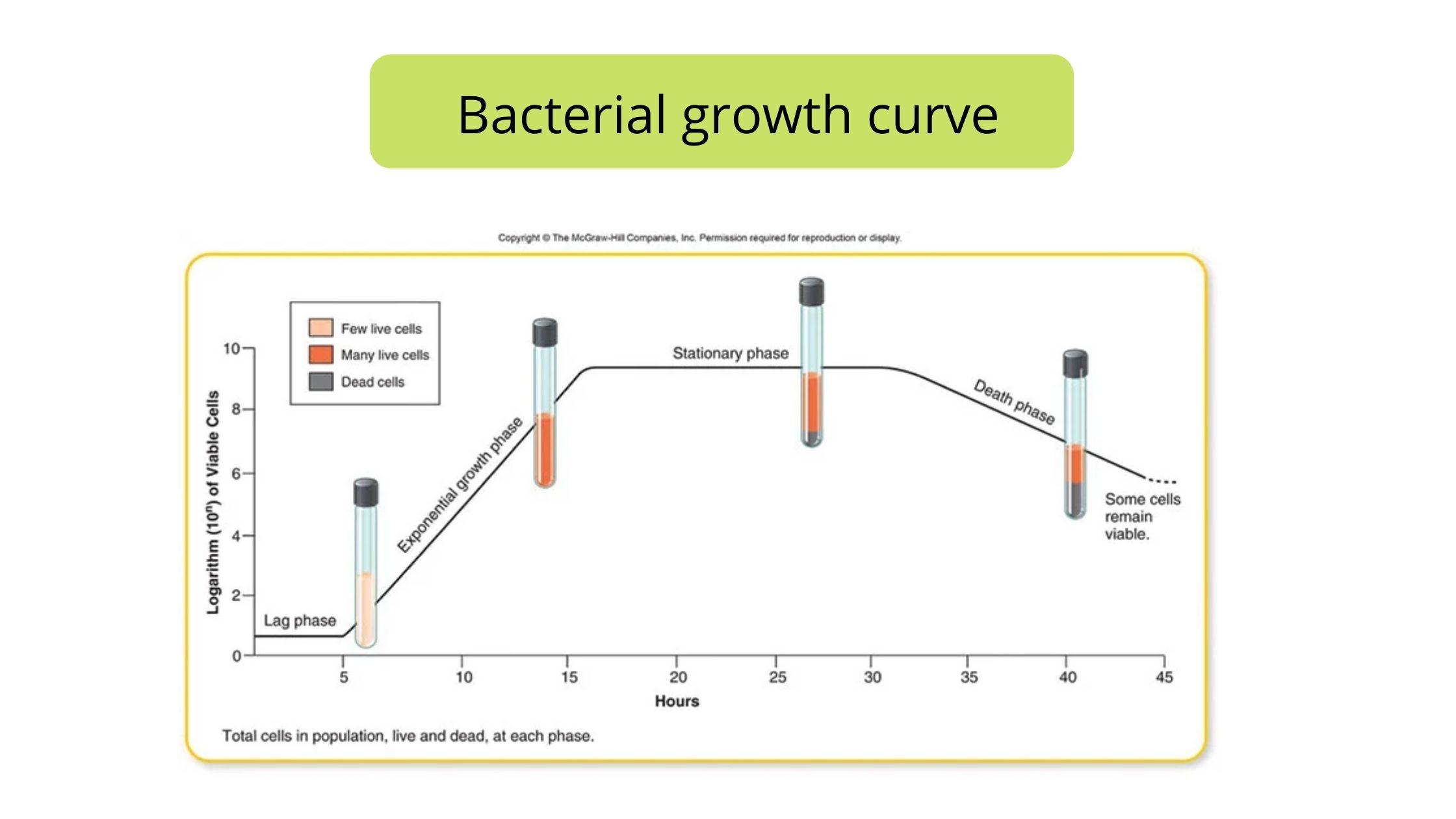
Foodborne Infection by Shigella – Shigellosis Food Poisoning
What is Shigella infection? Biological characteristics of Shigella Shigella bacteria possess several distinctive biological characteristics that contribute to their ability to cause infection and survive in various environments. Here are the key biological characteristics of Shigella: Sources and transmission of Shigella infection Epidemiology of Shigella infection The epidemiology of Shigella infection provides insights into the historical background, transmission dynamics, and global burden of … Read more