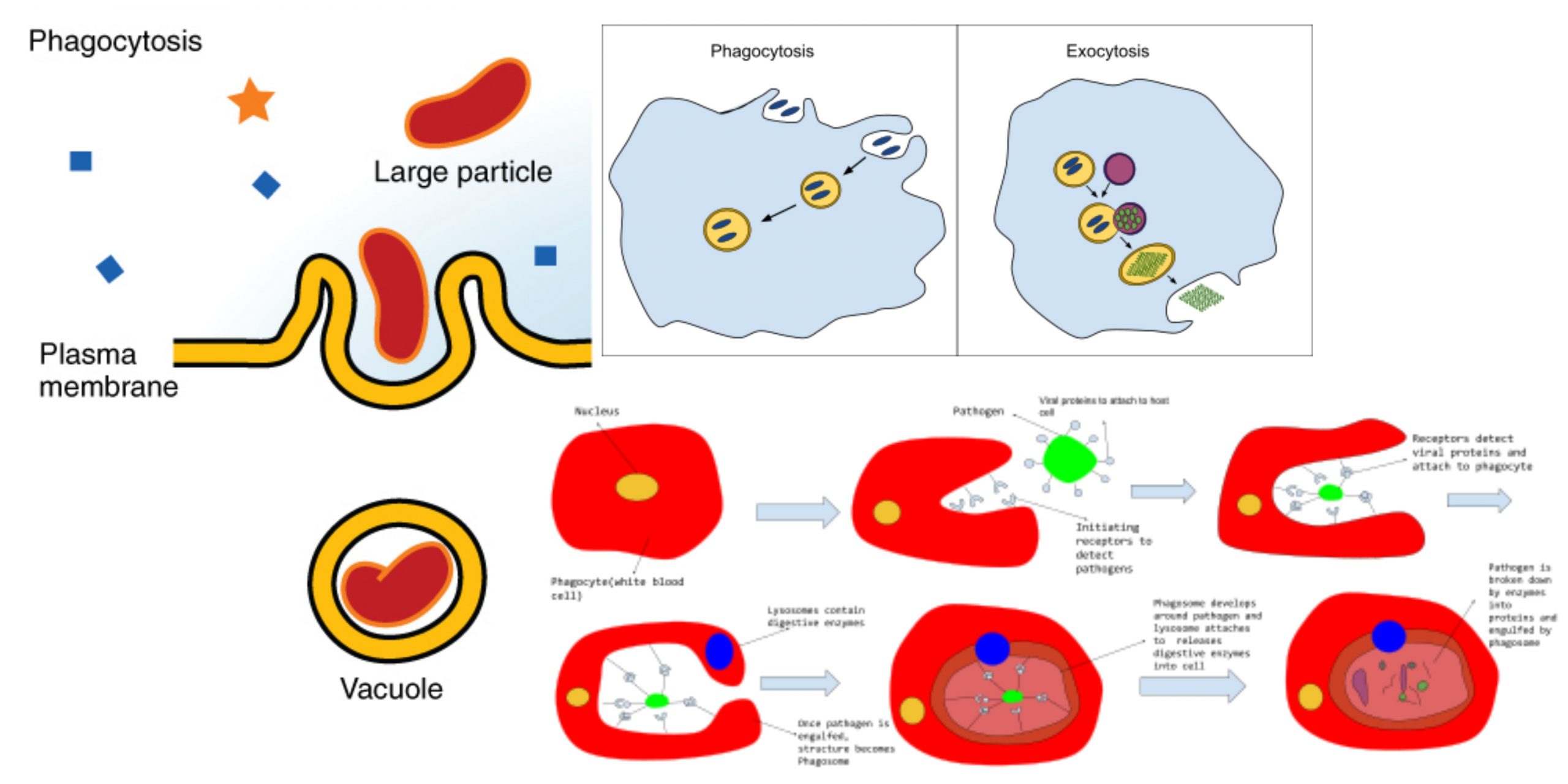
Tumor Antigen
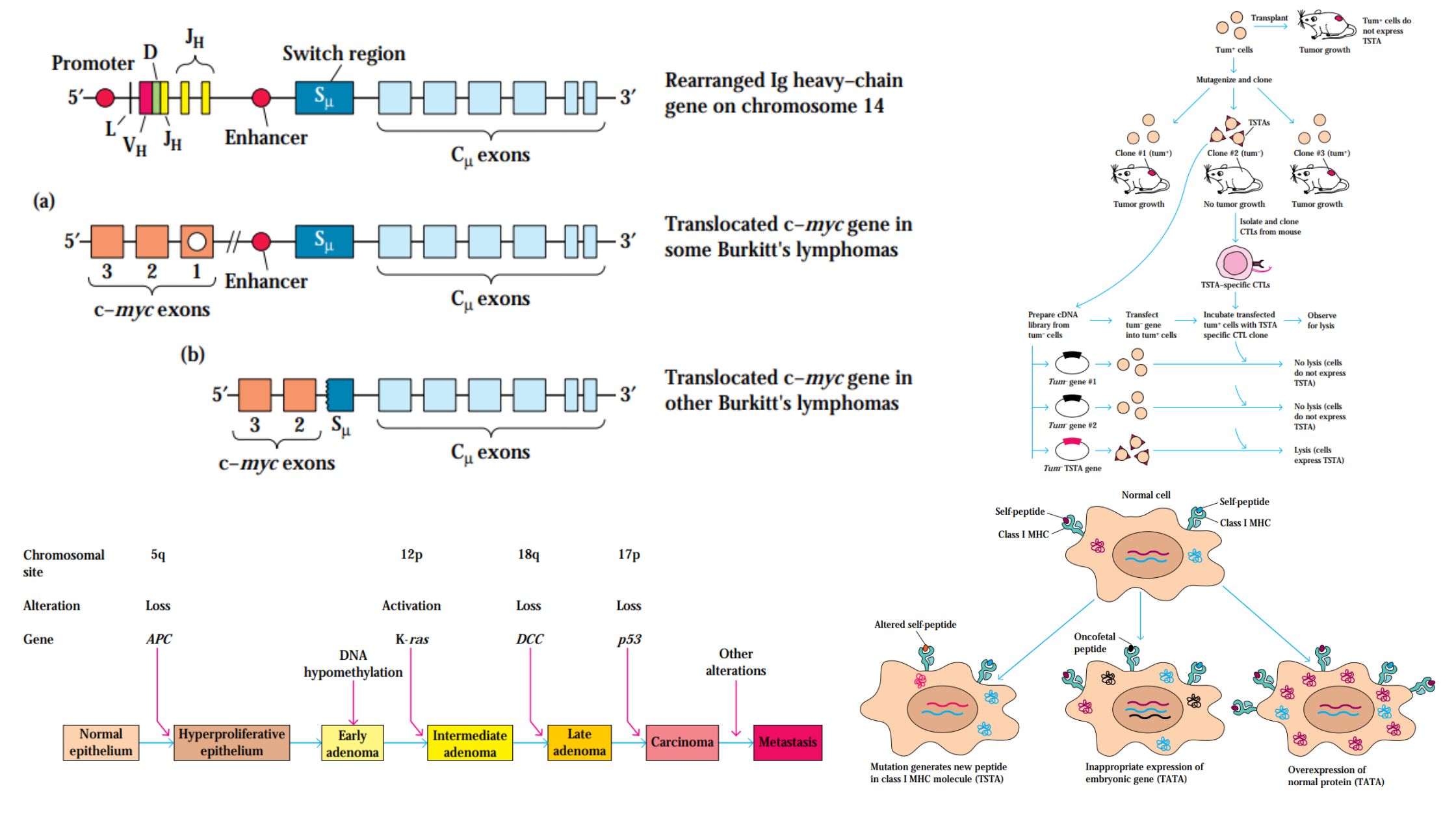
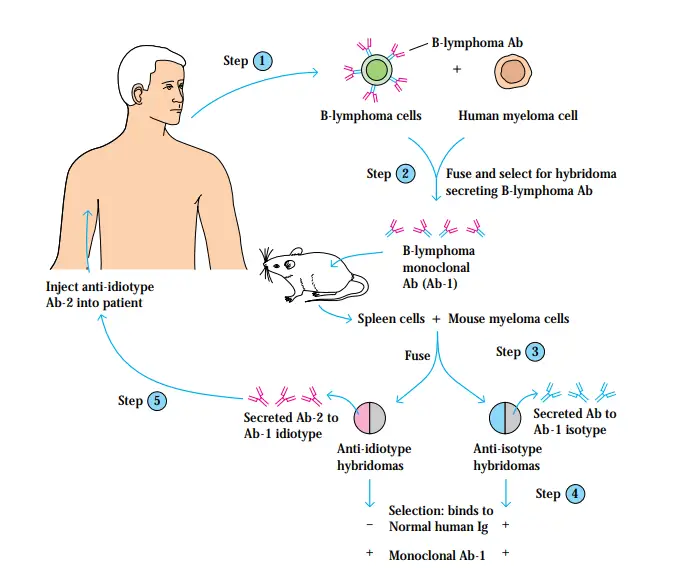
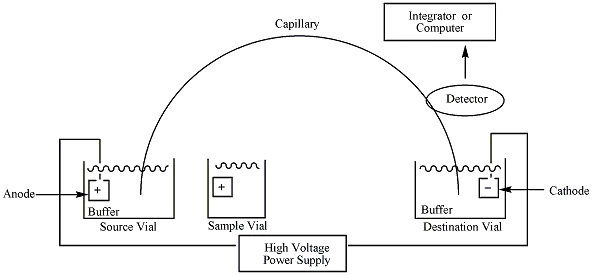
Tumors Tumor Antigens Some Antigens Are Tumor-Specific Antigens unique to cancers caused by chemical or physical carcinogens, as well as some virally induced malignancies, have been found. It is particularly difficult to demonstrate the presence of tumor-specific antigens on spontaneously developing tumours since the immune response to such tumours destroys all of the tumour cells … Read more