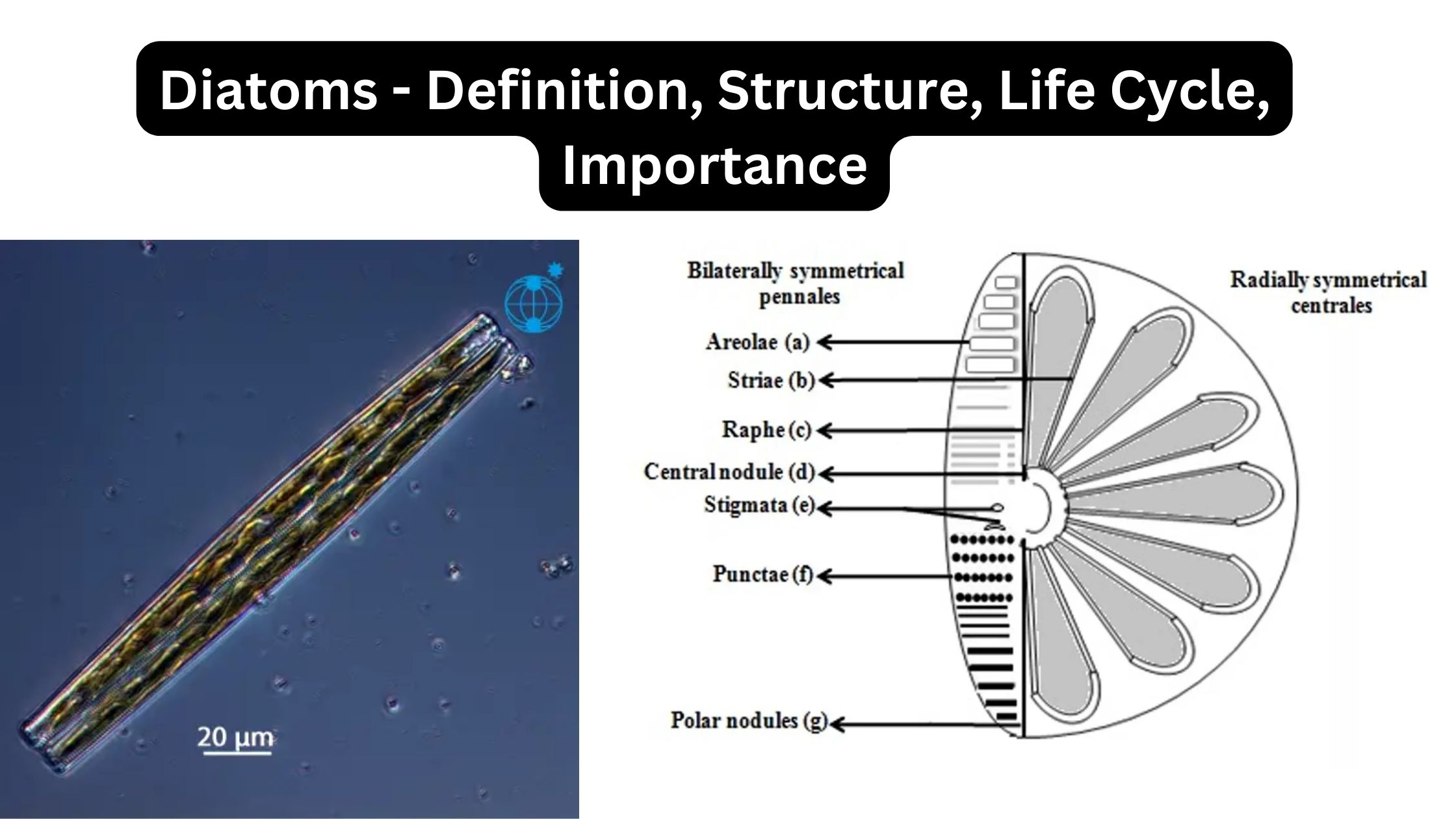
Cytotoxic T cells – Development, Activation, Functions
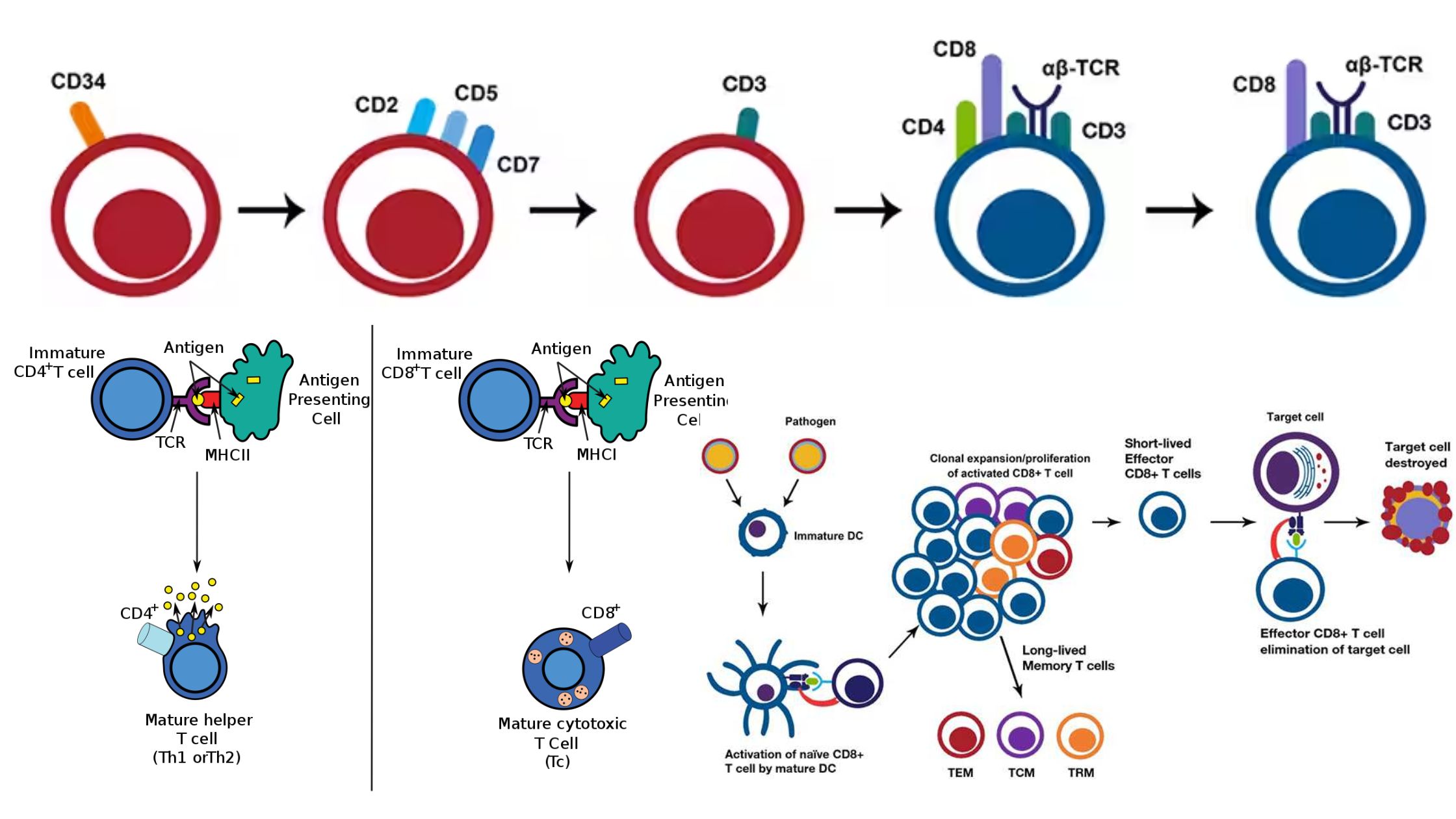
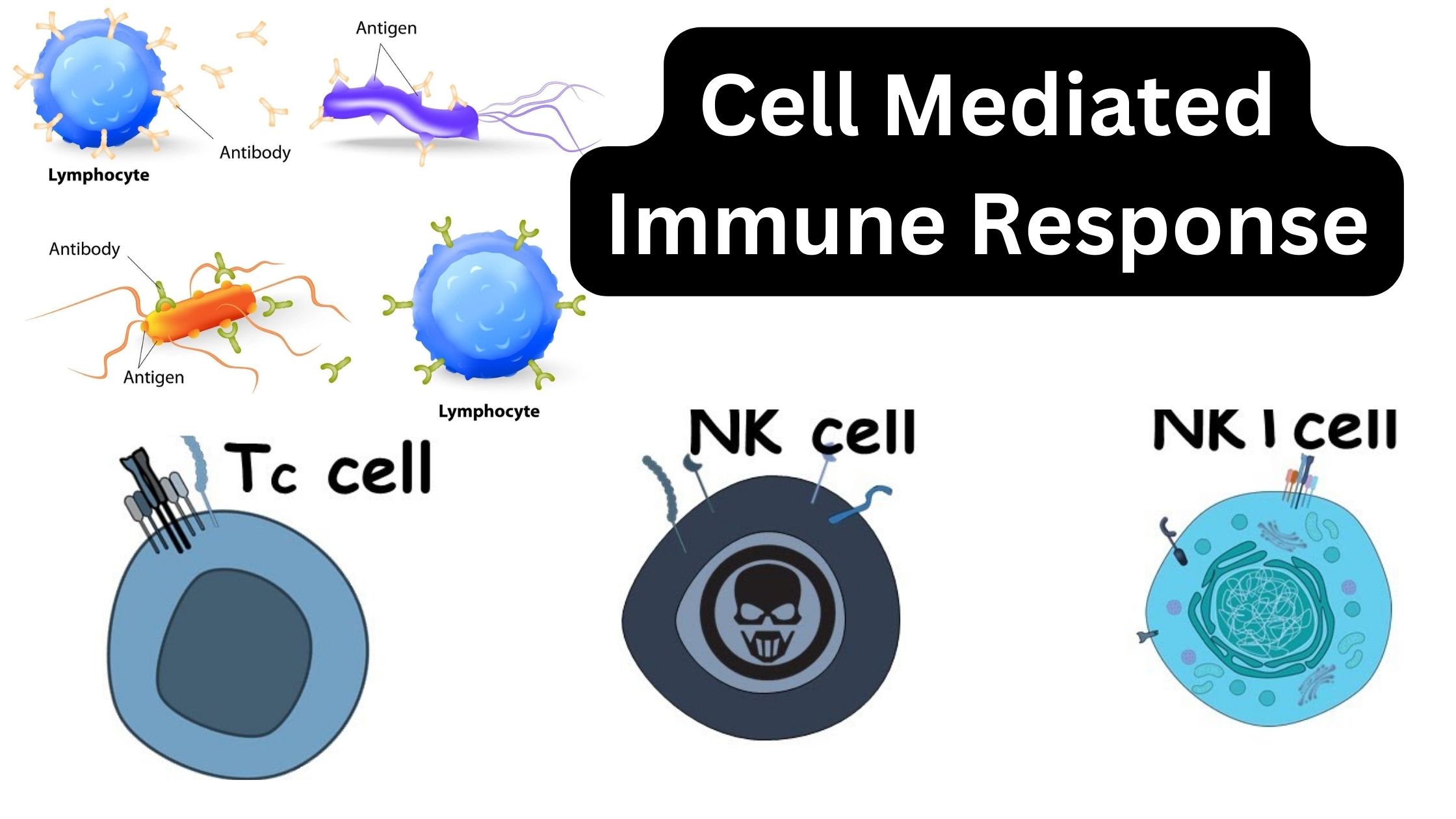
What is a Cytotoxic T cell? Development of CD8+ T cells Effector CTLs Are Generated from CTL Precursors Activation and differentiation of CD8+ T cells Cytotoxicity Mediated by CD8+ T Role in anti-viral immunity Role in anti-tumor immunity What are Memory CD8+ T cells? All of these effector and memory subsets work together to generate … Read more