Transfer-messenger RNA (tmRNA) – Definition, Structure, Properties
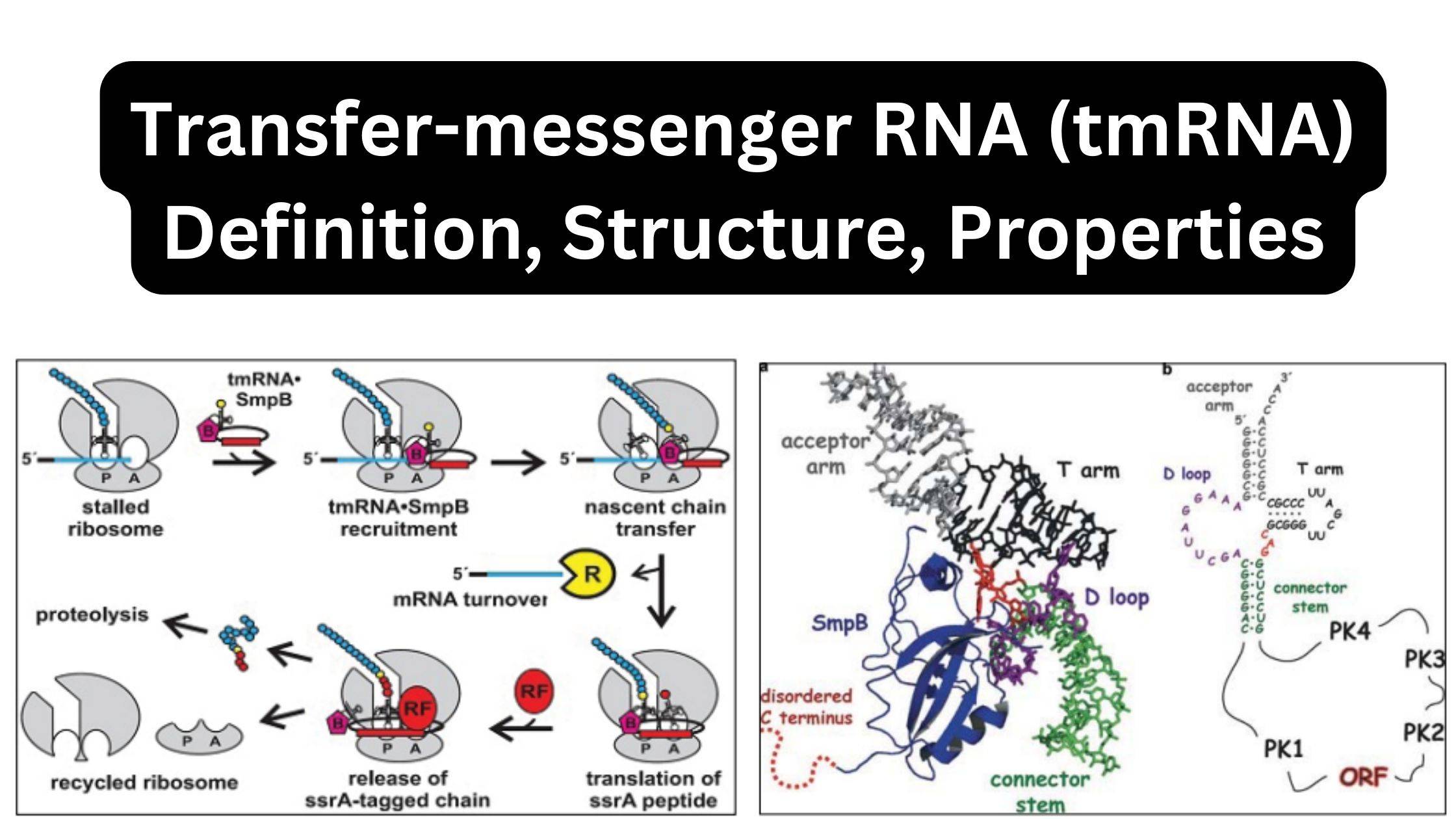
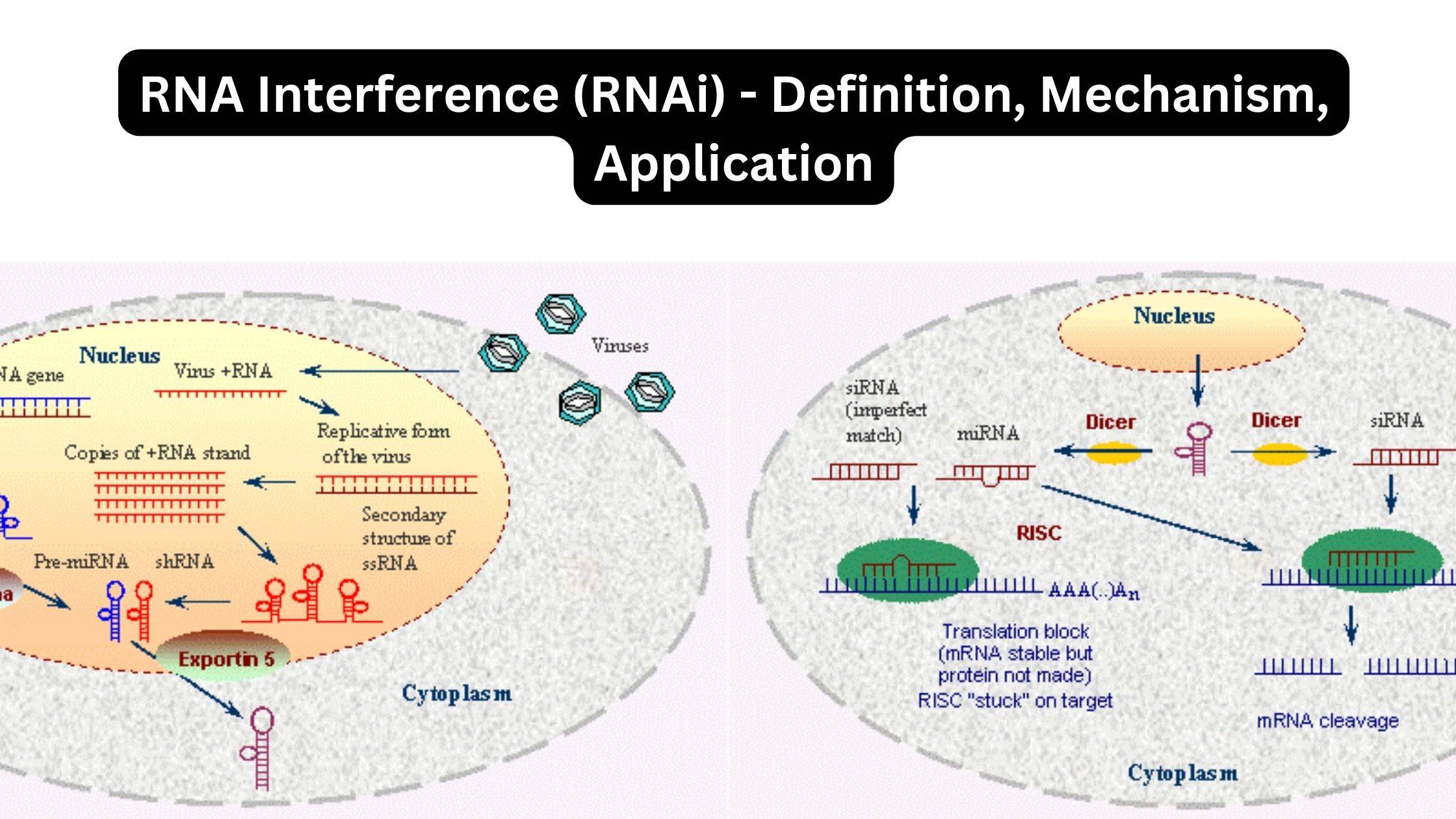
What is Transfer-messenger RNA (tmRNA)? History Properties of tmRNA tmRNA Structure tmRNA contain the following domains; tRNA-Mimic Domain Pseudoknots mRNA-Mimic Domain Protein Partners tmRNA Function ― Trans-Translation Trans-translation of tmRNA activity Steps Regulation of tmRNA activity Facts References