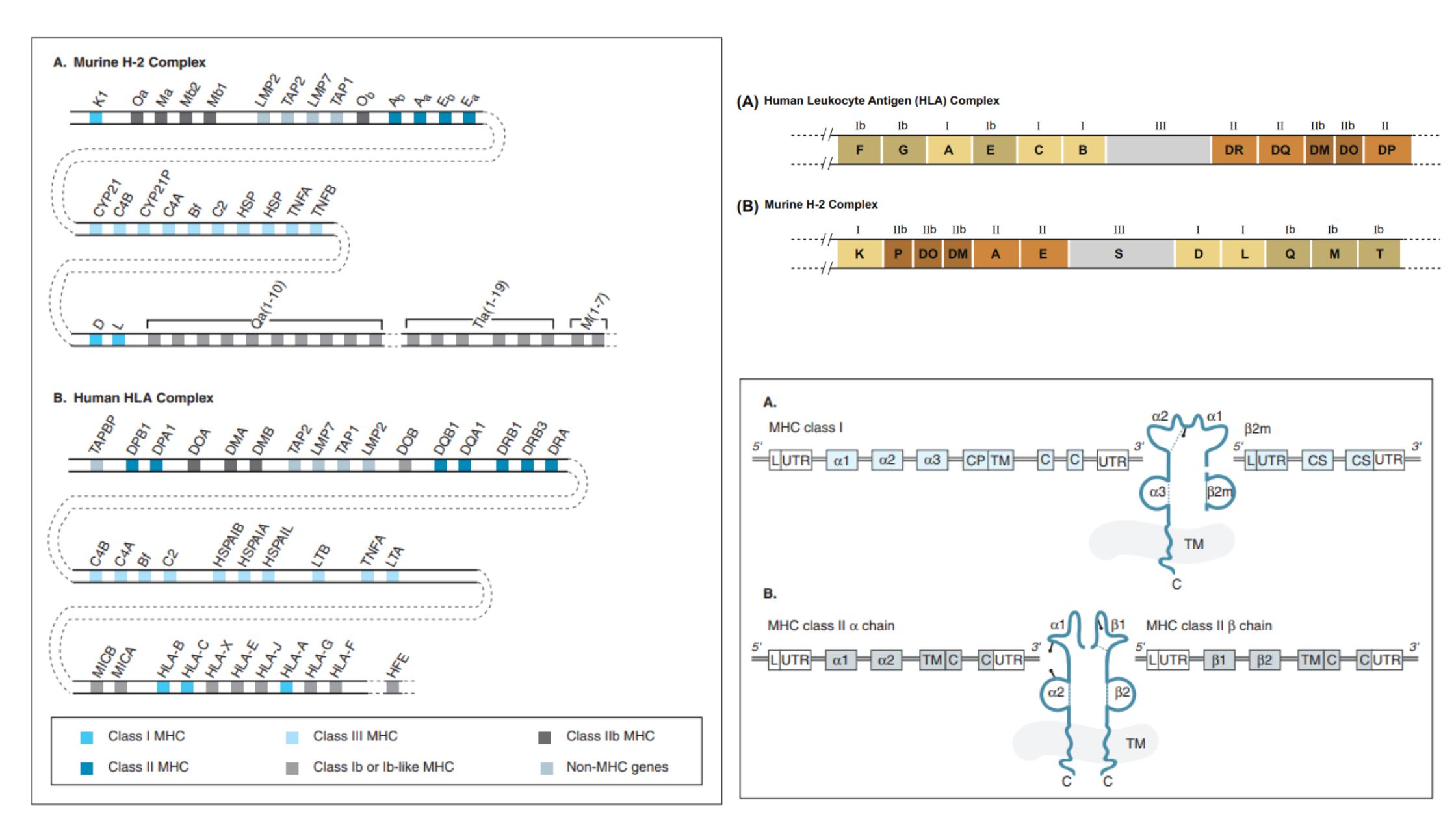
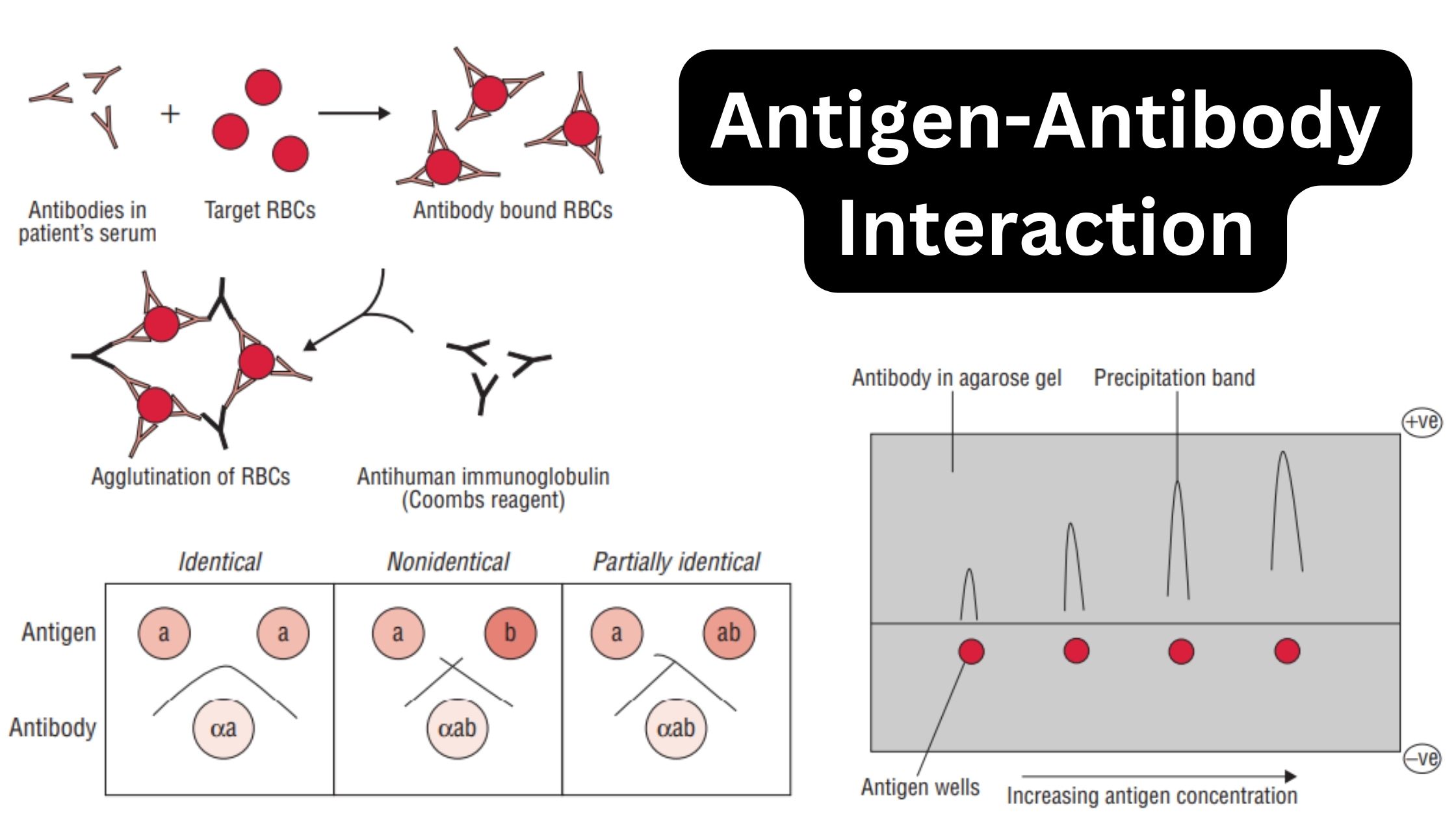
Active Immunity – Definition, Characteristics, Types, Examples
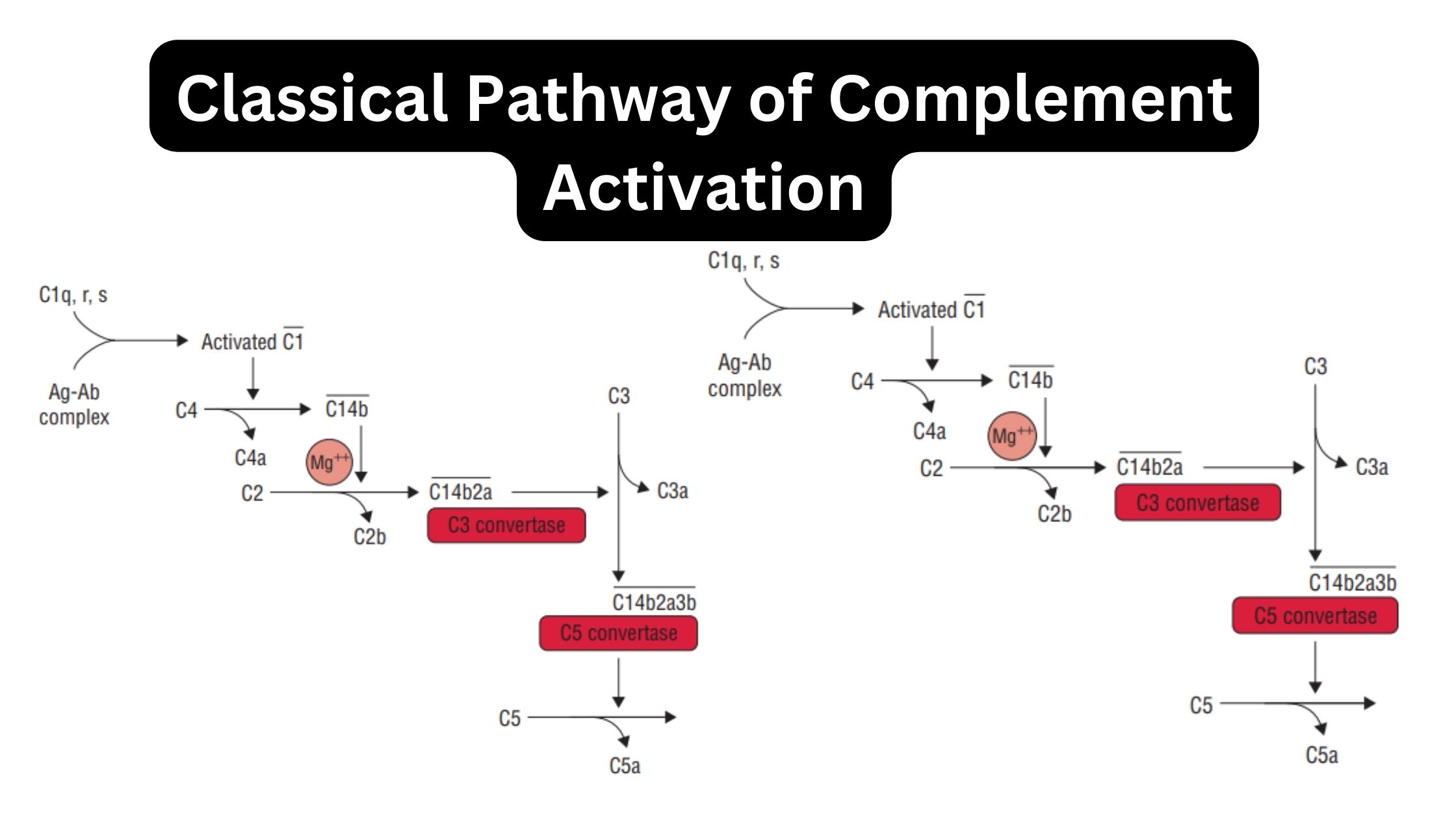
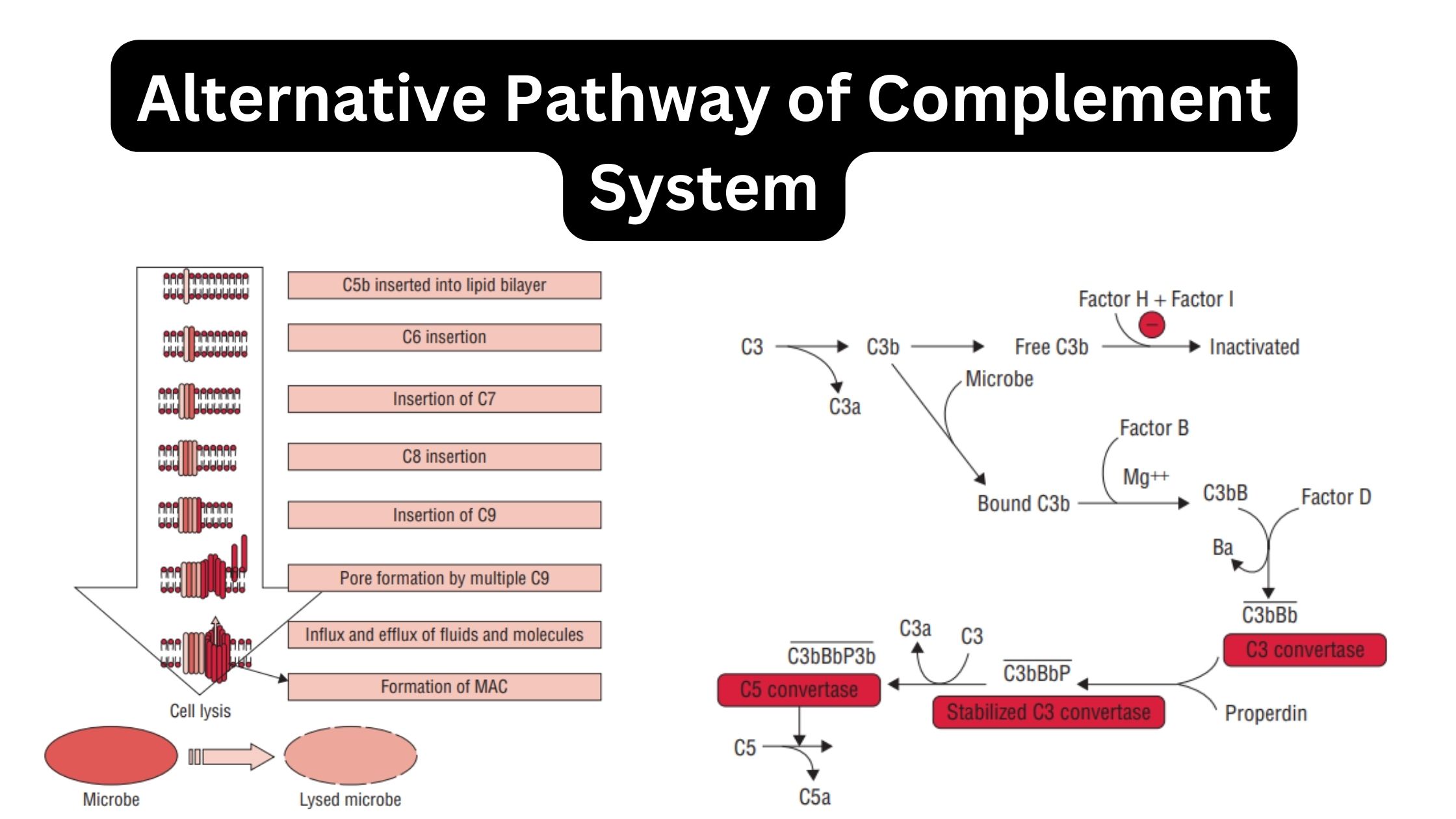
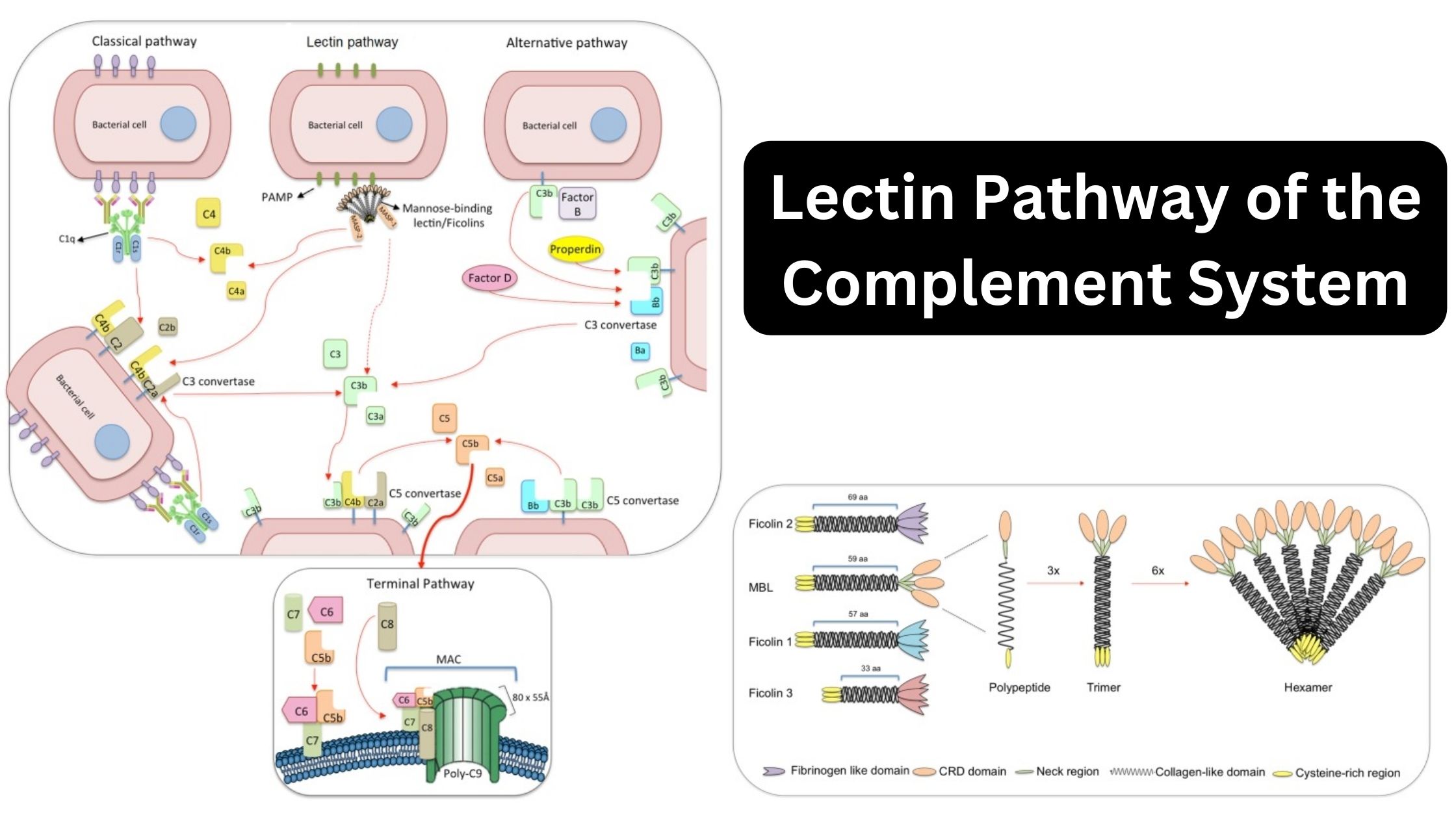
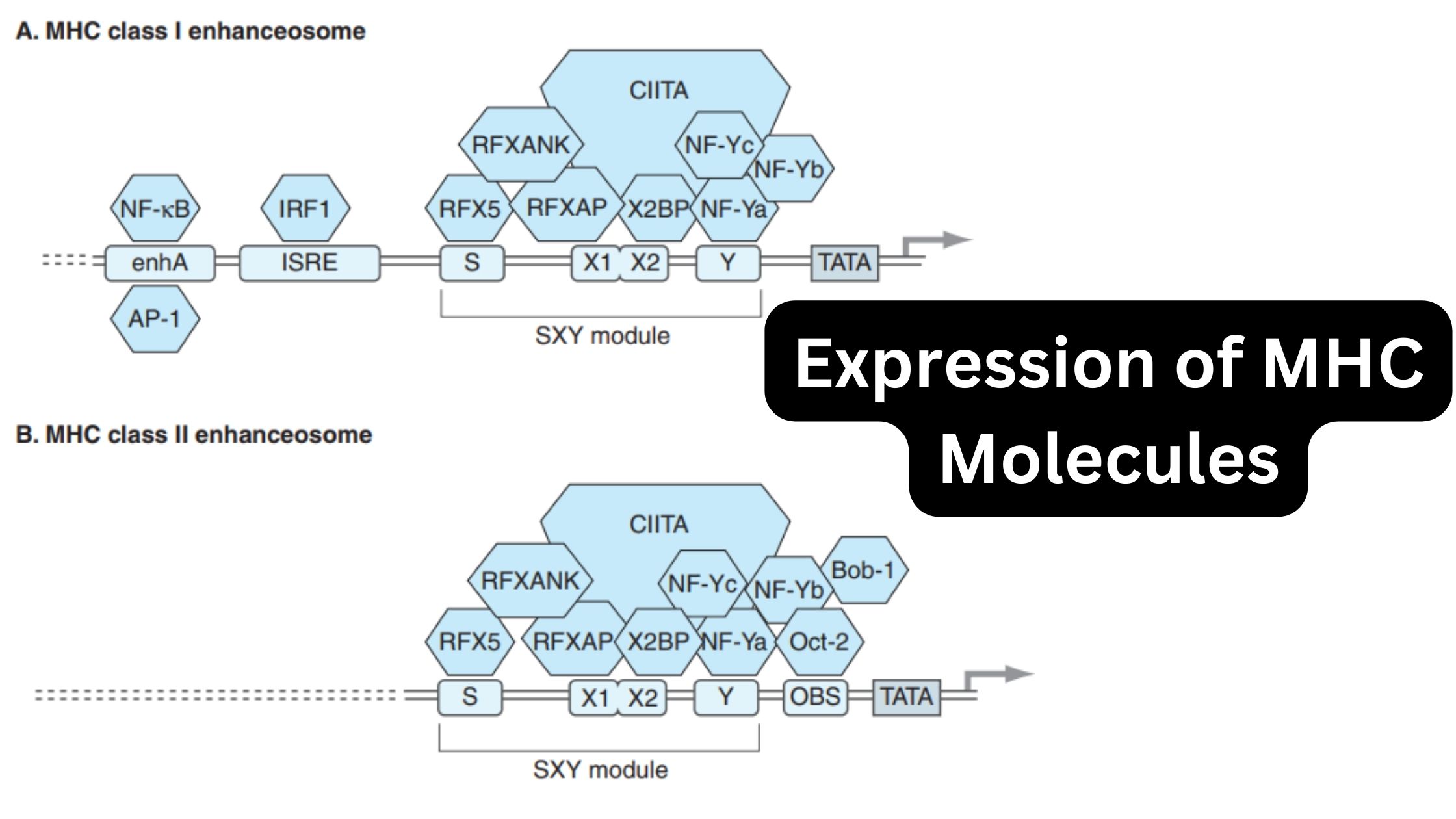
What is Active Immunity? Definition of Active Immunity Active immunity refers to the immunity that is acquired when the body’s own immune system produces antibodies in response to exposure to a foreign antigen, such as a pathogen or vaccine. It provides long-lasting protection against specific antigens. Characteristics of Active Immunity Active immunity possesses several key … Read more