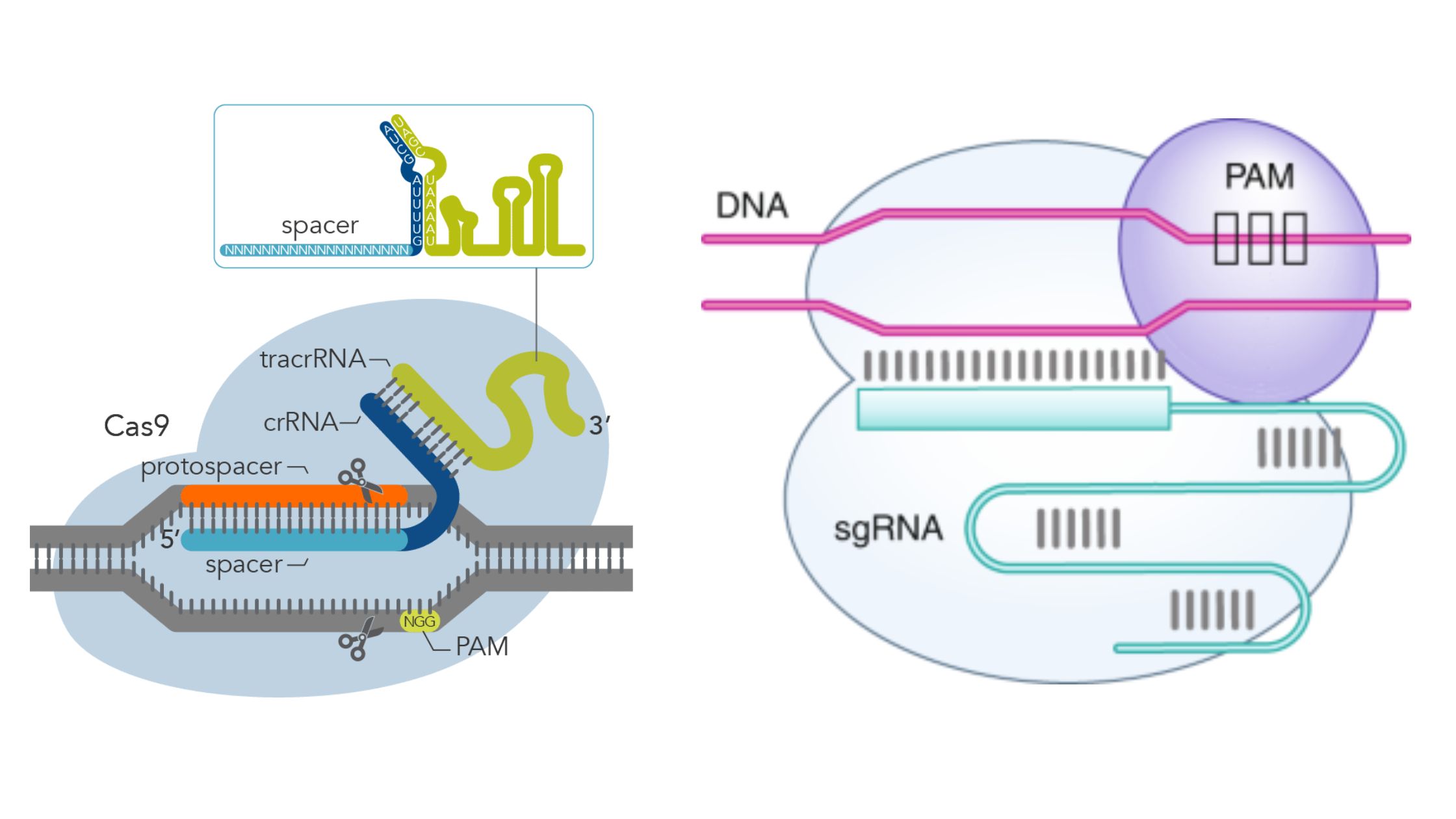
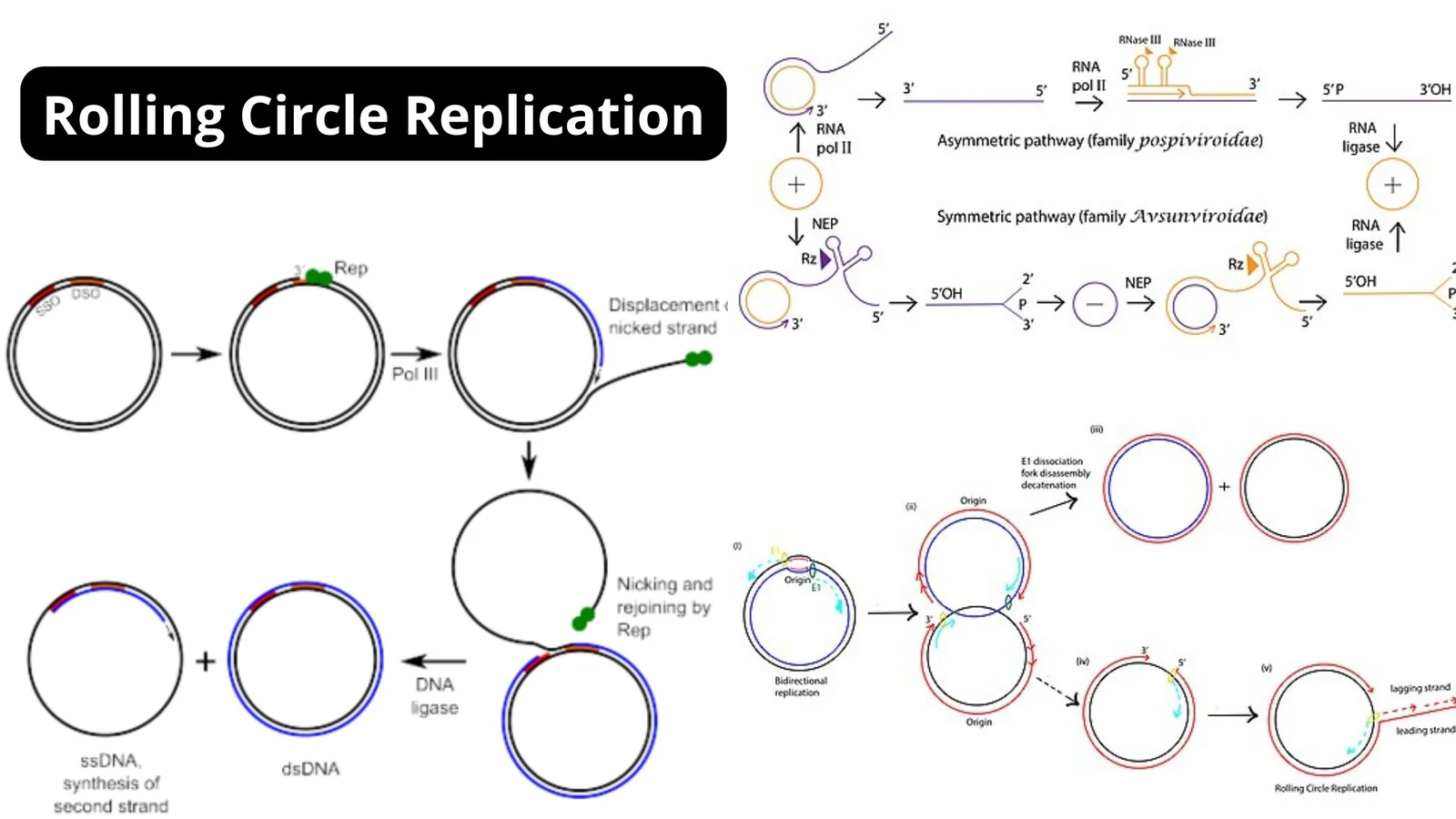
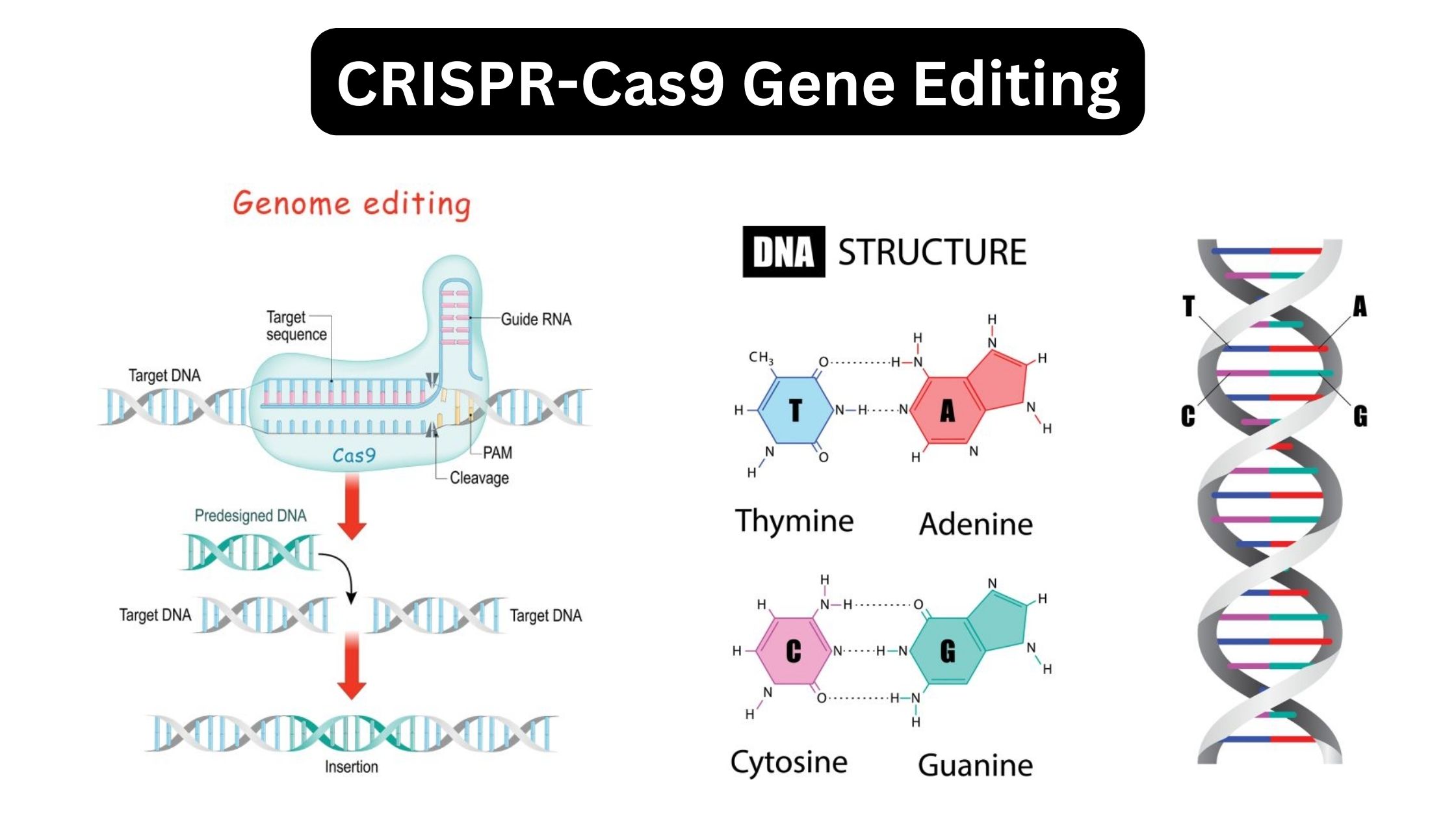
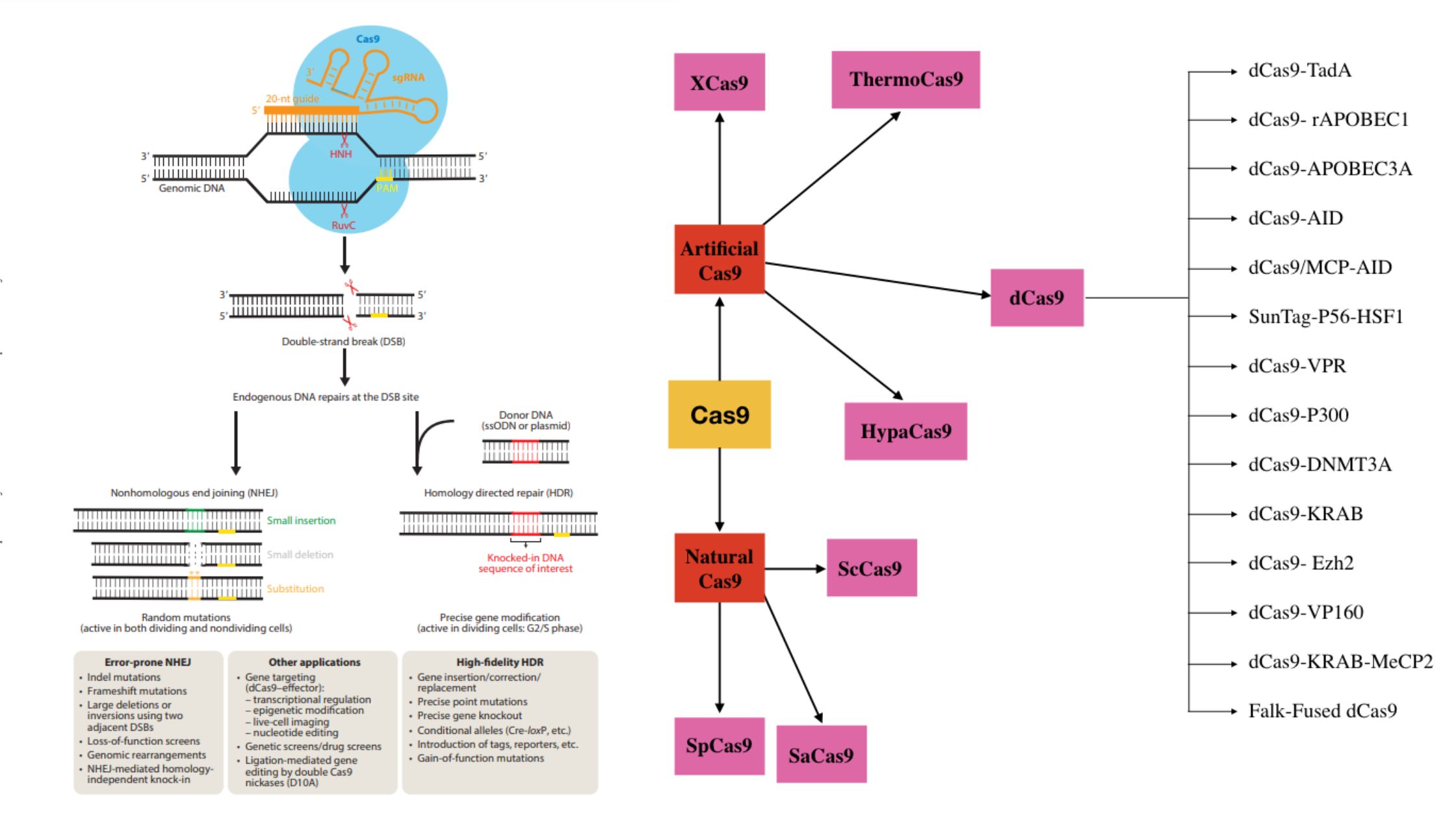
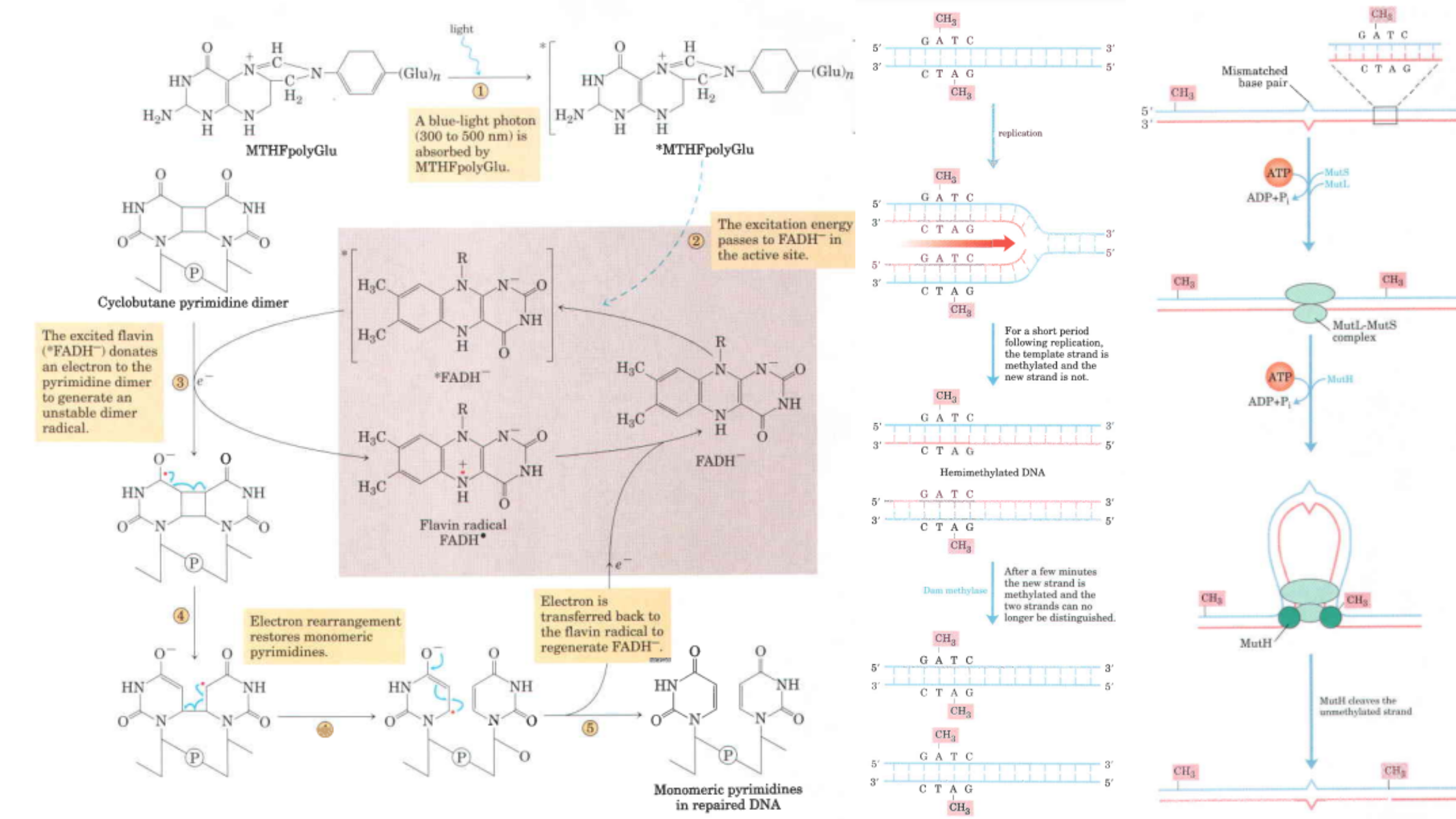
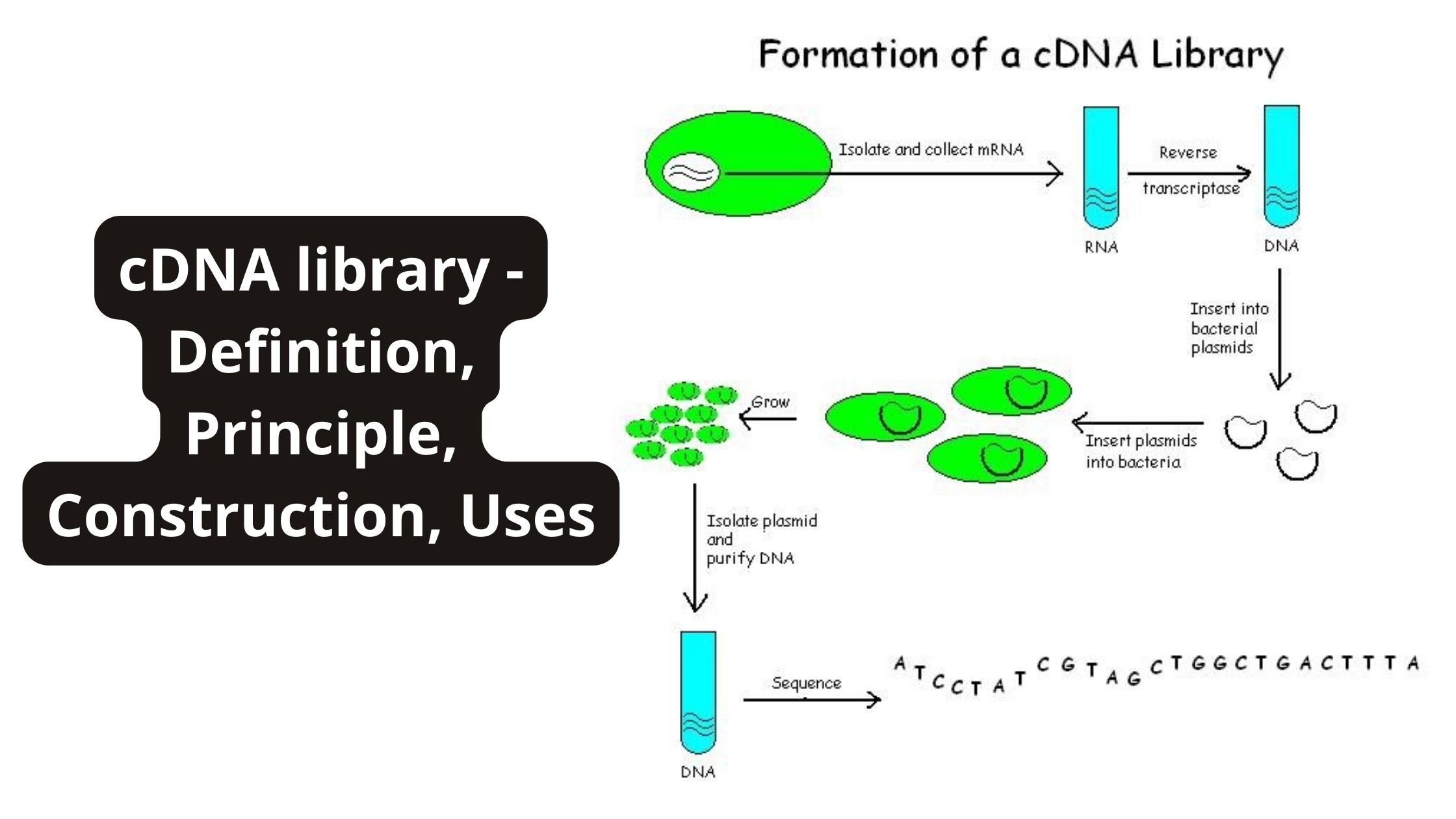
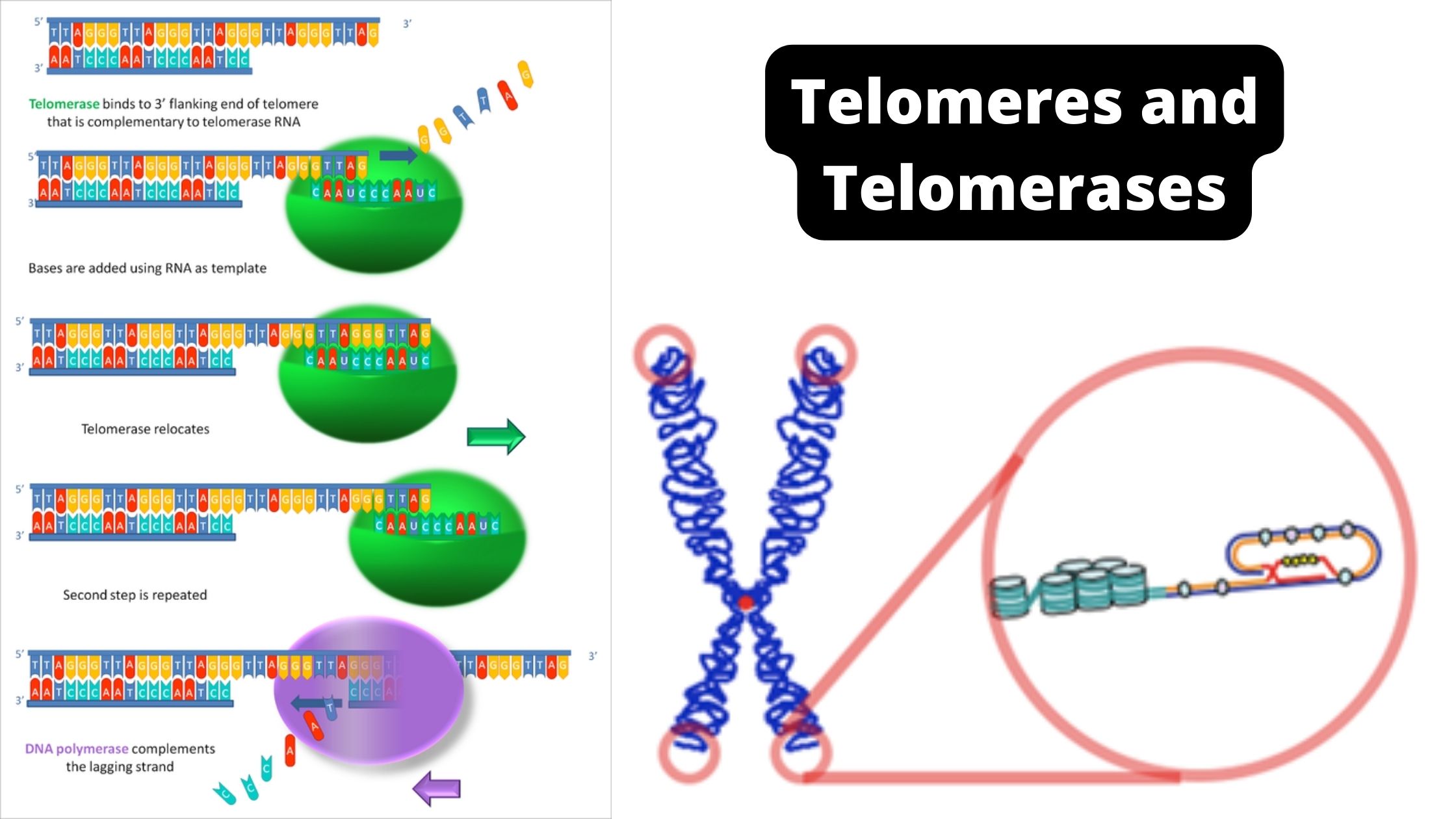
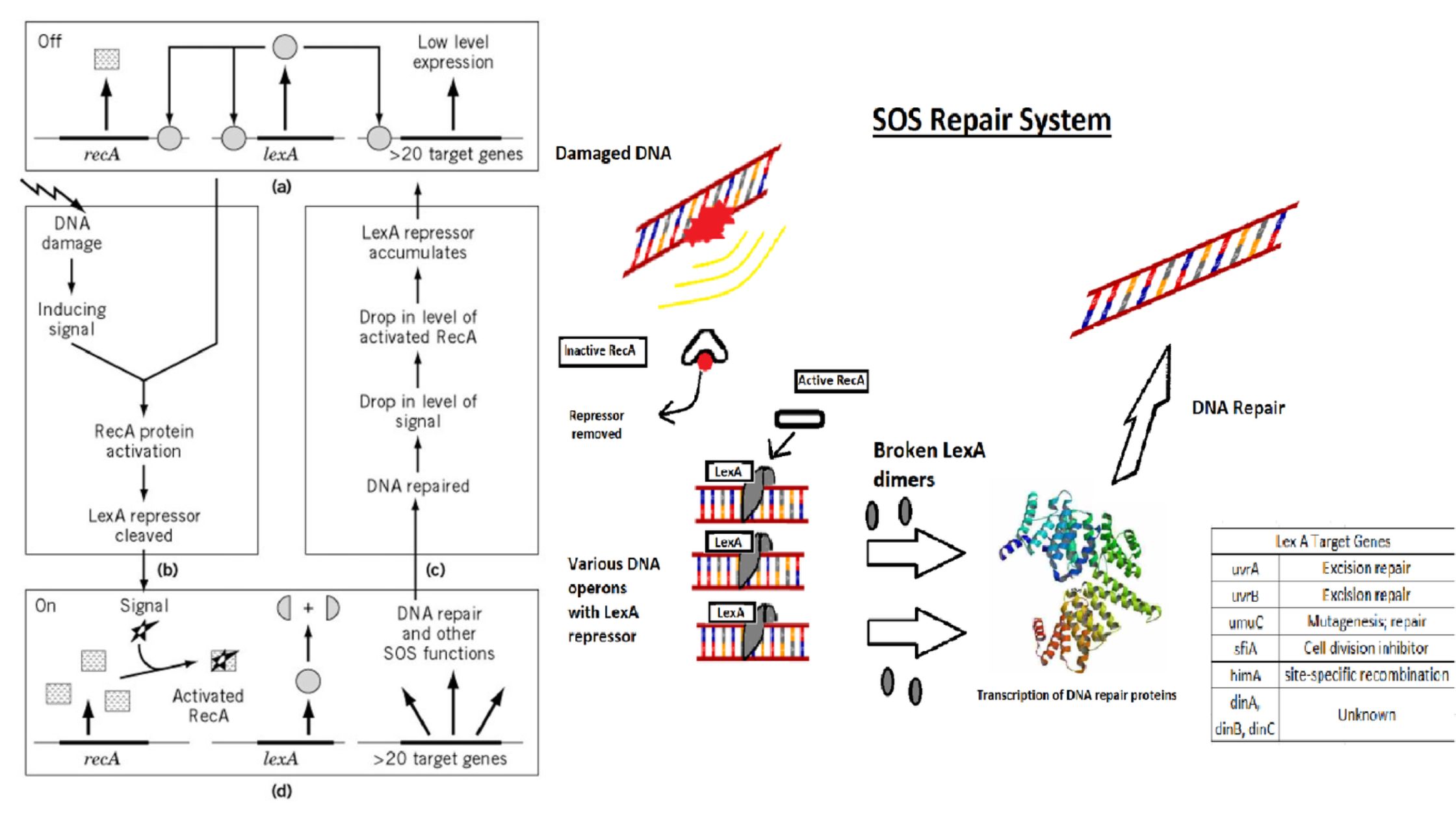
PAM Sequence (Protospacer adjacent motif) – Definition, Functions, Properties
What is PAM Sequence (Protospacer adjacent motif)? Protospacer Adjacent Motif, or PAM, is a type of two-factor authentication that tells Cas to only cut the foreign DNA that is invading. Properties of PAM sequence Spacers/protospacers PAM sequences Functions of PAM Sequence 1. Role of PAM in spacer acquisition 2. Role of PAM in interference 3. … Read more