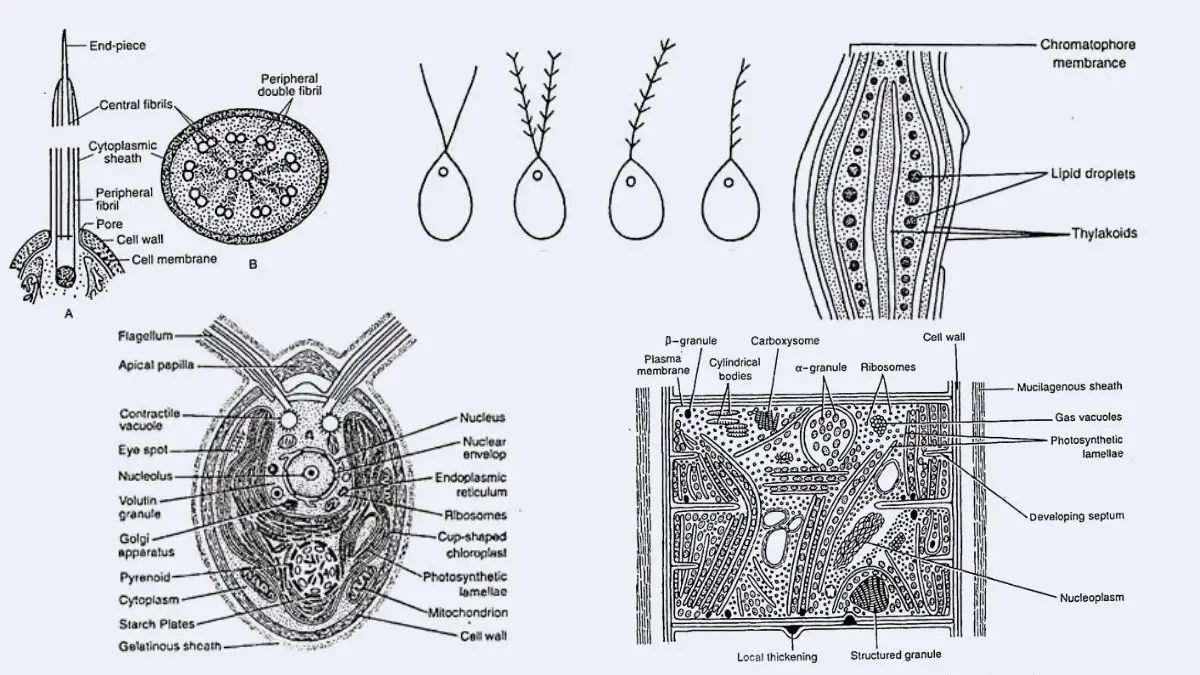
Algal Cultivation – Methods, Factors, Feature, Types, Uses
Algal cultivation means growing algae (microalgae or seaweeds) in controlled or partly controlled environments for useful biomass. The algae are supplied with light, carbon (often CO₂), water and nutrients so growth is promoted. In open ponds (raceway ponds etc.), cultures are exposed to ambient conditions, and mixing is provided to avoid shading and settling. Photobioreactors … Read more