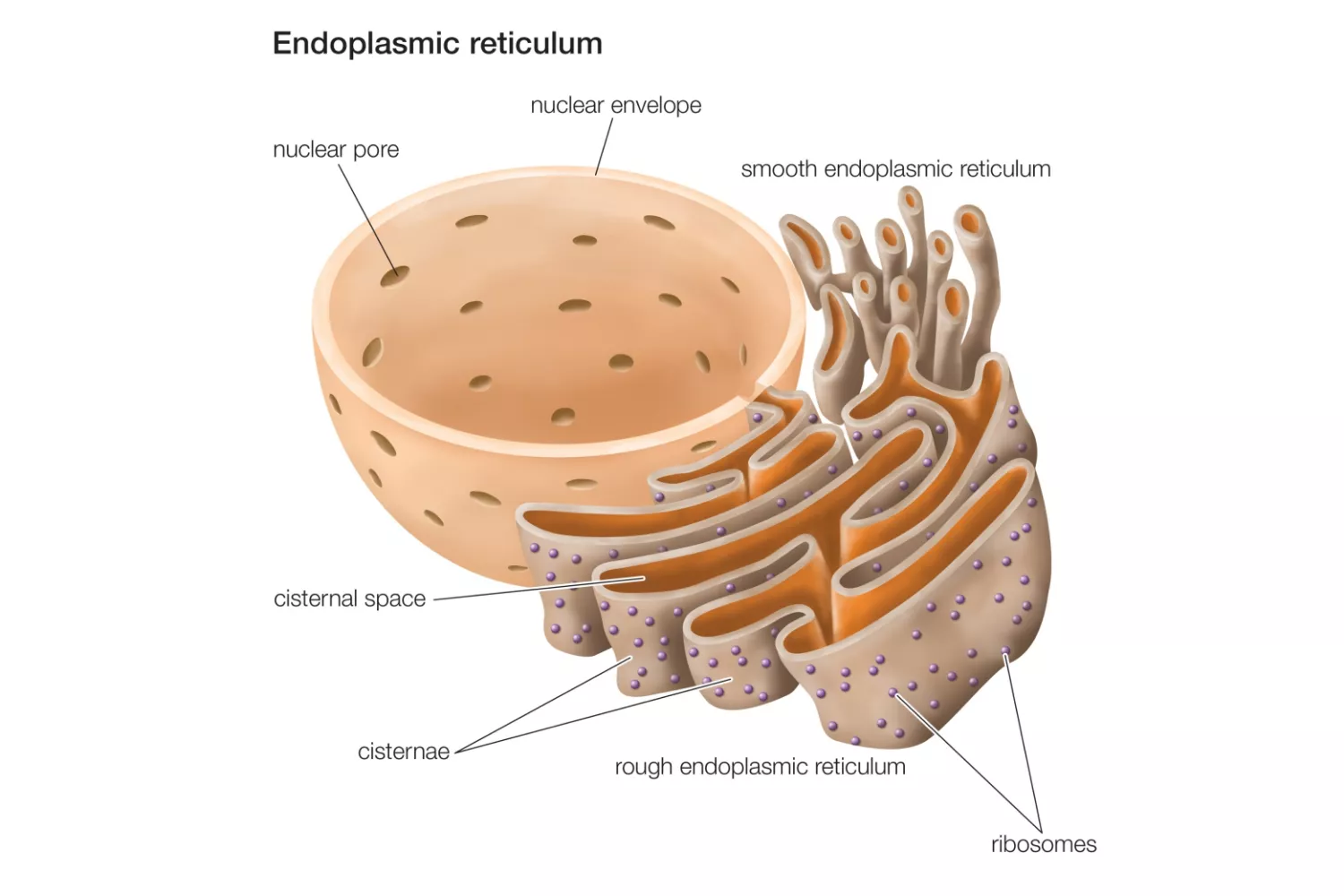
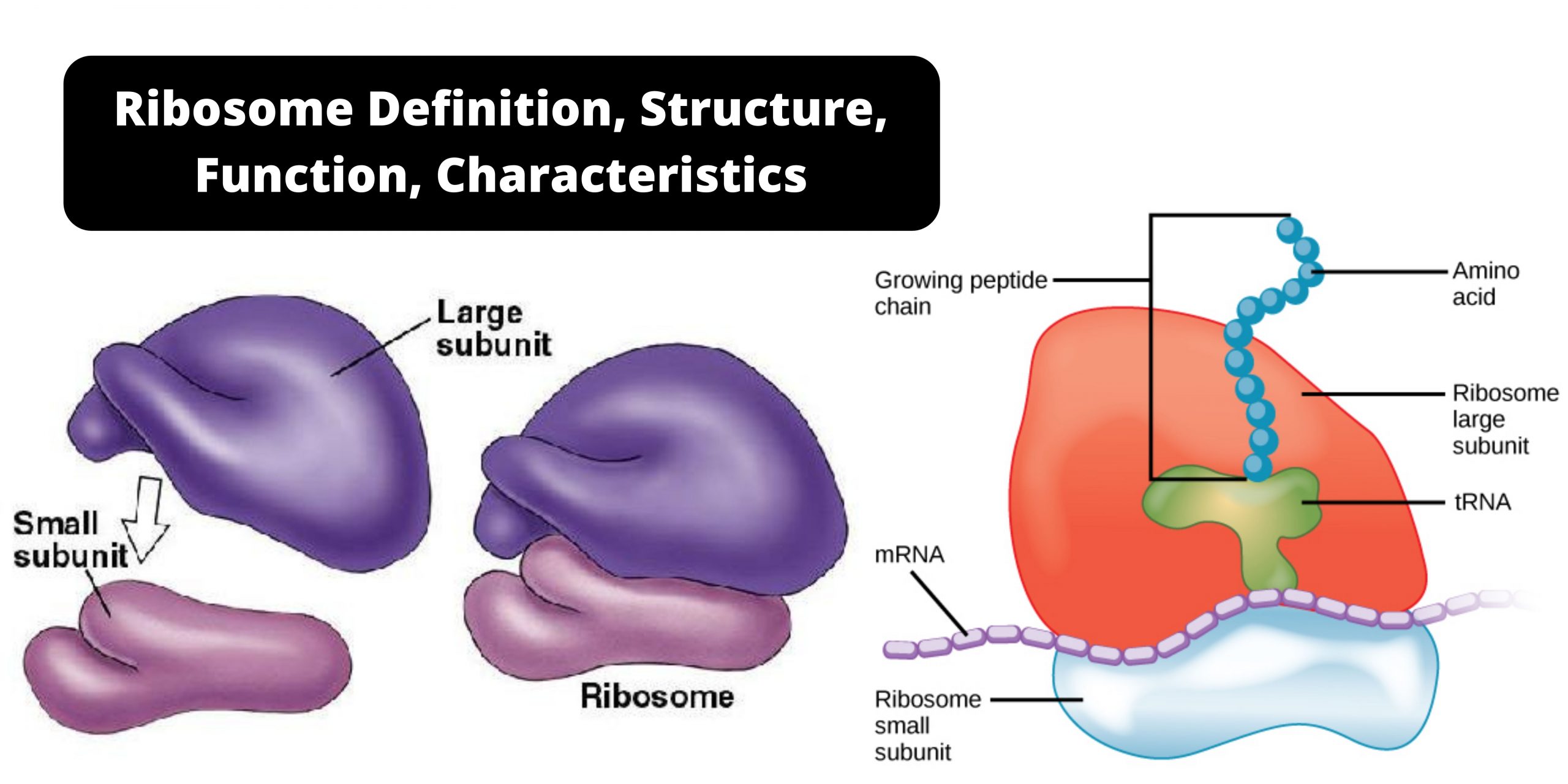
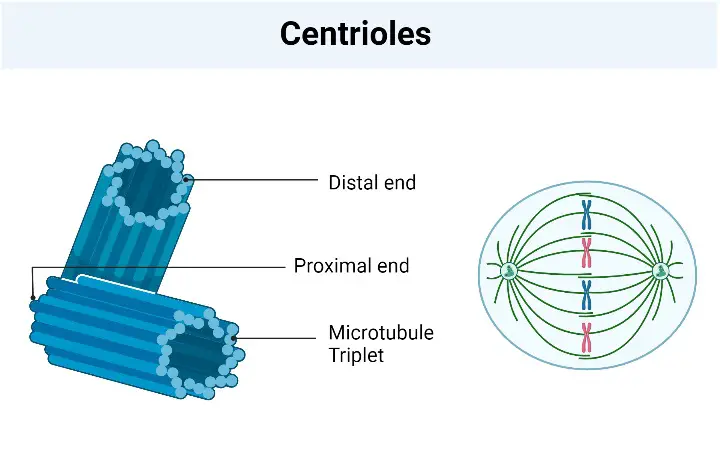
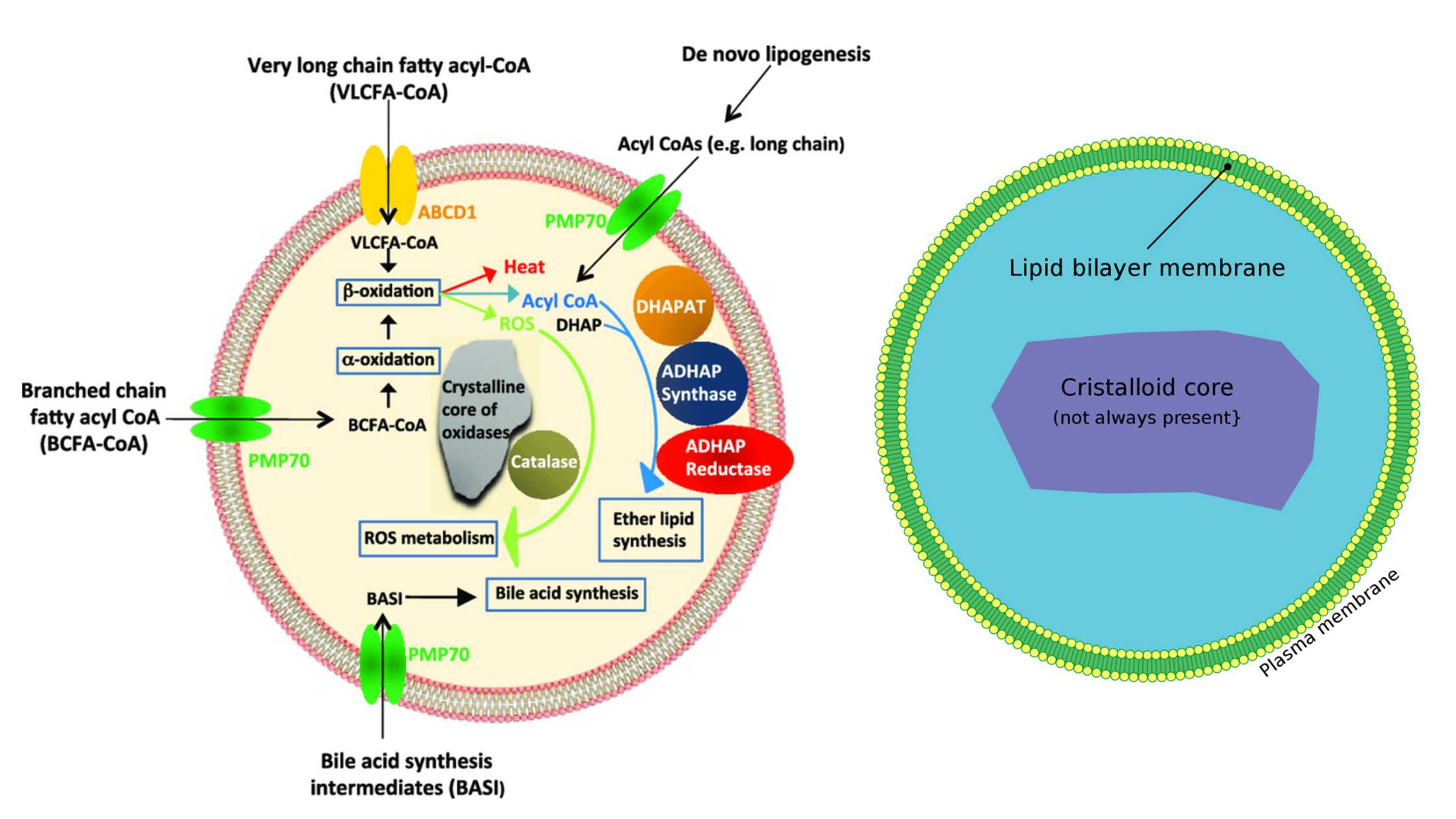
HeLa Cells – Definition, Characteristics, Significance, Applications
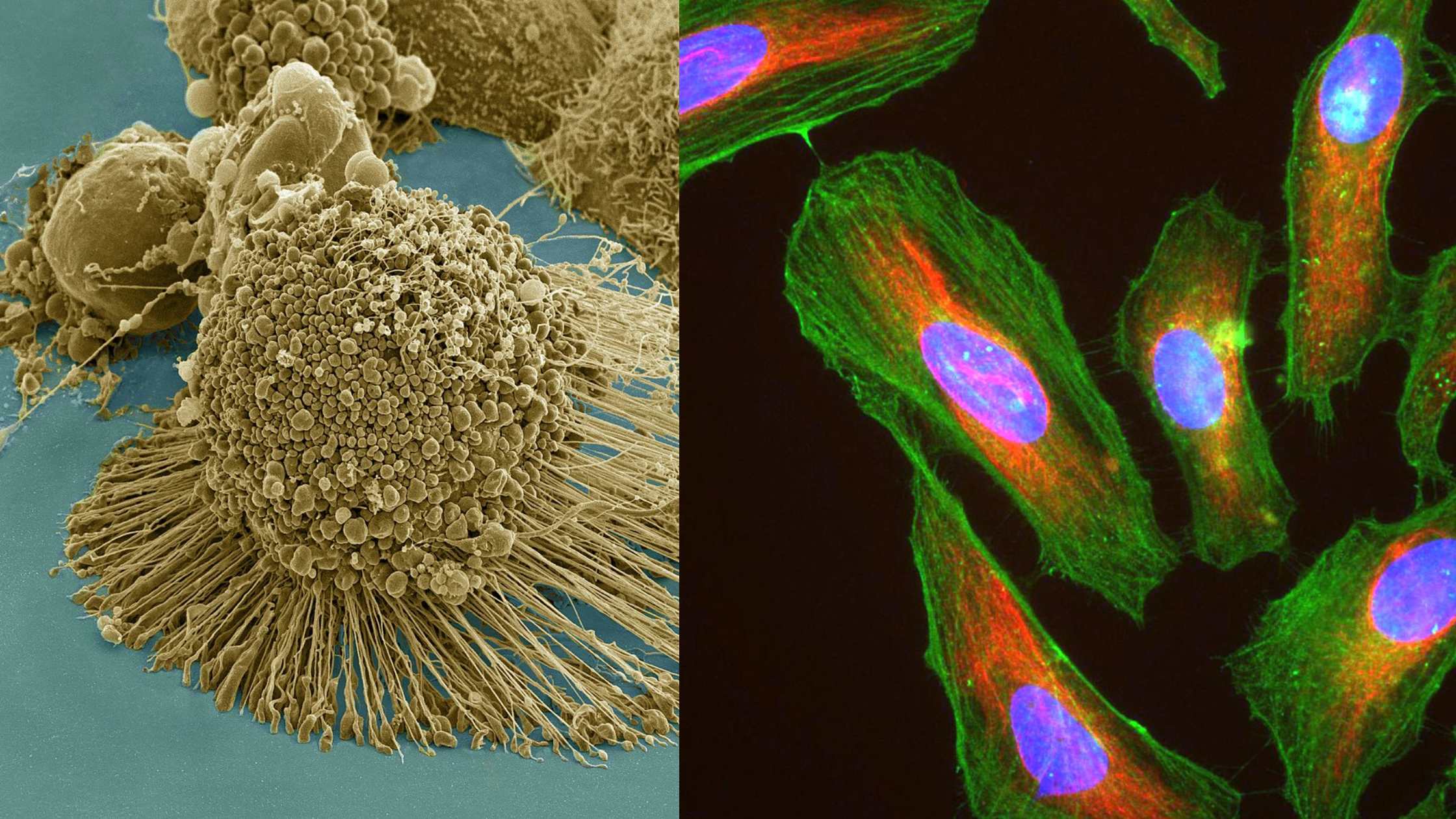
What Are HeLa Cells? Definition of HeLa Cells HeLa cells are an immortal human cell line derived from the cervical cancer tissue of a patient named Henrietta Lacks. First cultured in 1951, these cells have the unique ability to divide and proliferate indefinitely in vitro, making them invaluable for scientific and medical research. Their widespread … Read more