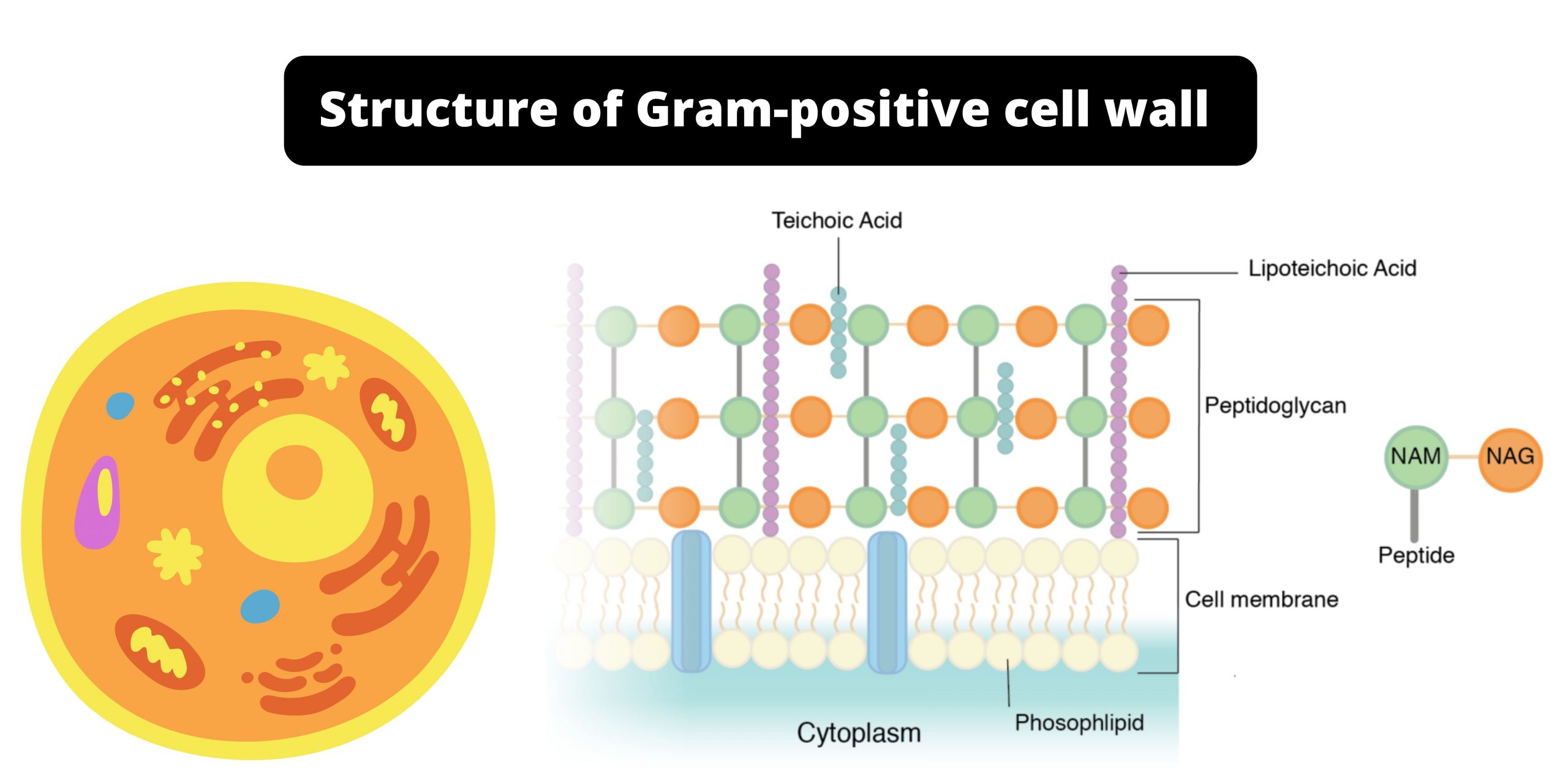
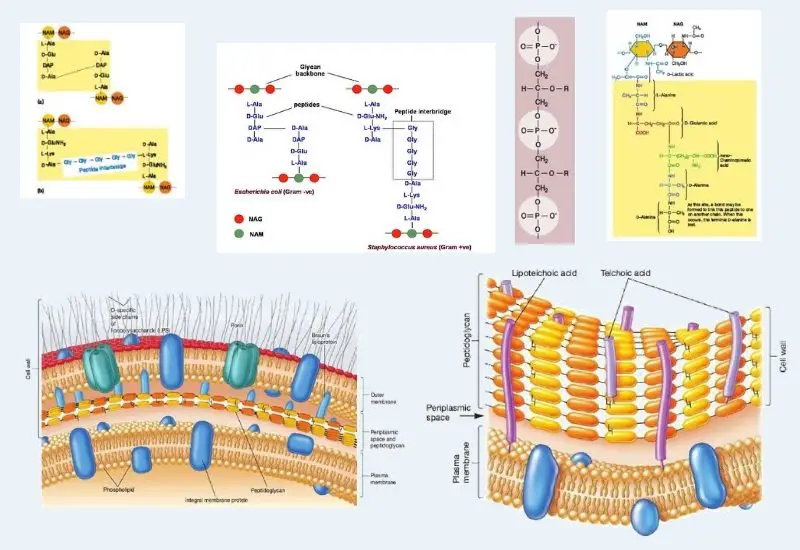
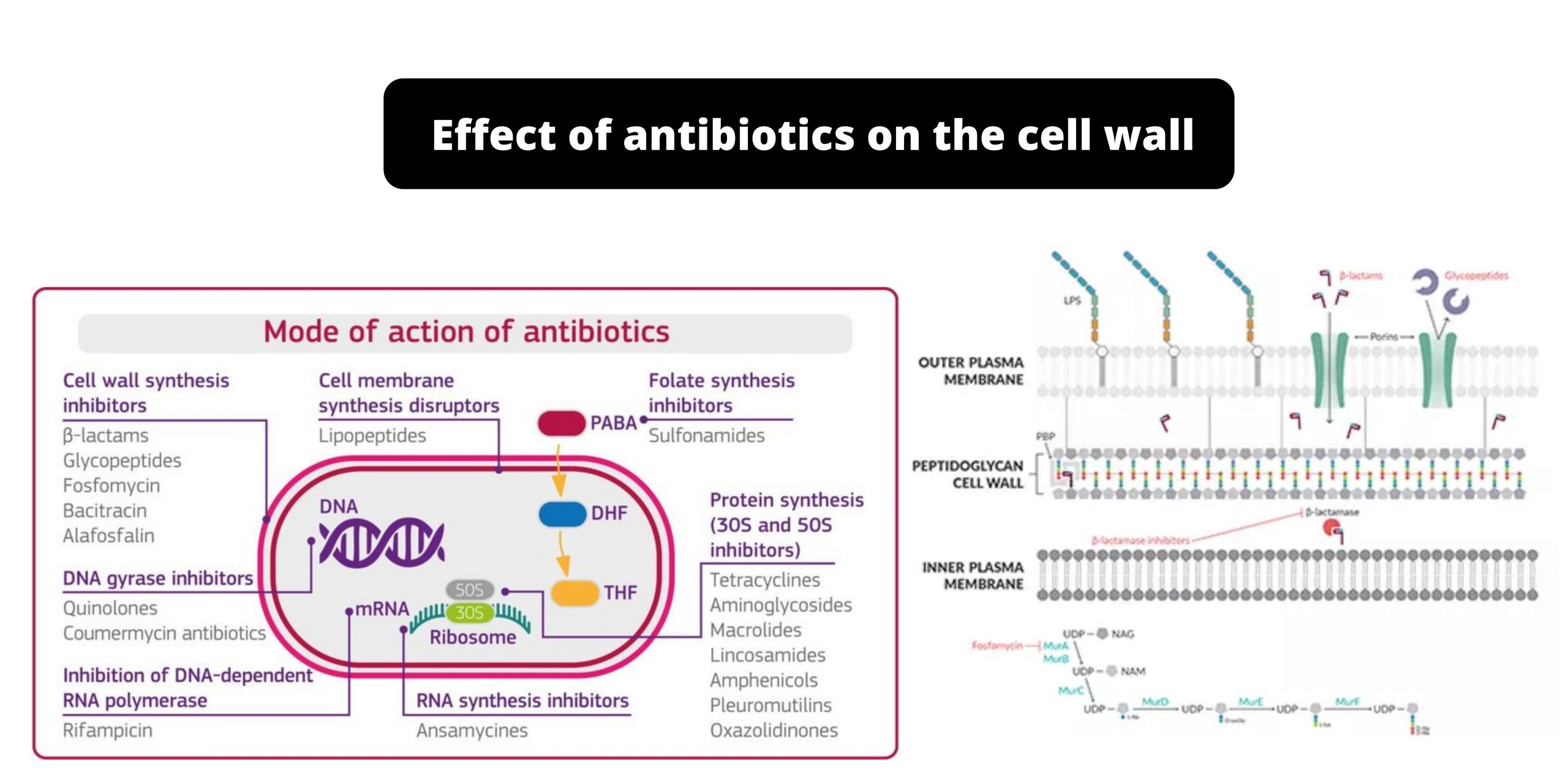
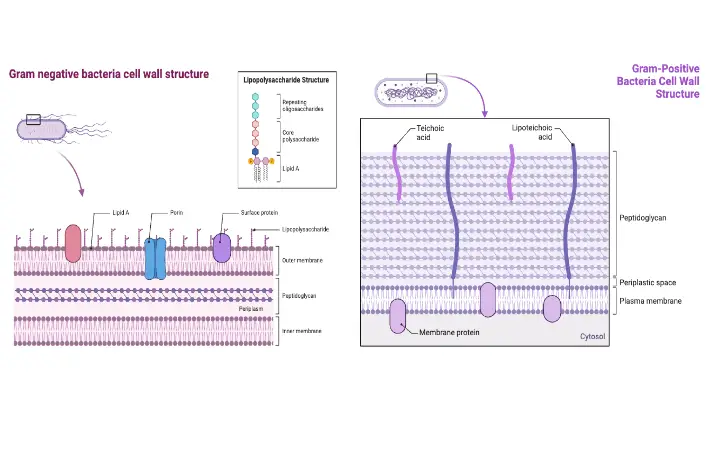
Structure of Gram-positive Cell Wall
Bacterial Cell Wall Characteristics of Peptidoglycan Peptidoglycan is a fundamental component of bacterial cell walls, forming a complex, mesh-like structure known as the sacculus. This structure is crucial for maintaining cell shape and integrity. Here are the key characteristics of peptidoglycan: Cell membrane of Gram-Positive Cell Wall The cell membrane of Gram-positive bacteria is a … Read more