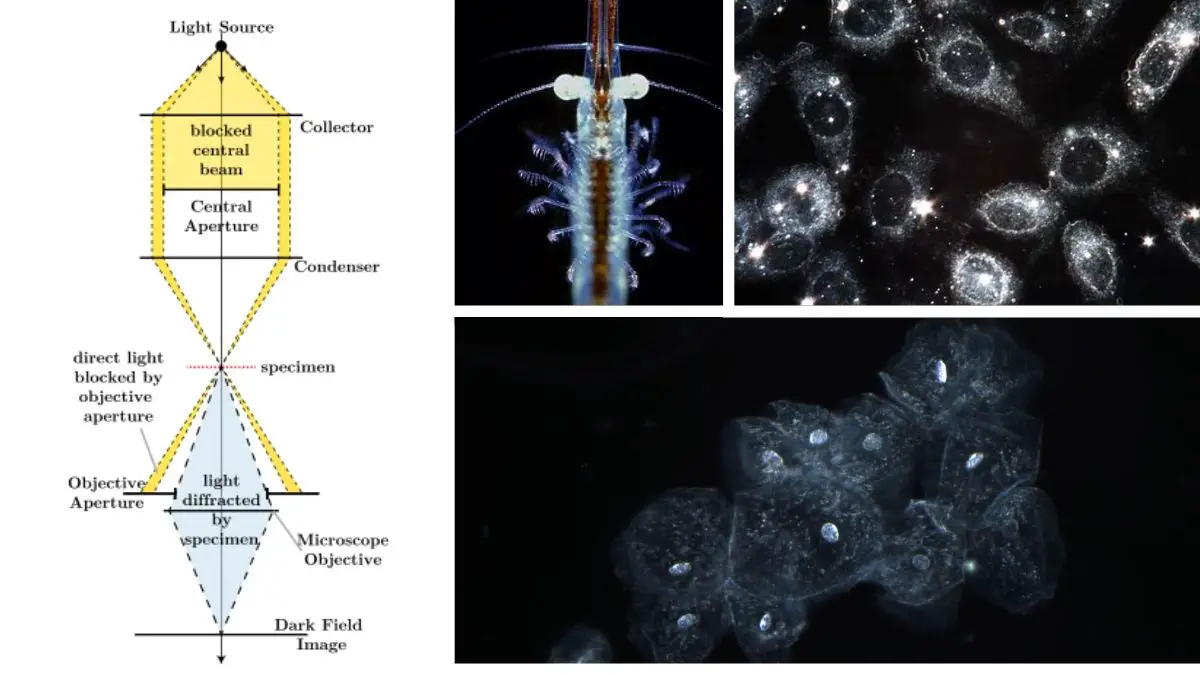
How are samples prepared for a transmission electron microscope?
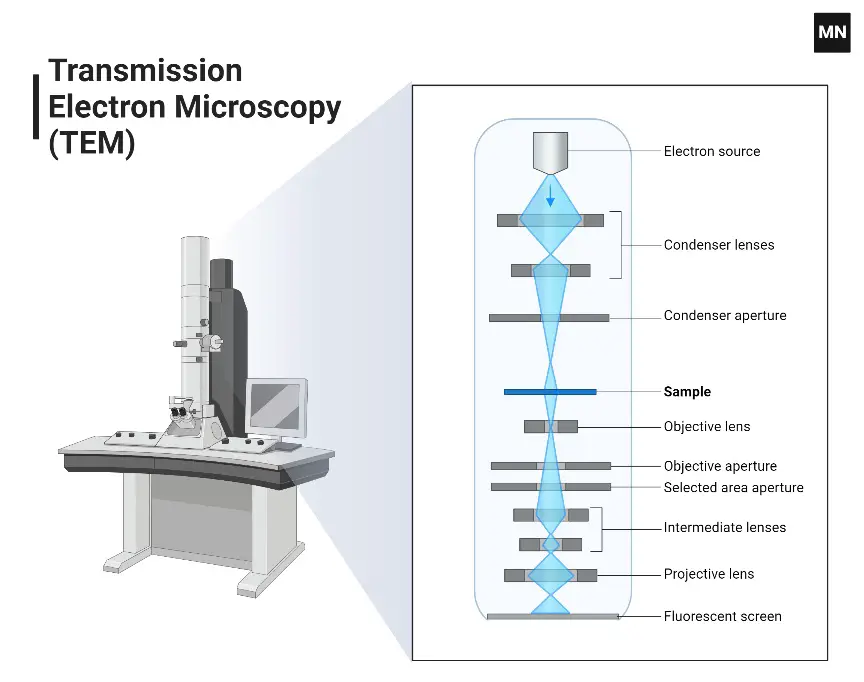
What is transmission electron microscope? A transmission electron microscope (TEM) is an electron microscope that transmits electrons through a sample to observe it. Scientists use transmission electron microscopes to analyze materials and examine their microstructural and compositional properties. A transmission electron microscope transmits a highly focused beam of electrons through a sample to observe and … Read more