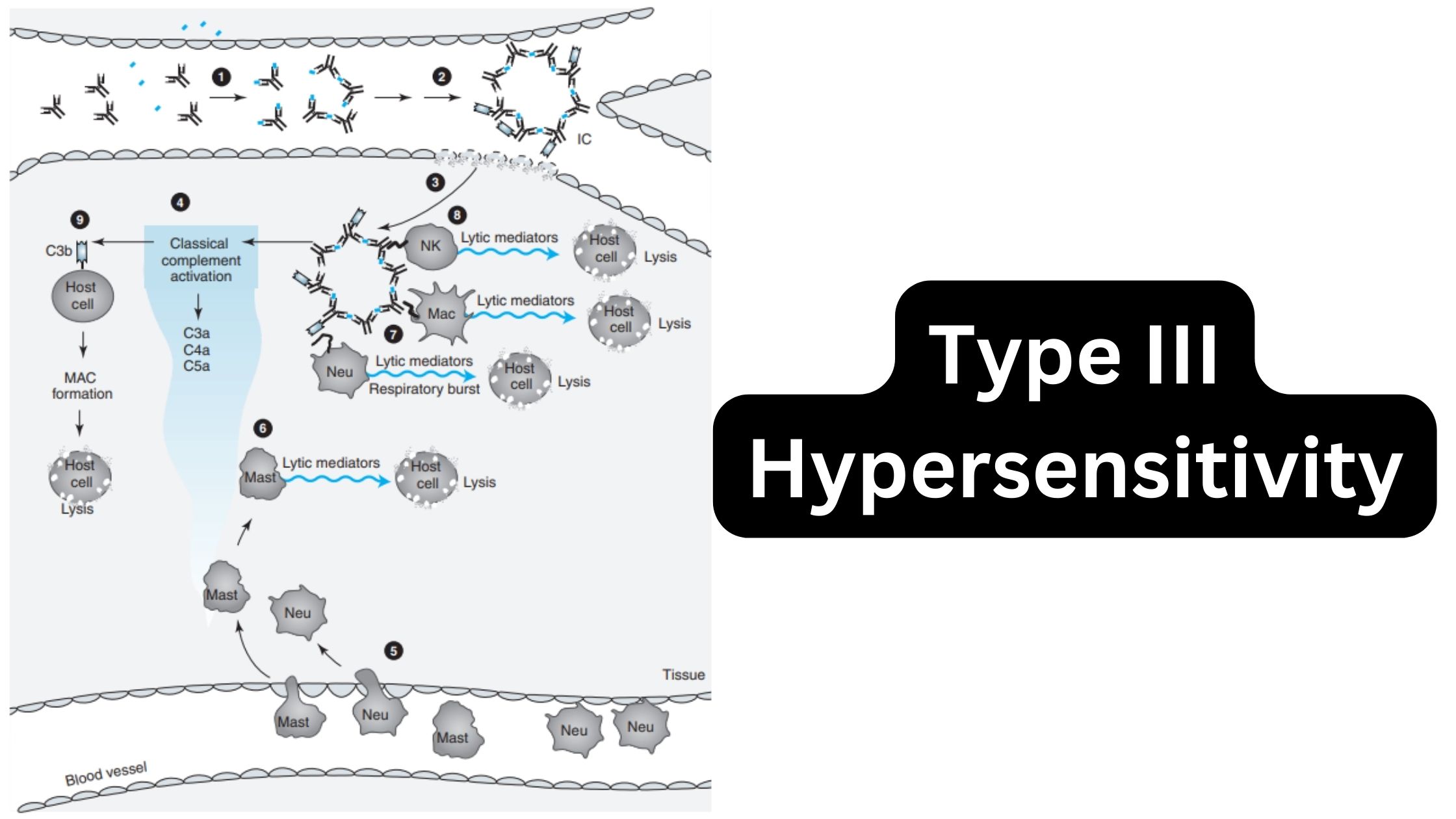
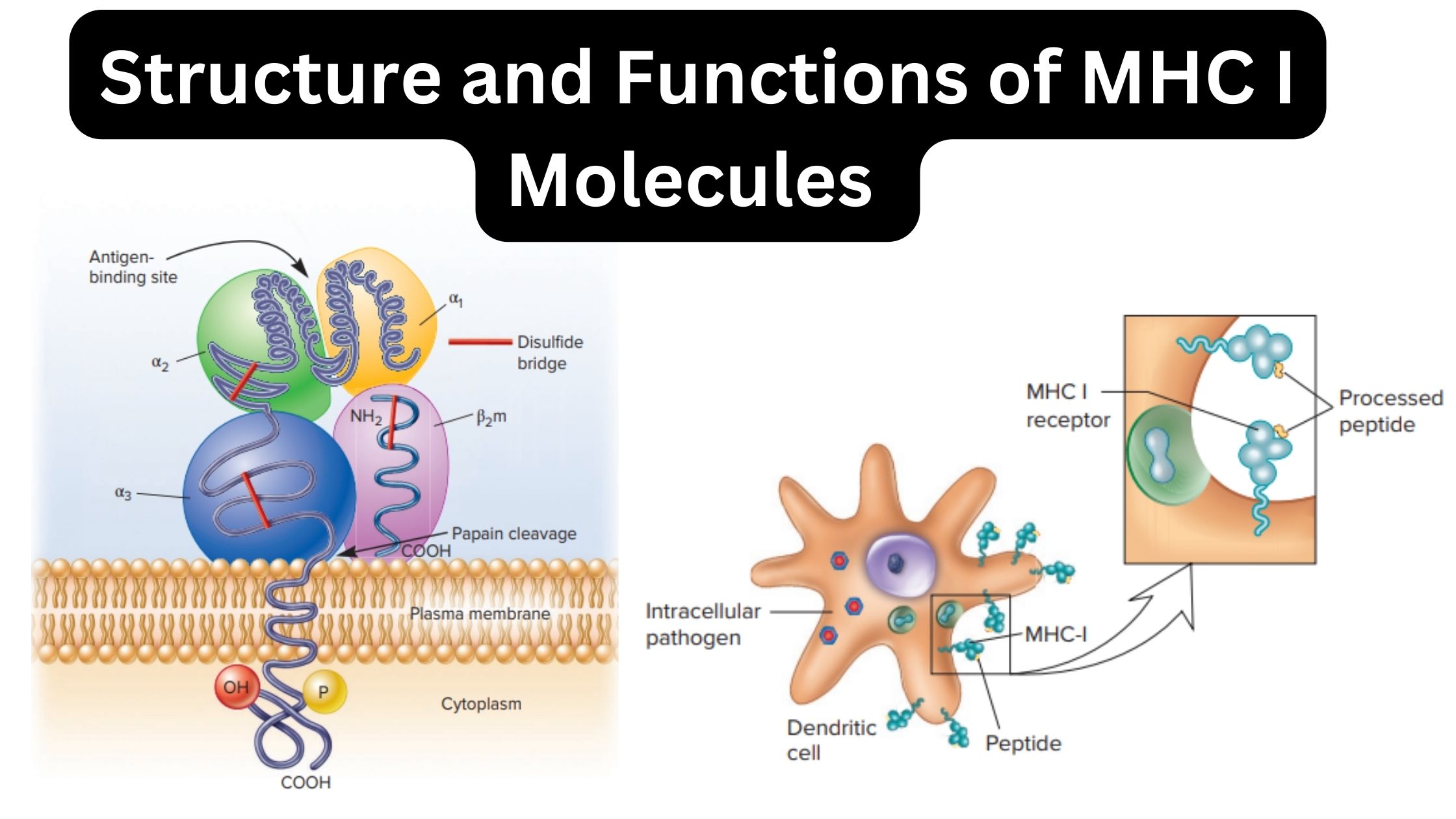
MHC Molecules (Major Histocompatibility Complex) – Definition, Properties, Class, Types, Pathways
What is Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC Molecules)? Definition of Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC Molecules) The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules are a set of cell surface proteins encoded by a cluster of genes that play a crucial role in intercellular recognition and immune responses. They present antigens derived from self-proteins or pathogens on the cell … Read more