Follow these step by step instruction to operate a compound microscope;
Contents
How to Use a Compound Microscope
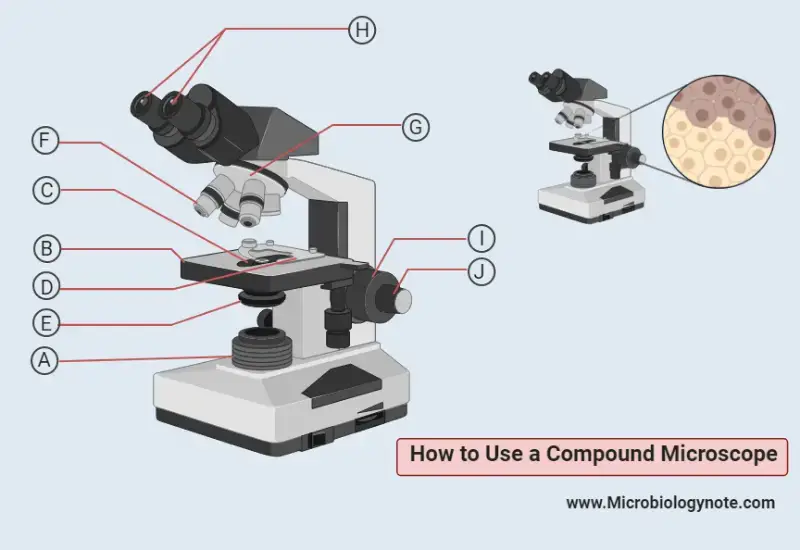
- First of all turn on the illuminator (A). In case of dimmer slowly raise the light intensity as the lamp warms up very quickly.
- In the second step place the experimental or examine slide or specimen above the stage (B) and make sure it is located exactly above the aperture (C). Then attach it to the stage with the help of stage clips (D).
- Always use a coverslip over the sample for a better image quality.
- Make sure the iris diaphragm (E) is completely open because it controls the amounts of light which will pass through the slide and lense. The maximum amount of light is better for a high-quality image.
- Now set the lowest power objective lens (F) above the sample by rotating the nosepiece (G).
- Look through the binocular eyepieces or eyepiece (H) and make sure the amount of light is enough for a better quality image and its comfort to the eye. If not then adjust the iris diaphragm until the amount of light is satisfactory.
- Now bring the image in focus by adjusting the coarse adjustment knob (I).
- For further sharp focus images of specimens use the fine adjustment knob (J).
- Set the higher power objective lens by rotating the nosepiece and create a more detailed image with a minimal amount of refocusing.
Important Note on handling a Compound microscope
- Before use a microscope clean the objective lenses, eyepiece by using lens paper, and make sure no dirt remains on the lenses.
- Avoid accidental touch to the glass part of the objective lens.
- Covered your microscope when not in use or keep in a microscope case.
- Use your 2 hands when transferring a microscope.
- Always clean the immersion oil lens after the use of immersion oil on it.
- For best quality images always use a coverslip.
- Use the dimmer to control the light.
- Use iris diaphragm to control resolution and contrast.
- At first, use the lower magnifications to find out the interested part of the specimen and then adjust further.
Related Posts
- Trinocular Microscope – Definition, Principle, Parts, Protocol, Uses
- Coarse Adjustment and Fine Adjustment Knob of Microscope
- Working Distance – Definition, Measurement, Types, Importance
- Pocket Microscope – Definition, Parts, Principle, Uses, Types
- Polarizing Microscopes – Principle, Definition, Parts, Applications