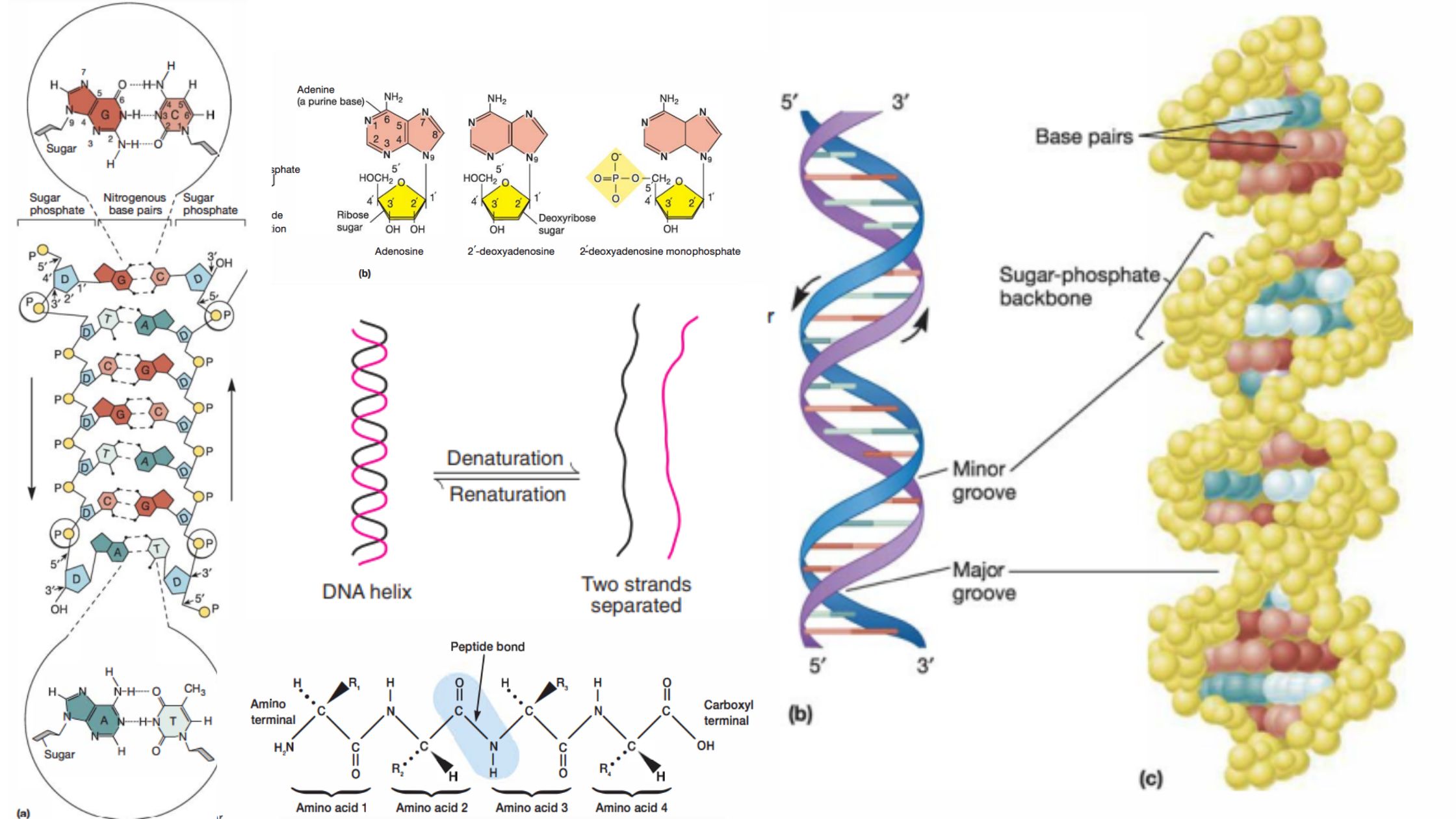
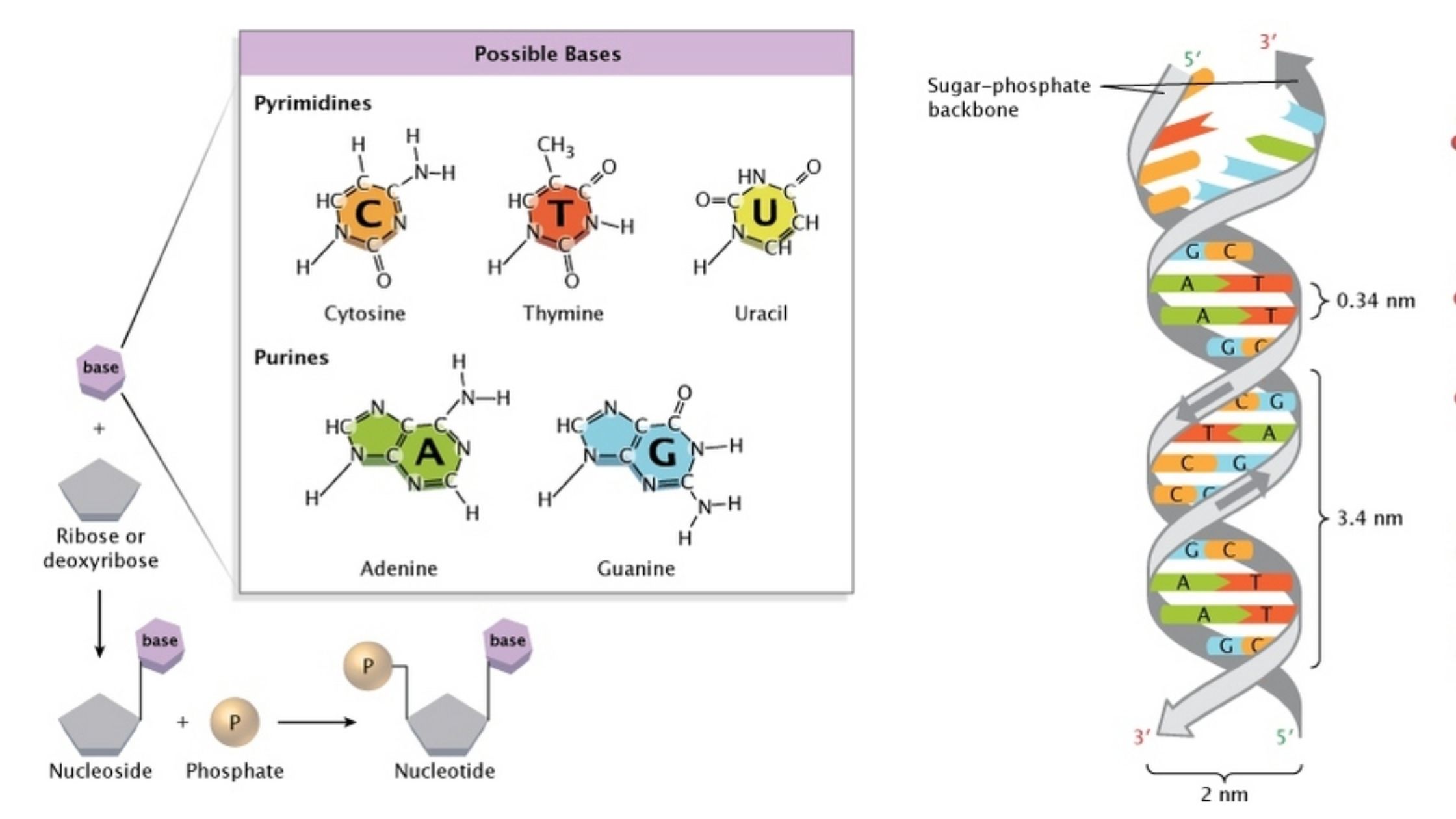
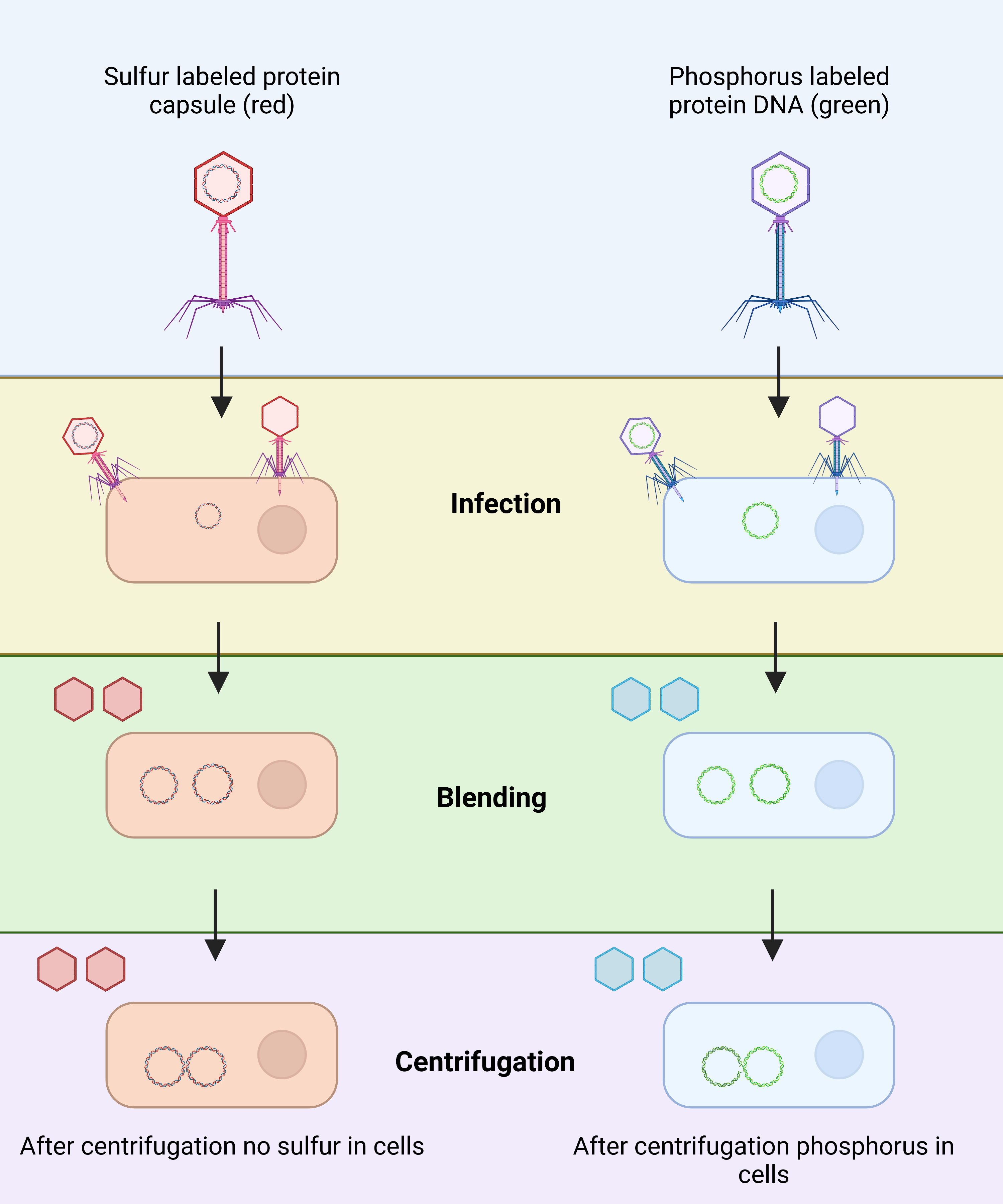
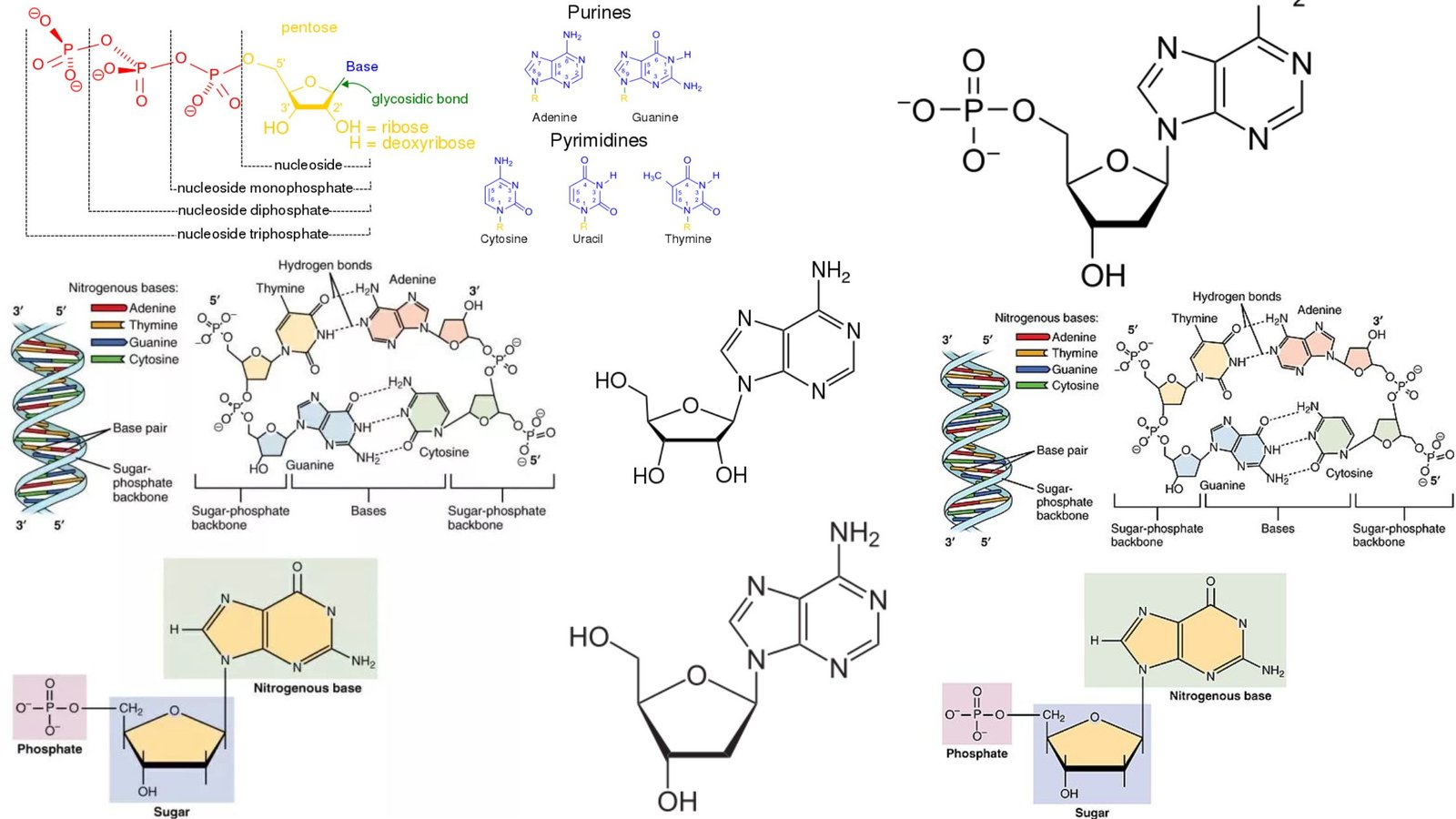
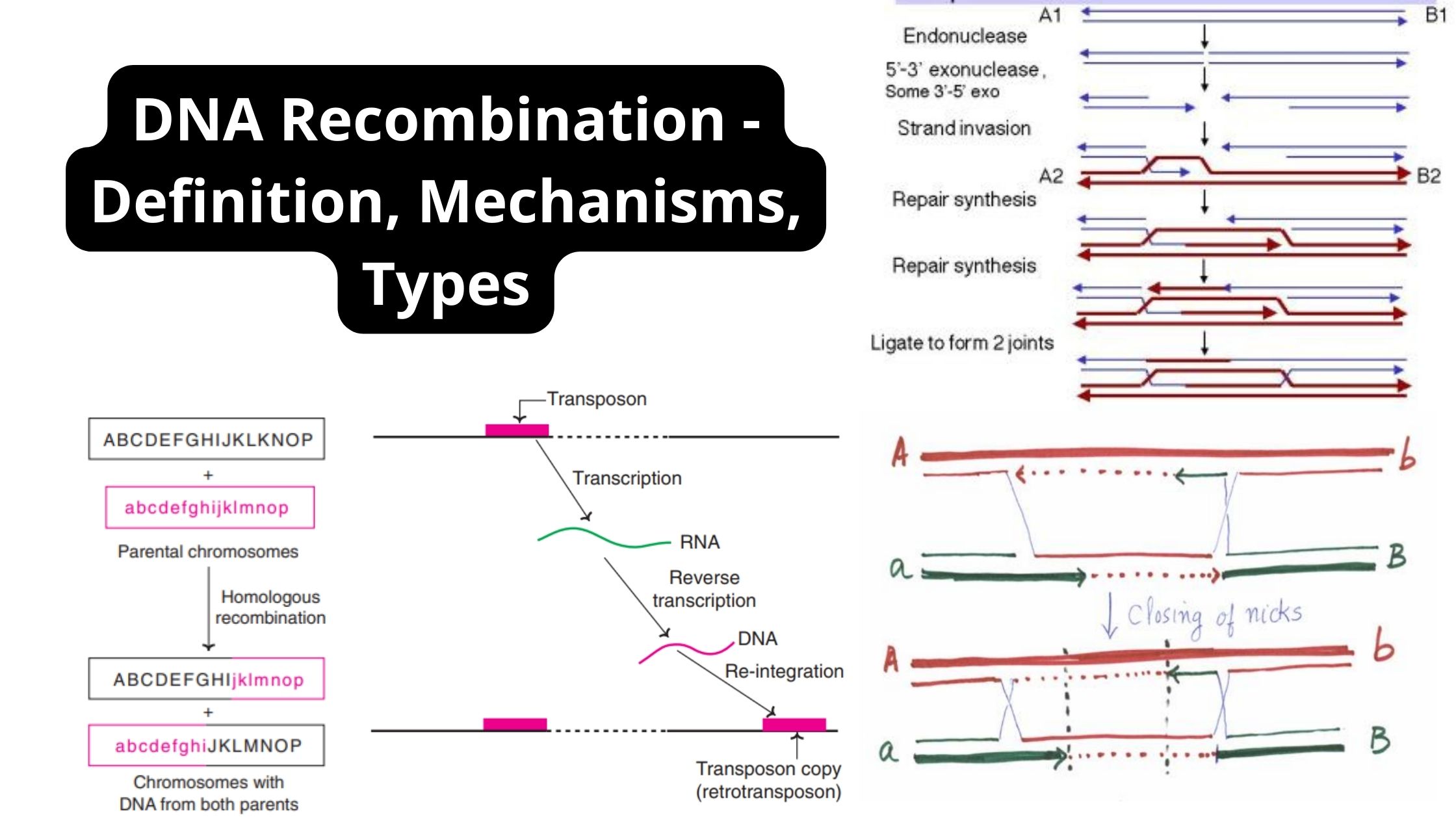
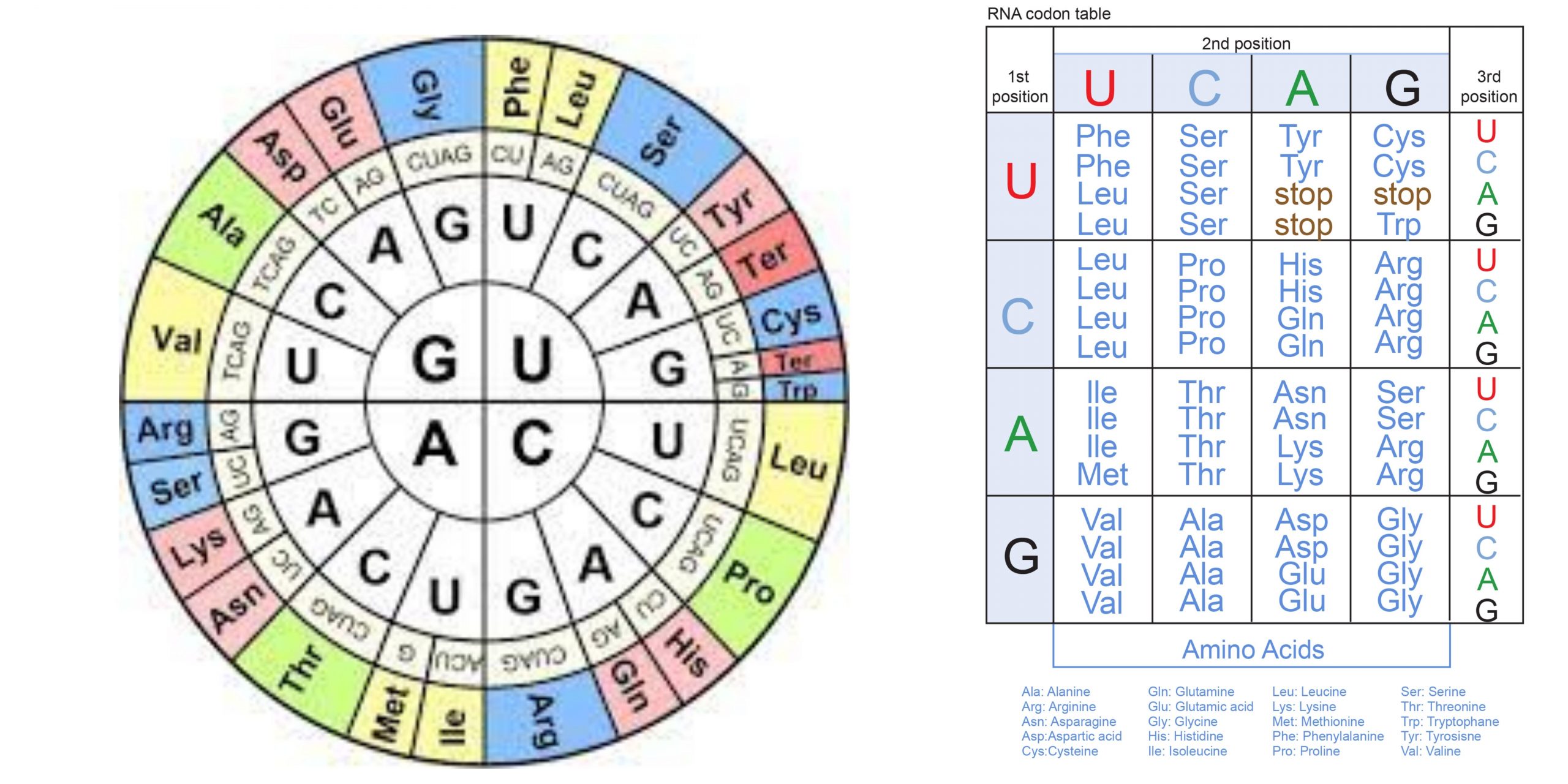
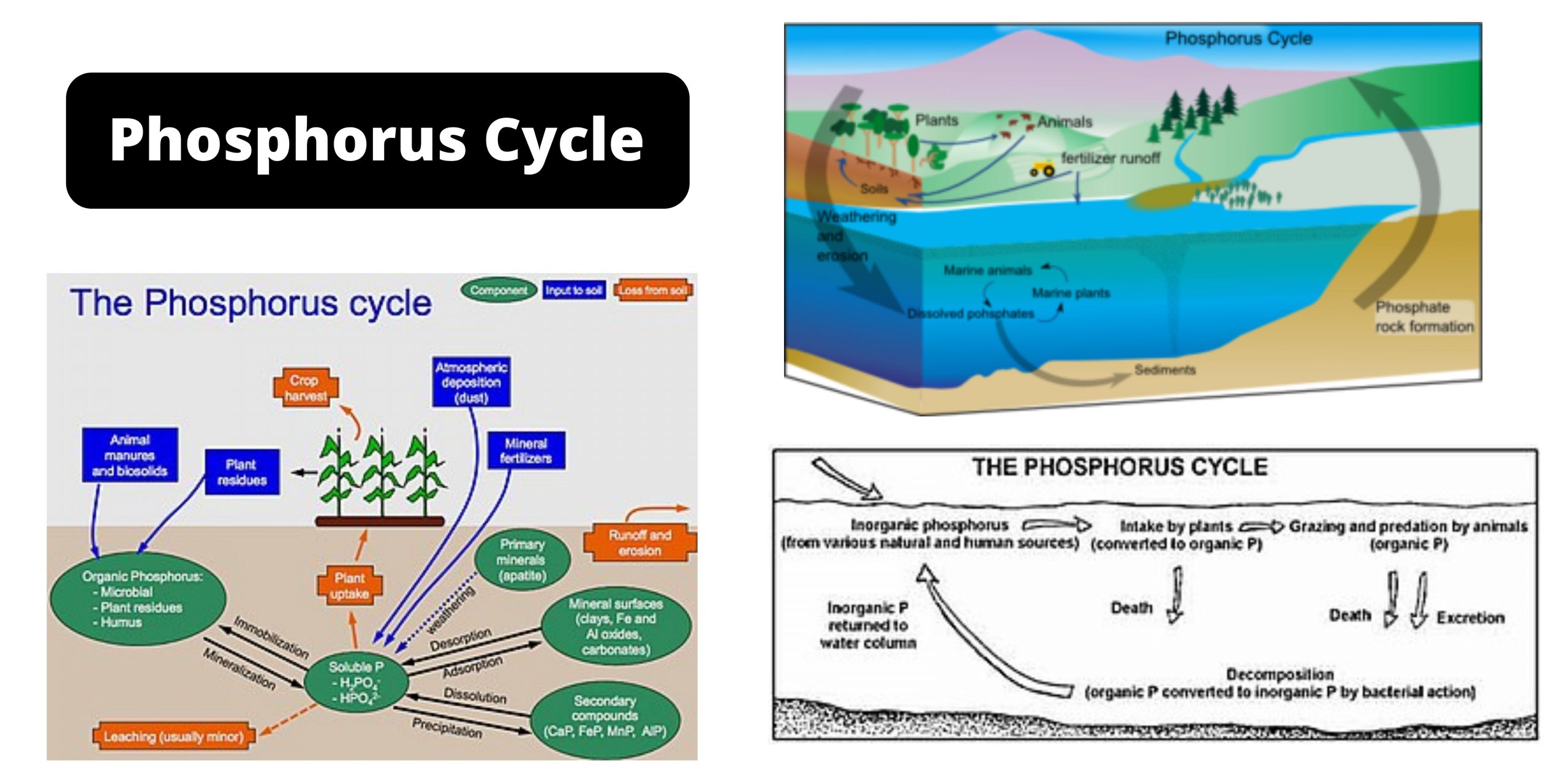
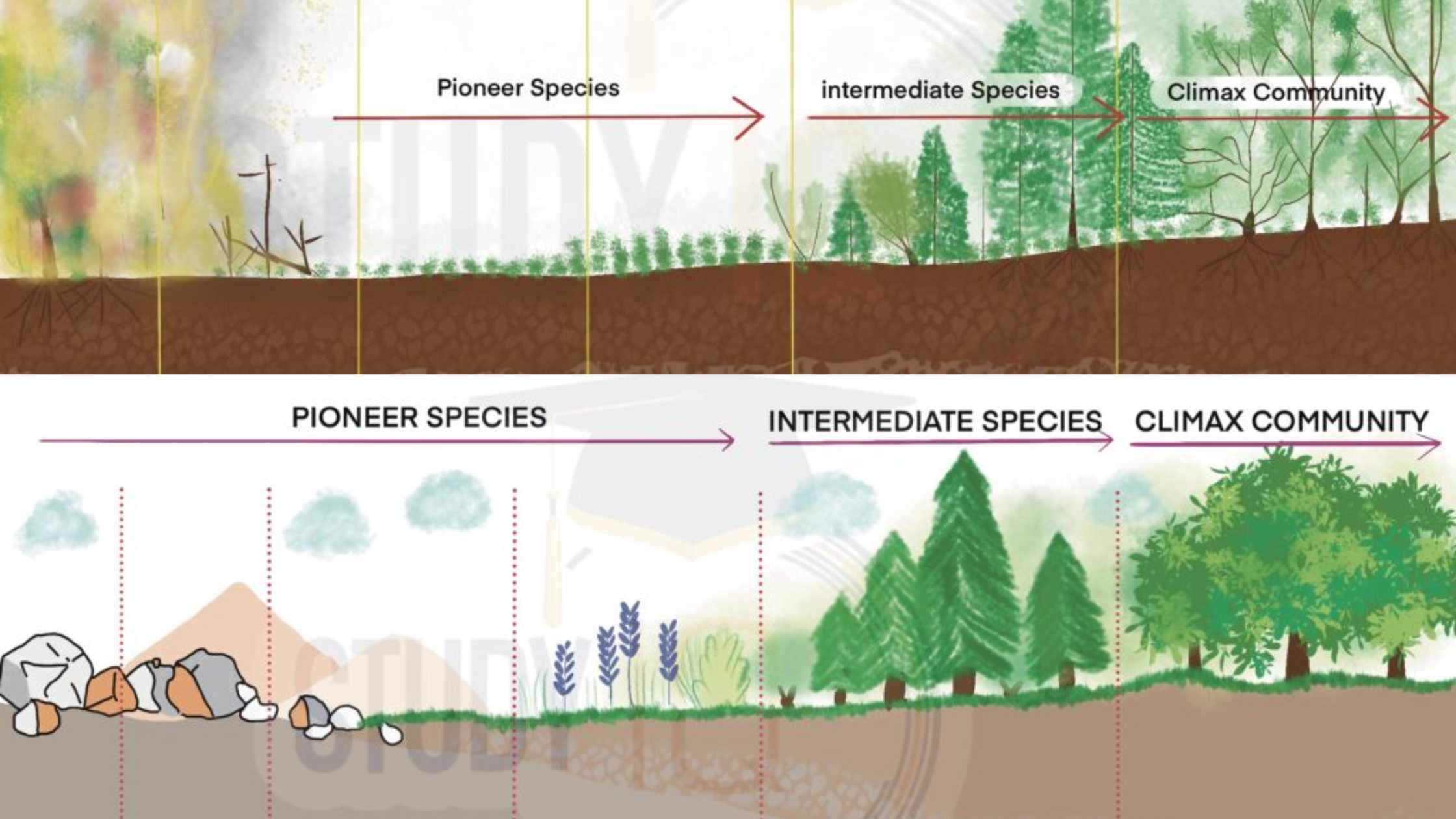
DNA – Definition, Structure, Properties, Types, Functions
What is DNA? DNA is a polymer of deoxyribonucleotides stuck together (or simply deoxynucleotides). It is made up of deoxyadenylate (dAMP), deoxyguanylate (dGMP), deoxycytidylate (dCMP), and deoxythymidylate (dTMP) units (dTMP) (Some authors prefer to use TMP instead of deoxythymidylate because it is only found in DNA.) History of DNA The history of DNA begins with … Read more