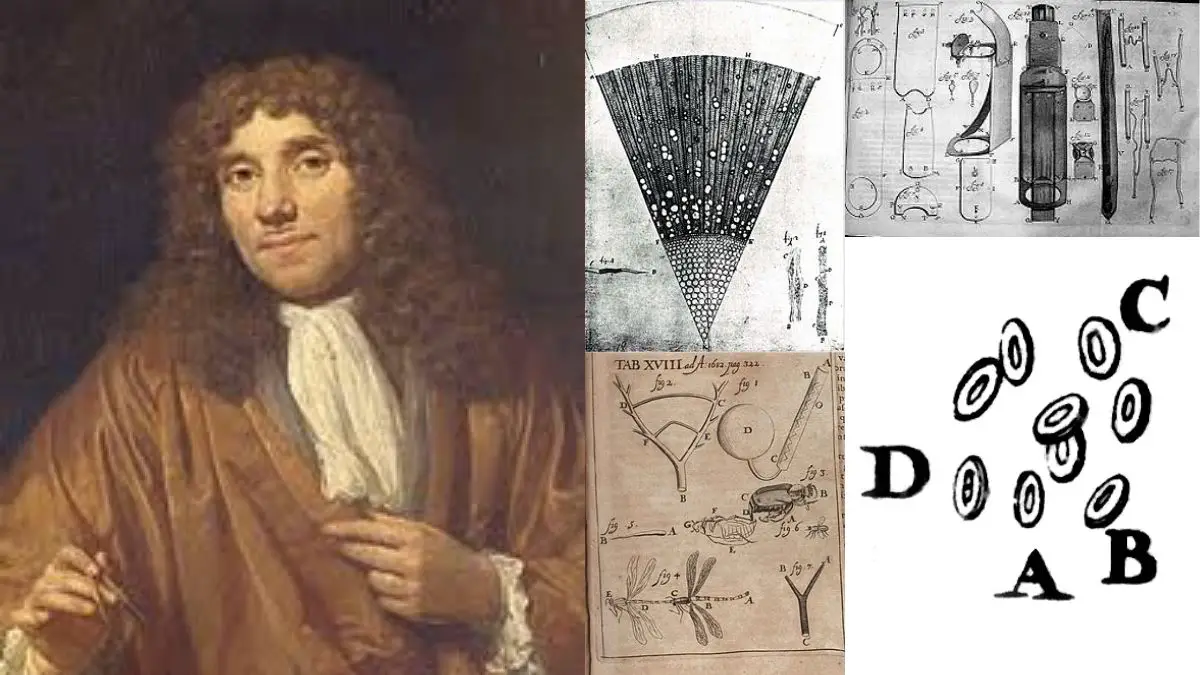
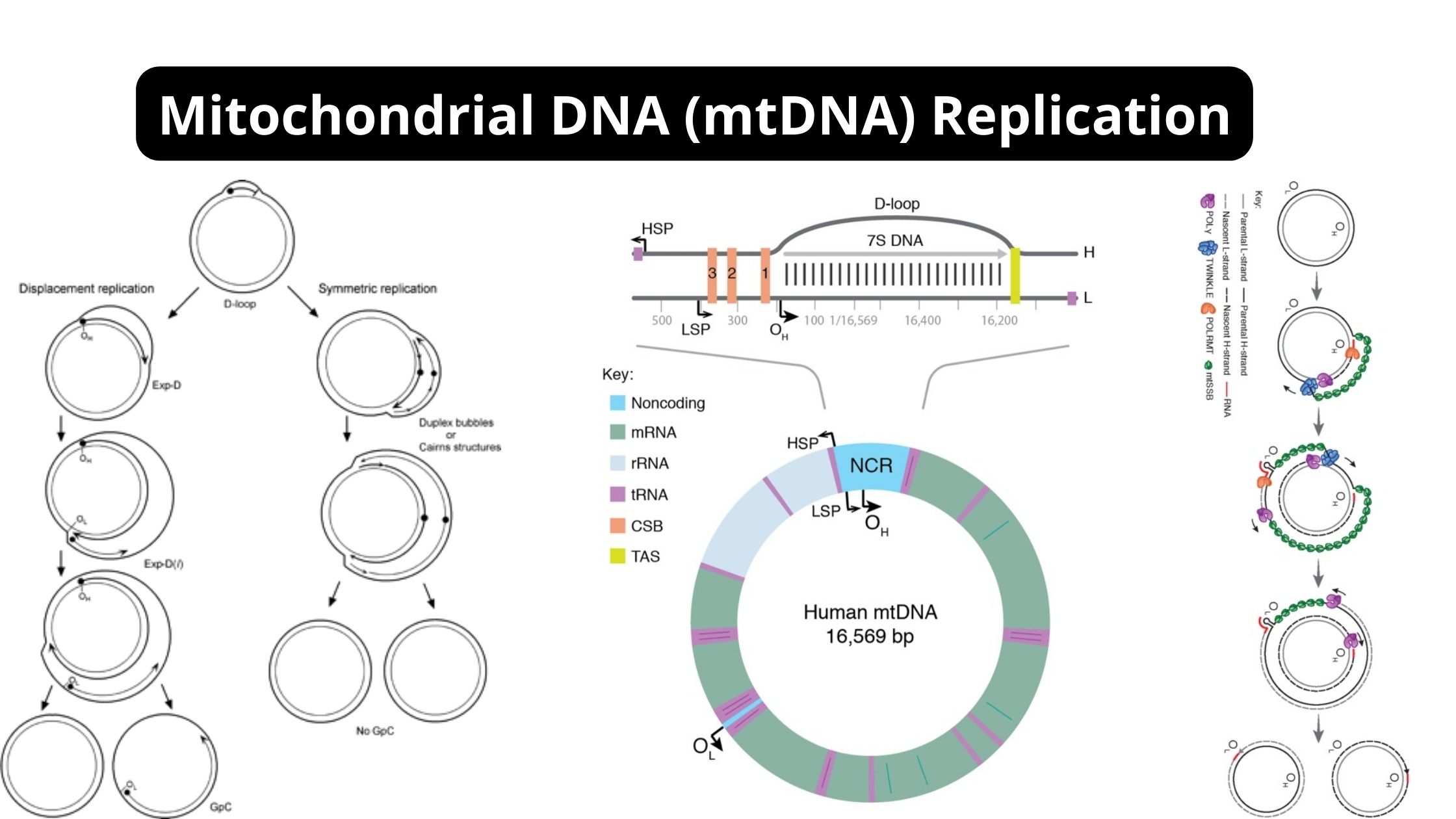
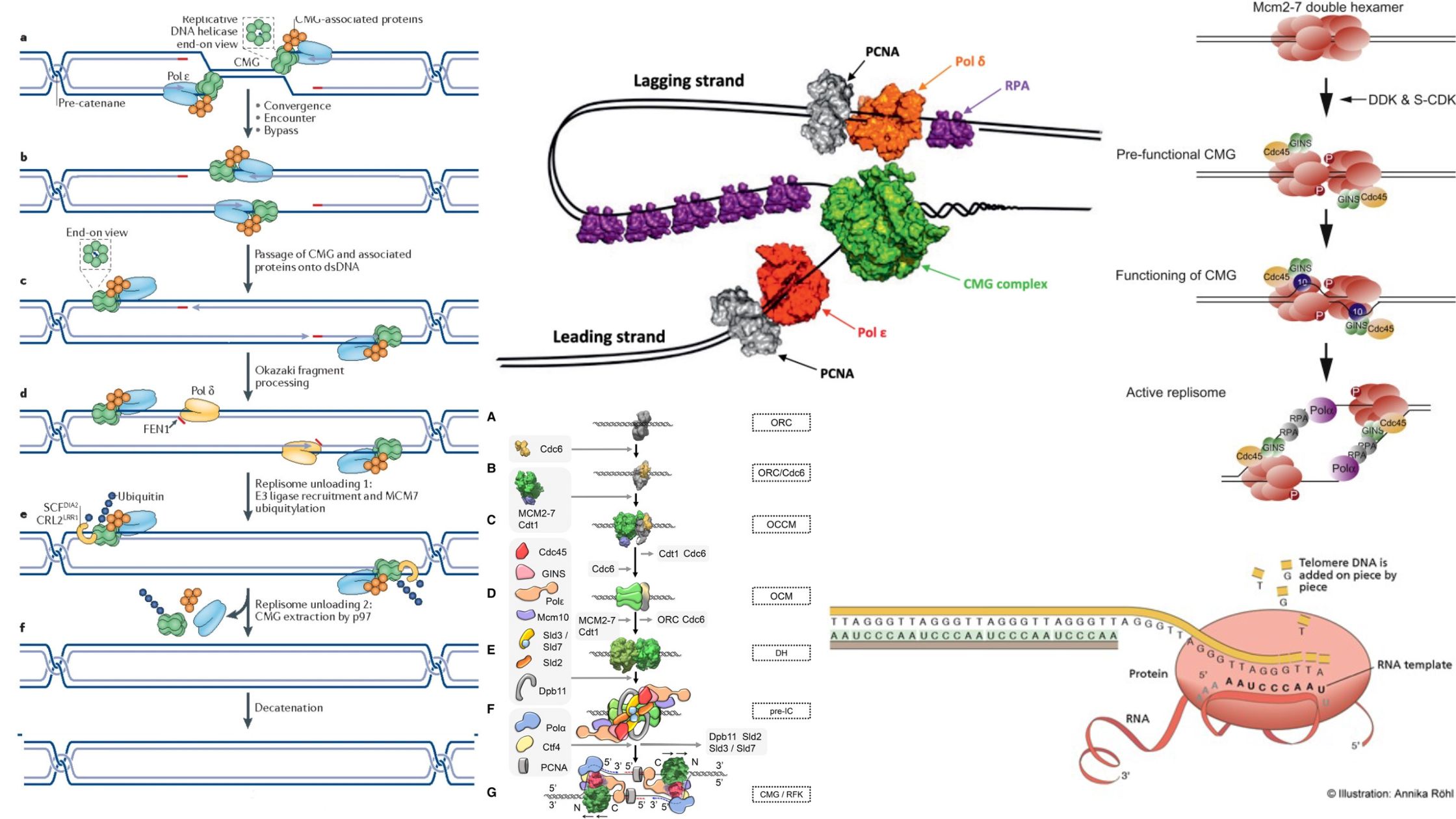
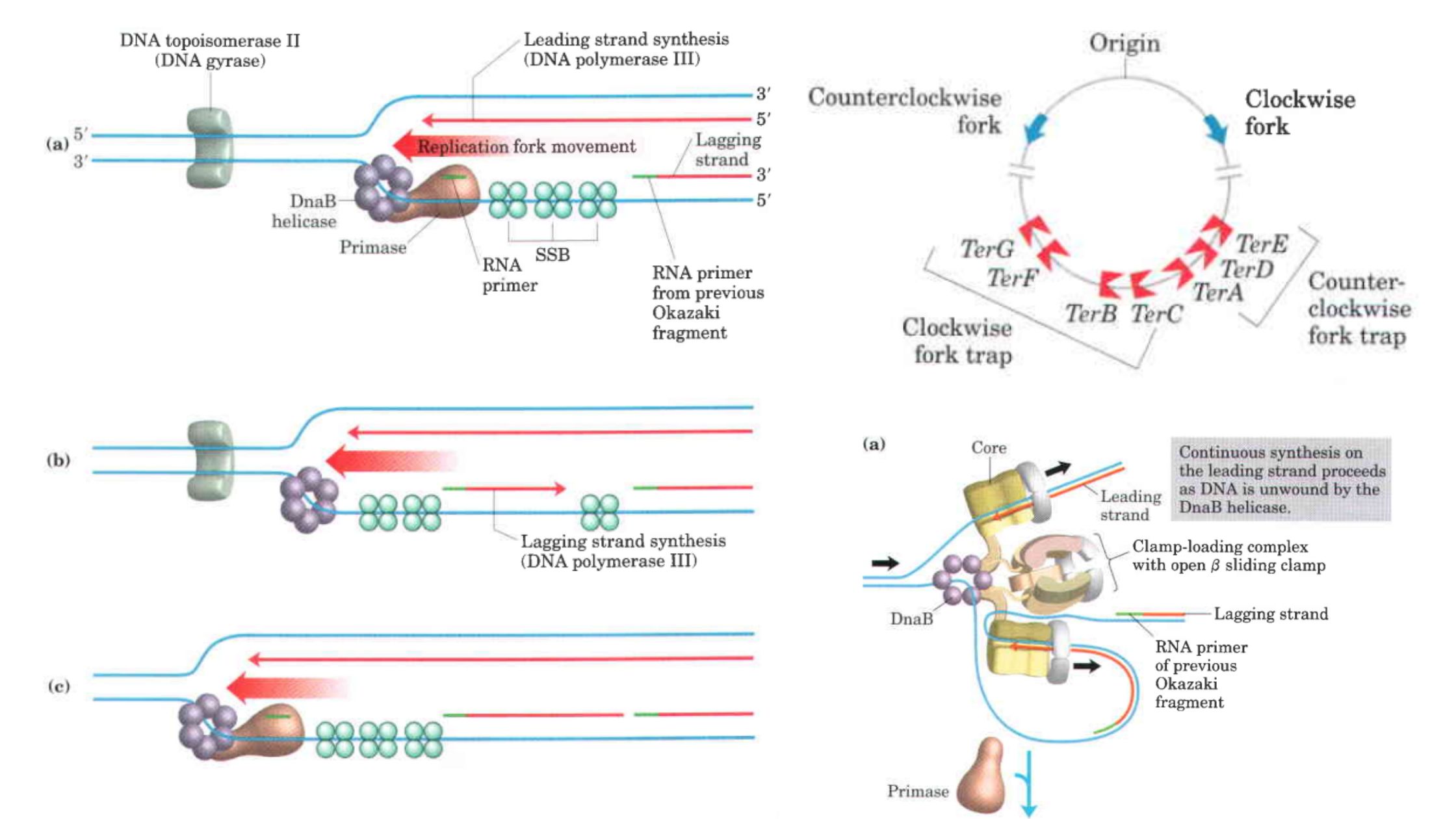
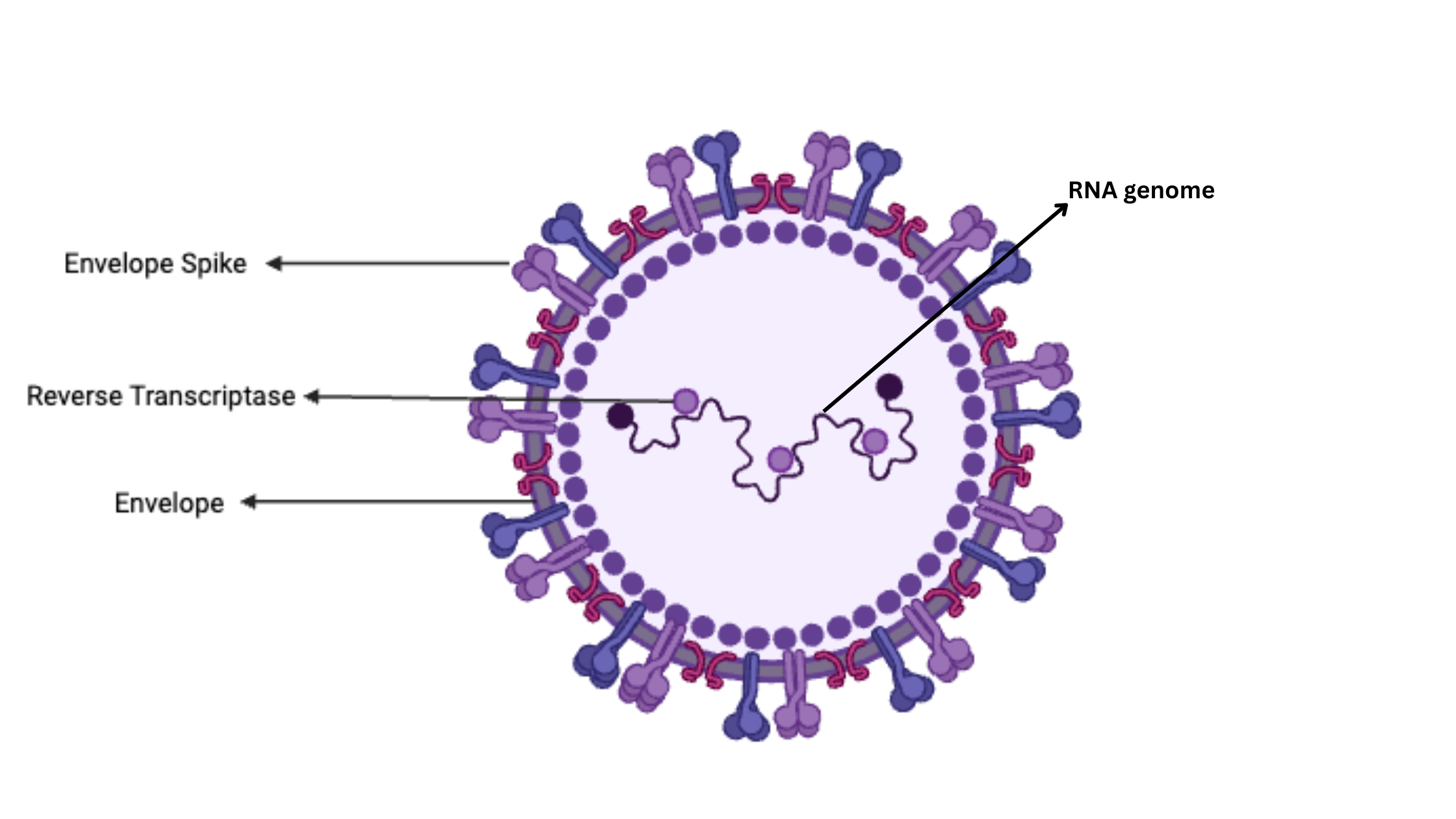
Contributions of Antonie van Leeuwenhoek
Who was Antonie van Leeuwenhoek? Anton Van Leeuwenhoek and Cell Theory Contribution of Antonie van Leeuwenhoek Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, a Dutch scientist and businessman, made several pioneering contributions to the field of microbiology, fundamentally altering our understanding of the microscopic world. His meticulous observations and discoveries laid the foundation for modern biology and greatly influenced … Read more