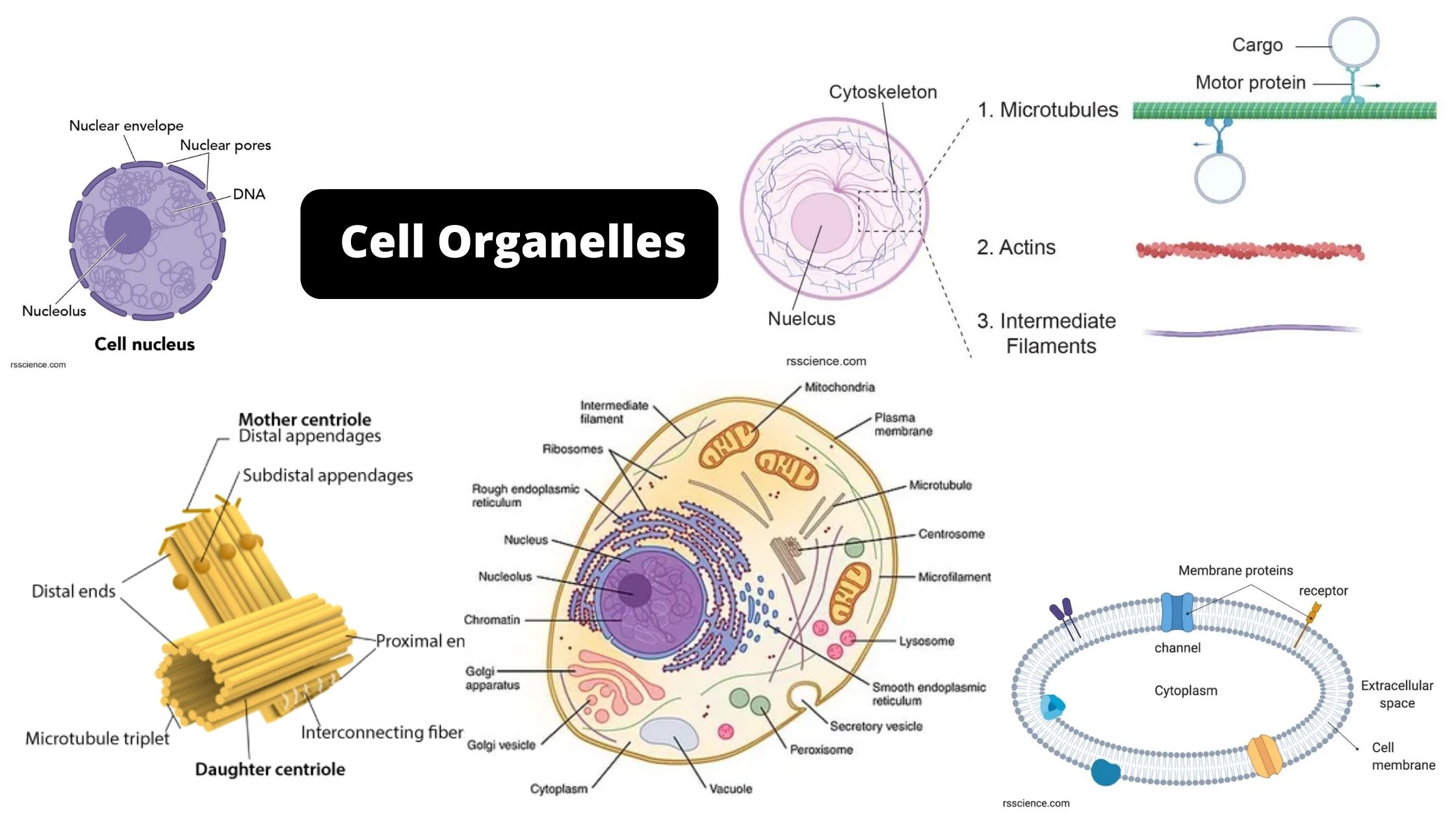
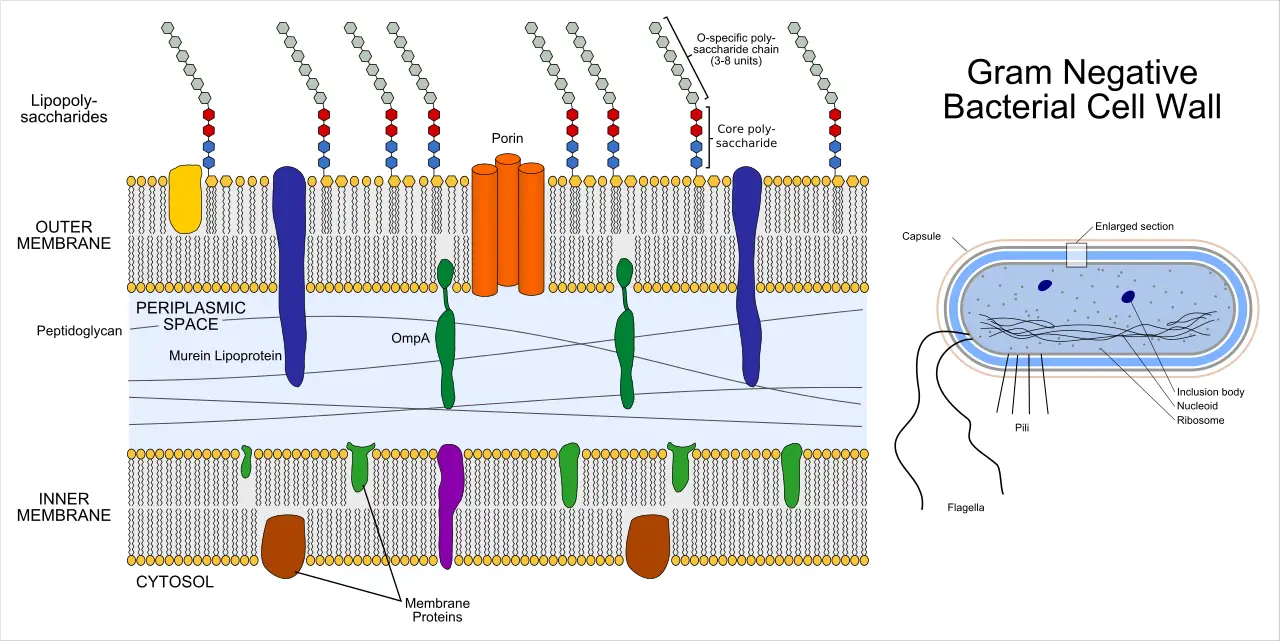
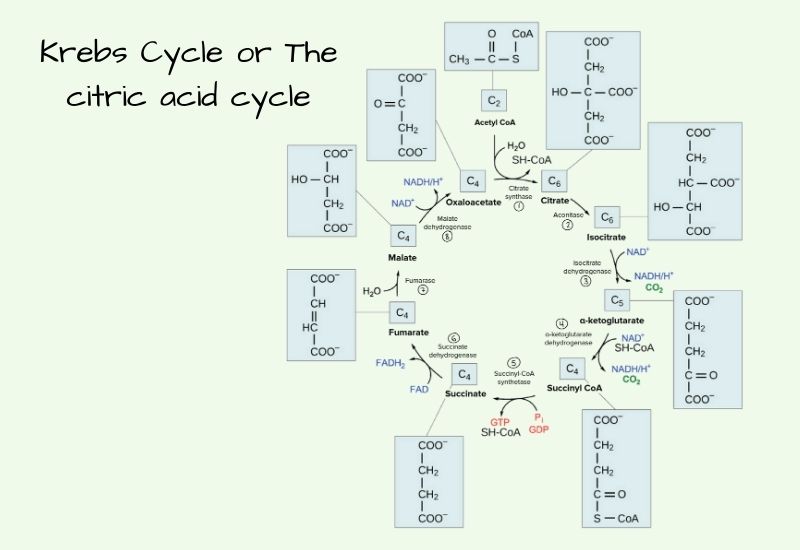
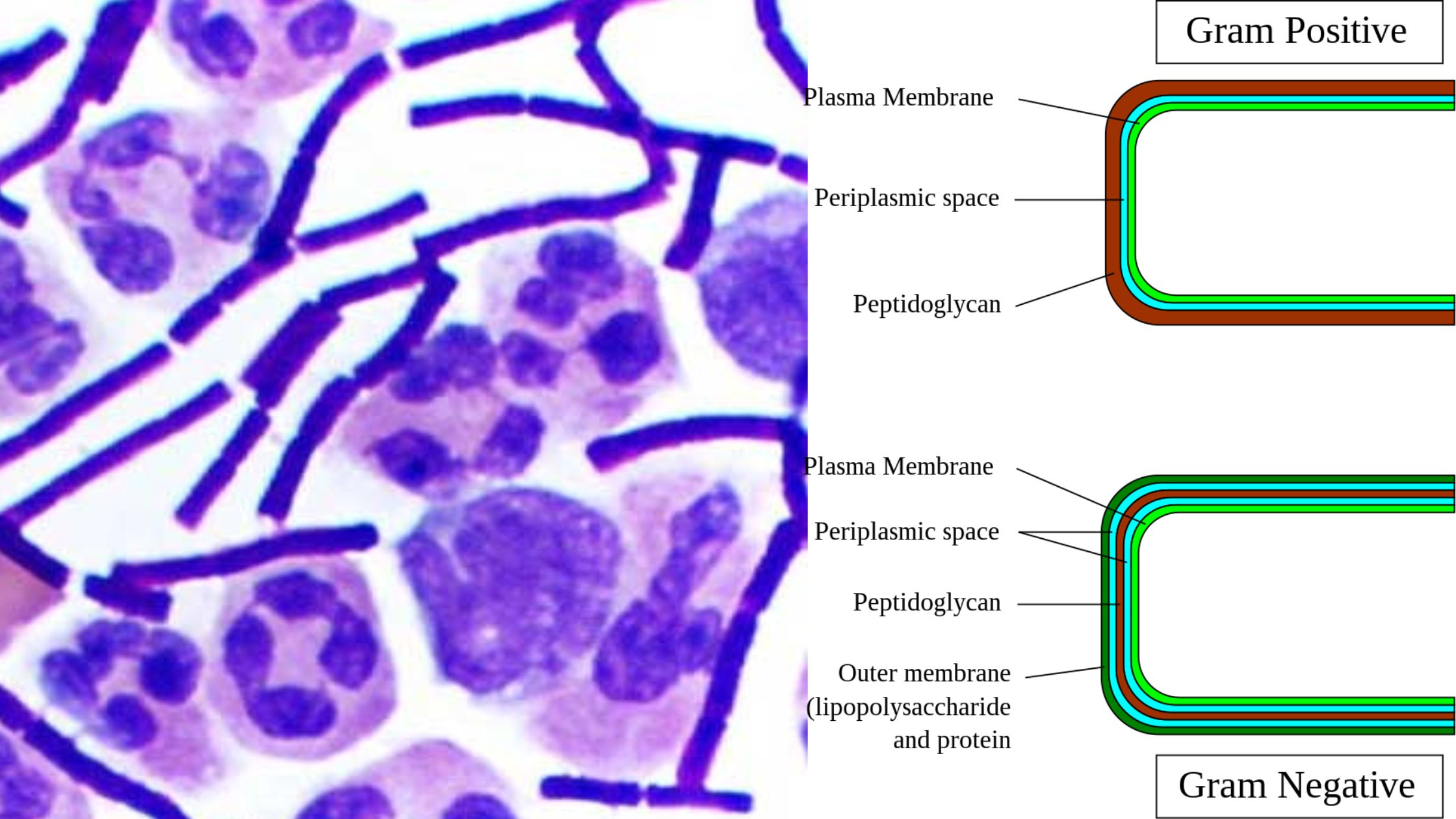
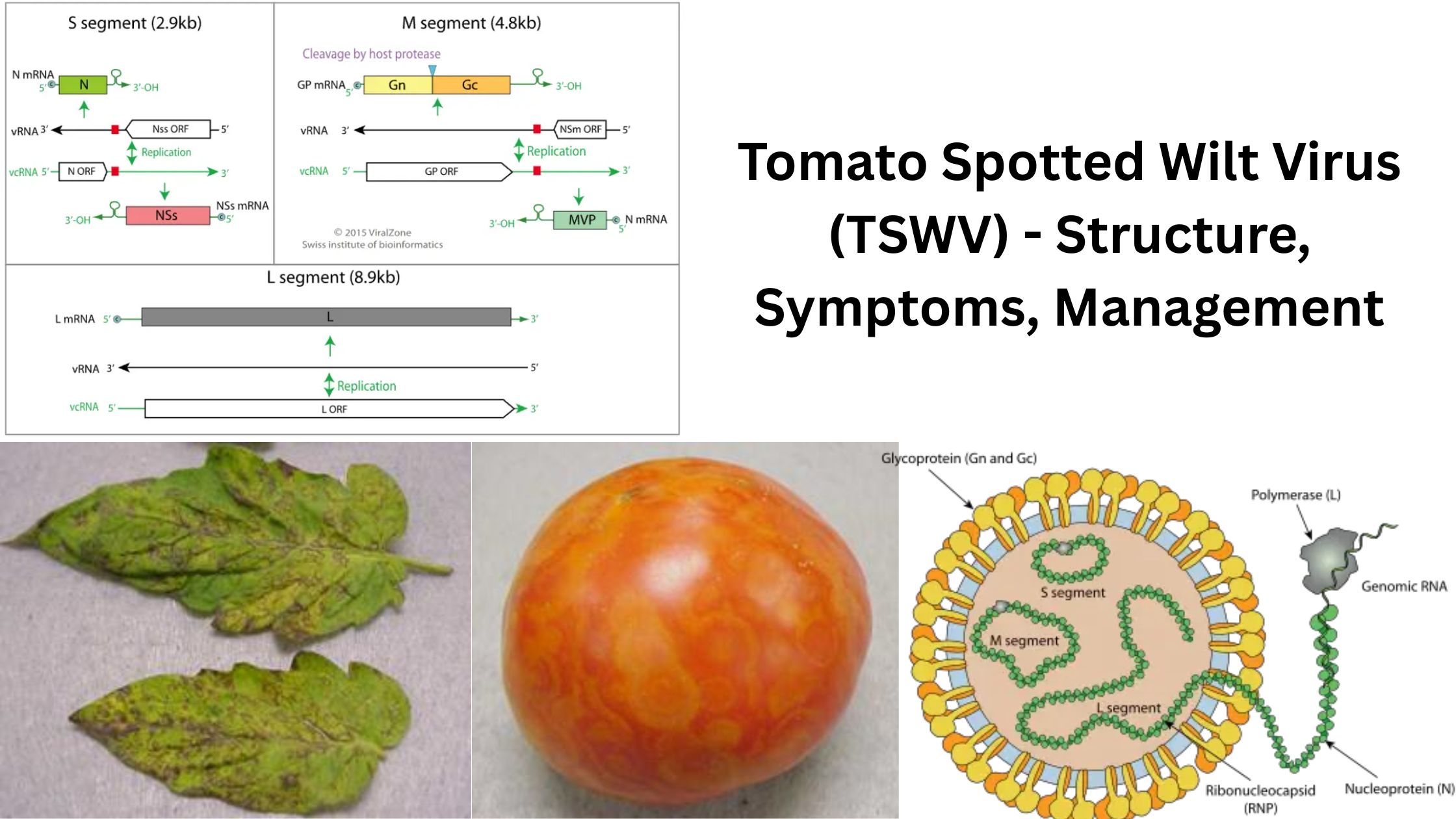
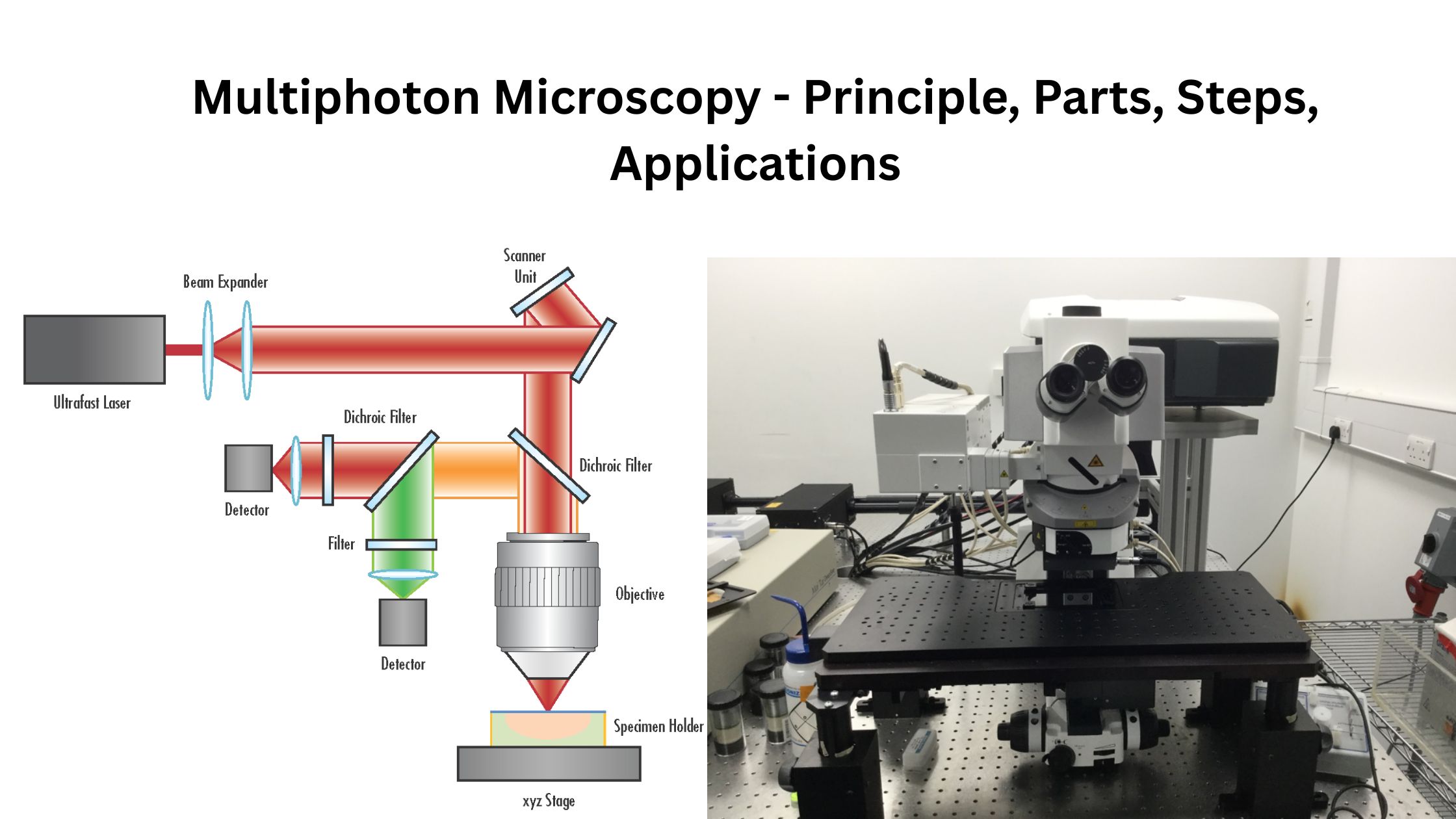
Chlamydomonas – Life Cycle, Habitat, Structure, Examples
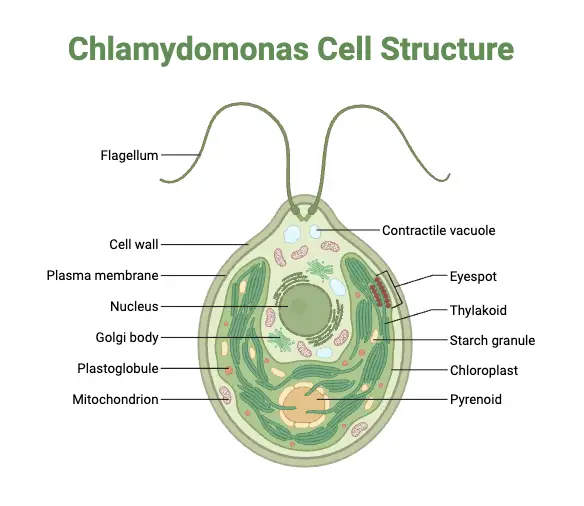
Chlamydomonas is a tiny, single-celled green algae you’d likely find in ponds, soil, or even damp tree bark. Imagine a microscopic organism shaped like a oval, sporting two whip-like tails called flagella that let it zip through water. What’s cool about it? Despite its simplicity, it’s a powerhouse in science. Researchers love studying it because … Read more