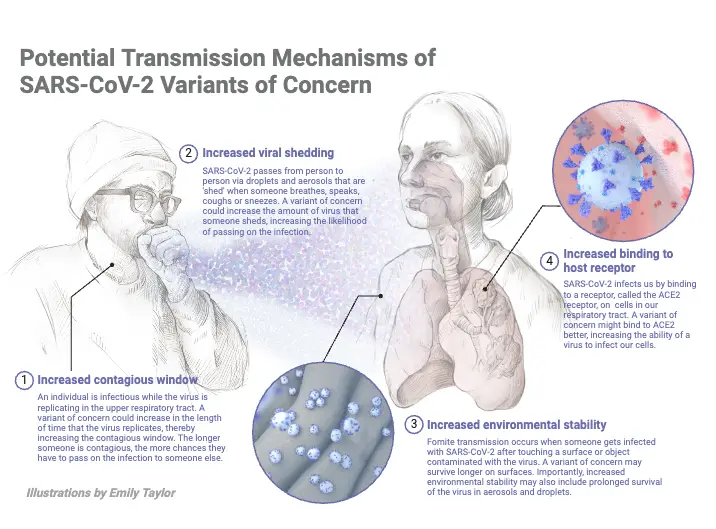
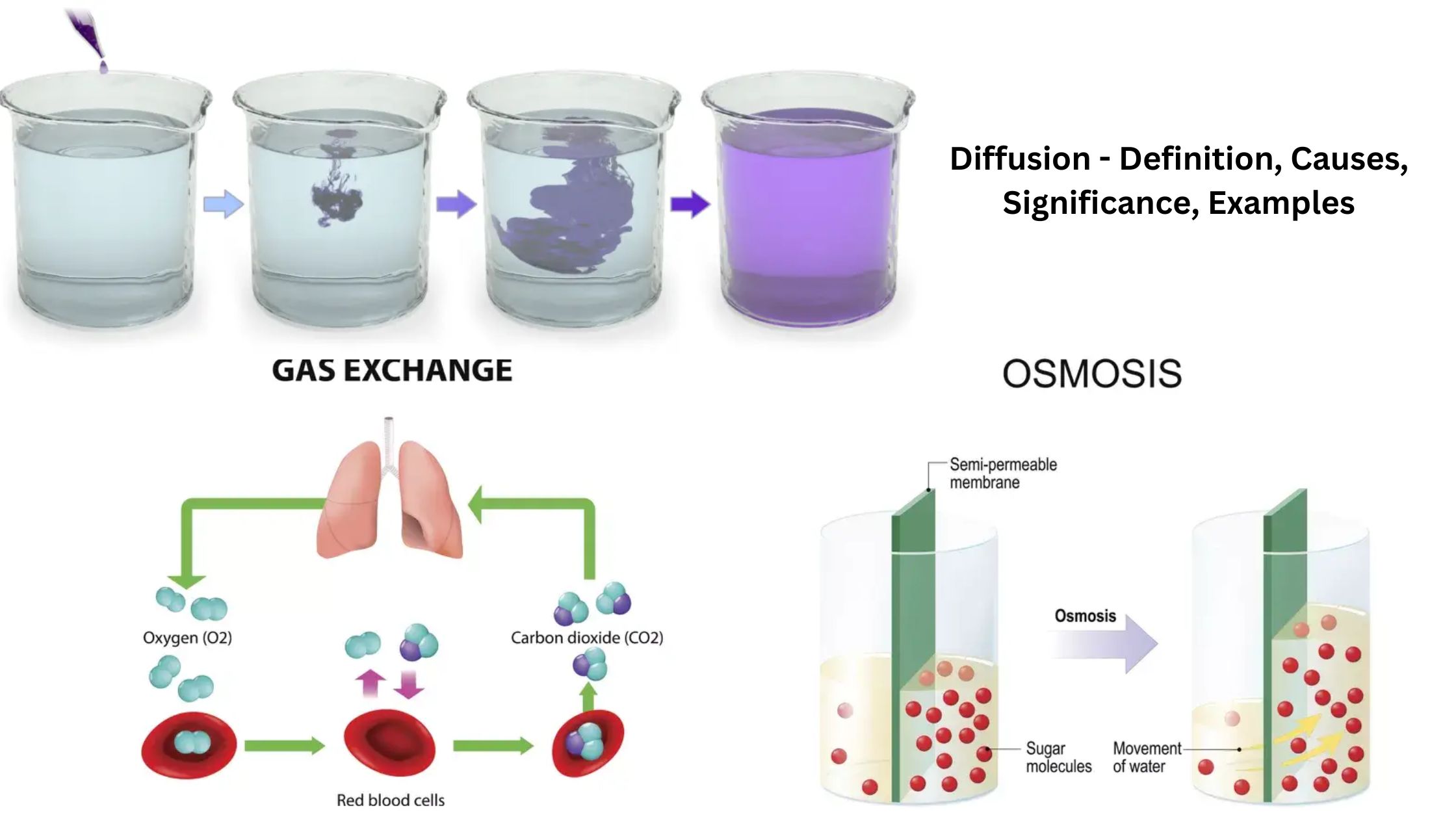
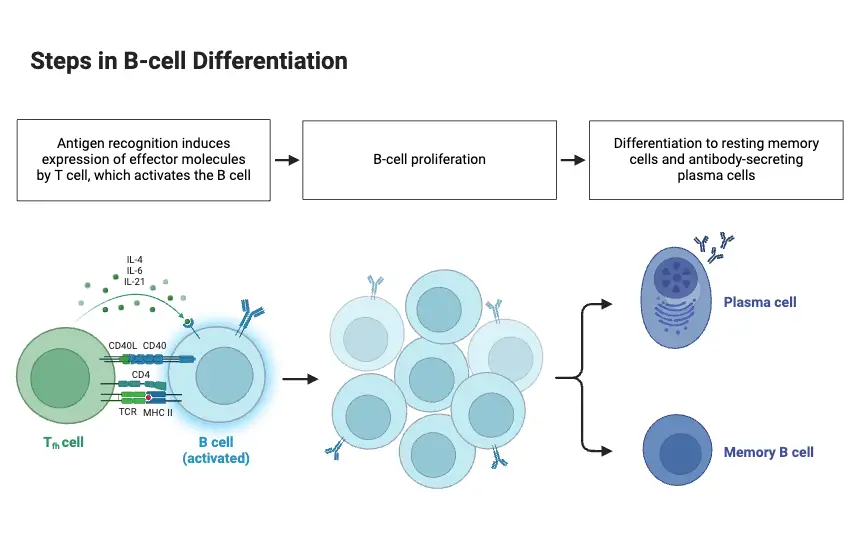
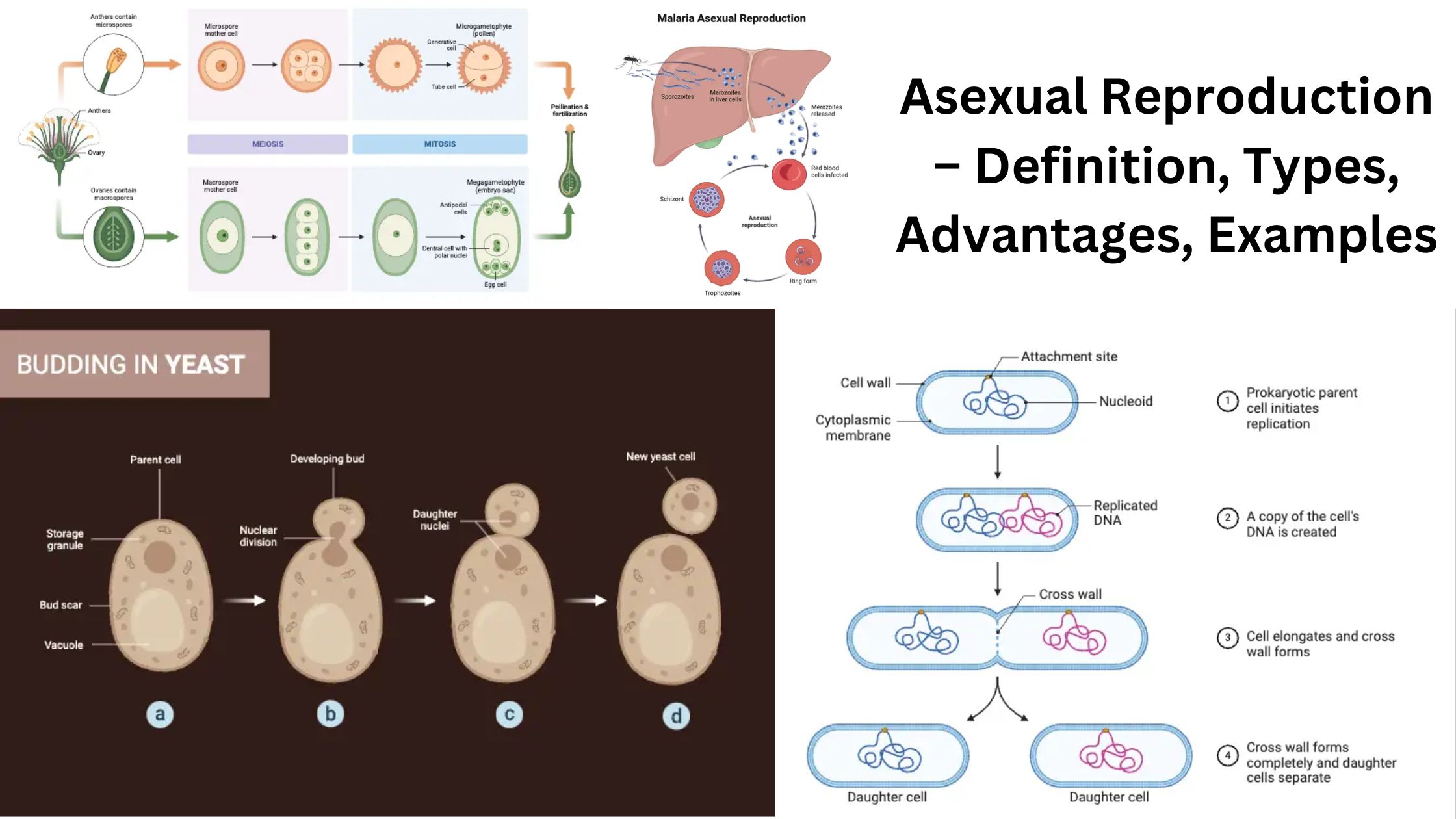
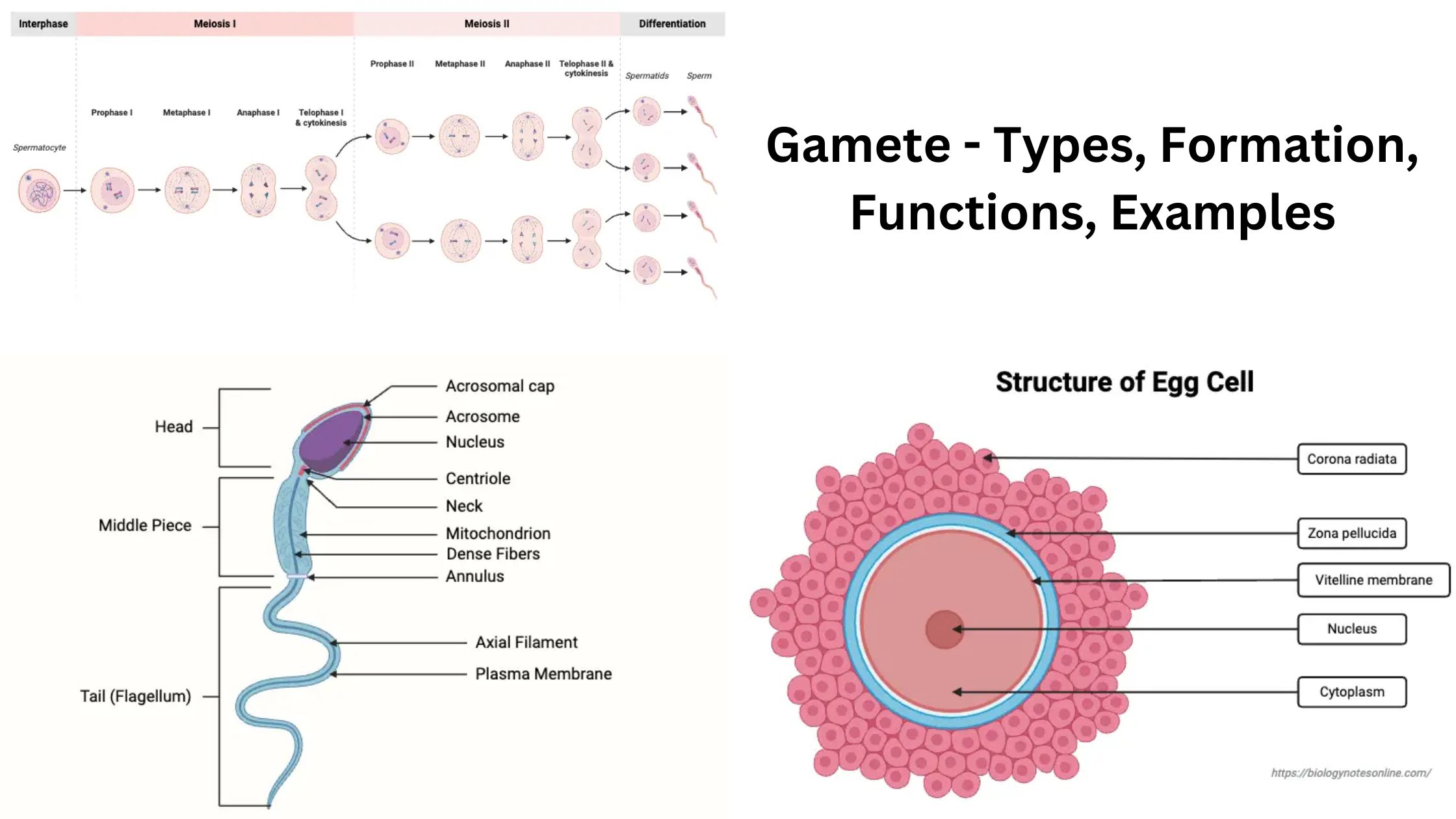
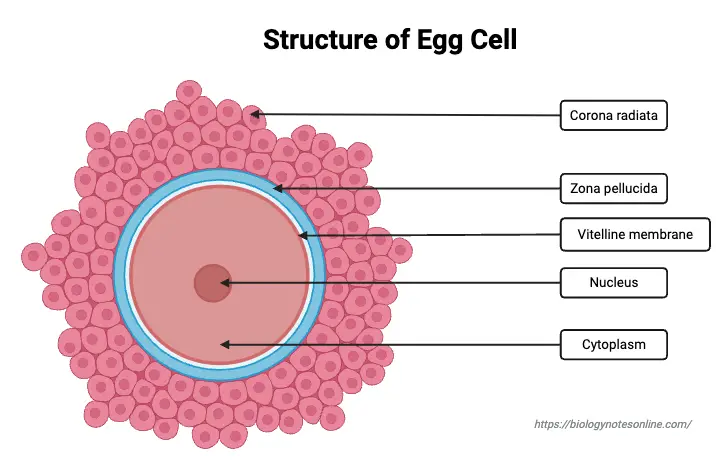
Communicable Diseases – Types, Transmission, Control
What is Communicable Disease? Types of Communicable Diseases Communicable diseases are illnesses caused by pathogens, which can spread from one person or animal to another. These diseases are typically transmitted through various means, such as direct contact, contaminated food or water, blood, or bodily fluids. Here’s a breakdown of the main types of communicable diseases. … Read more