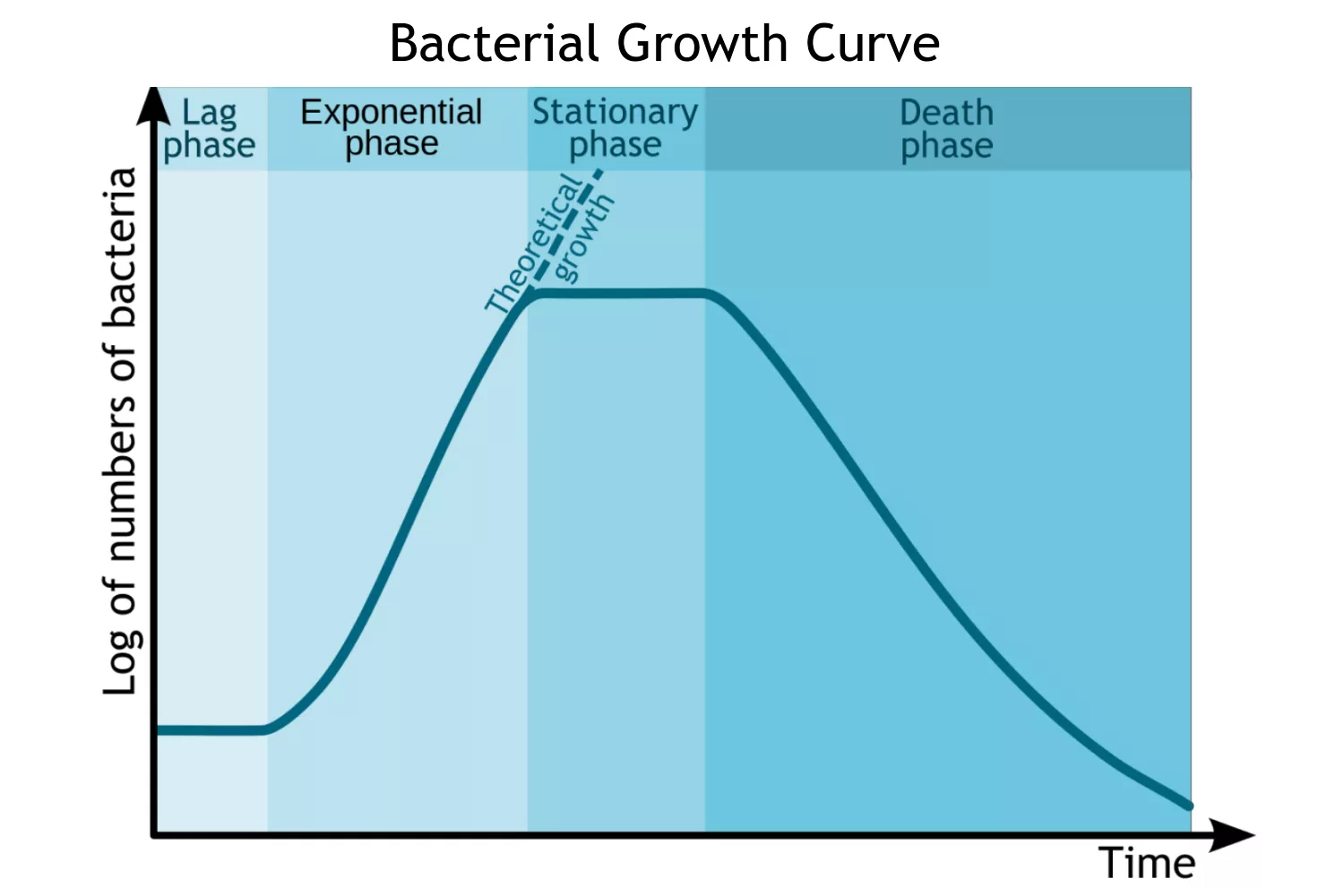
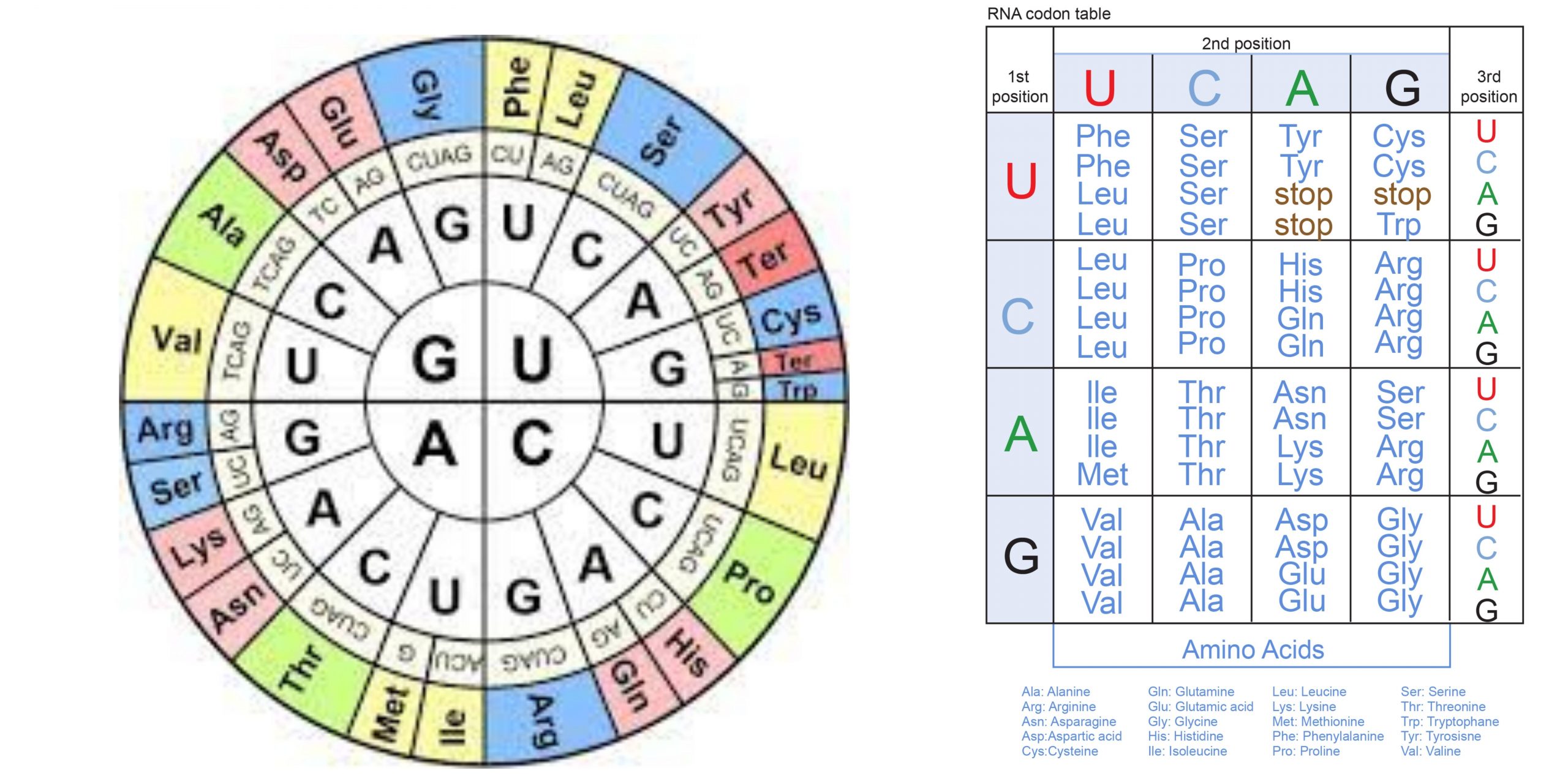
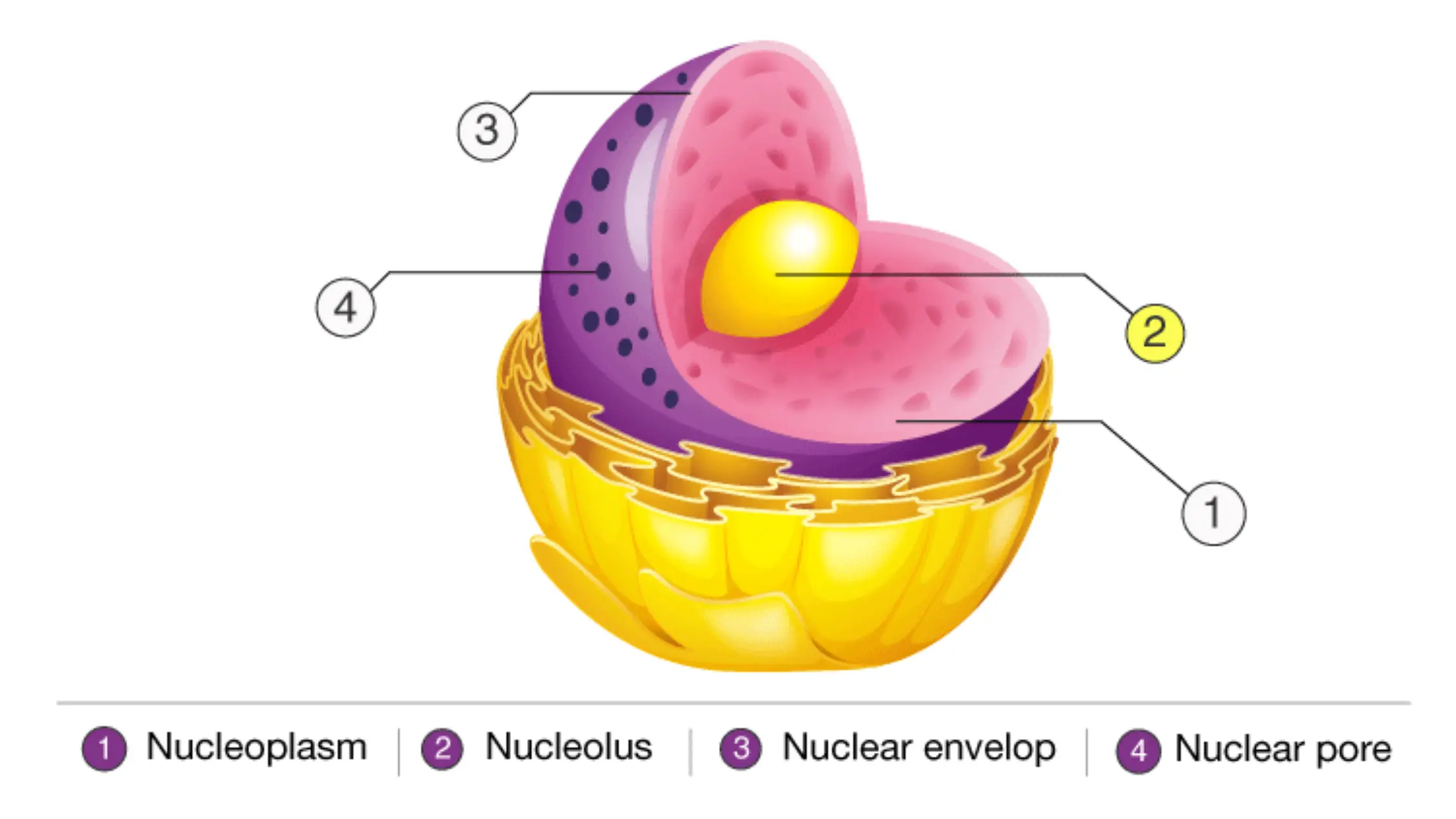
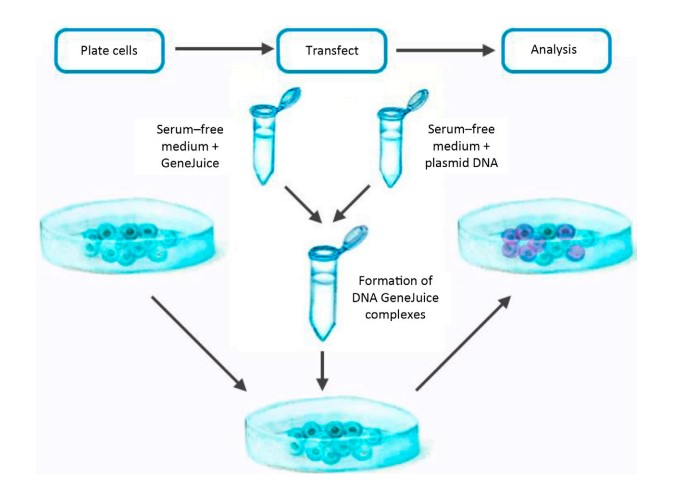
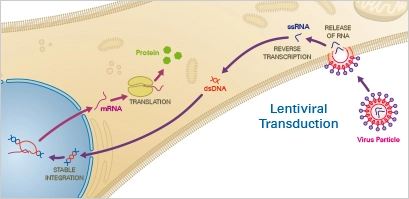
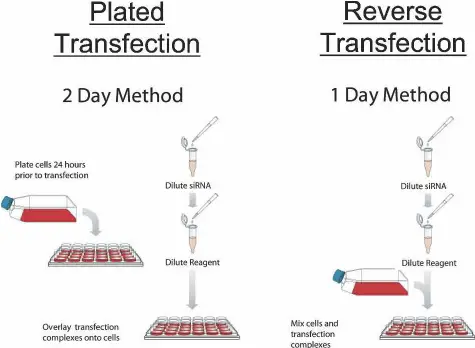
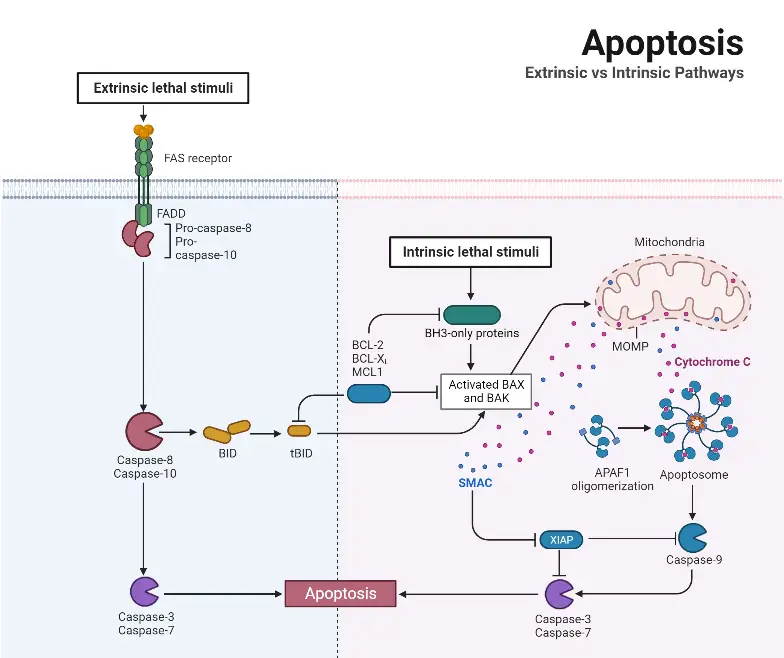
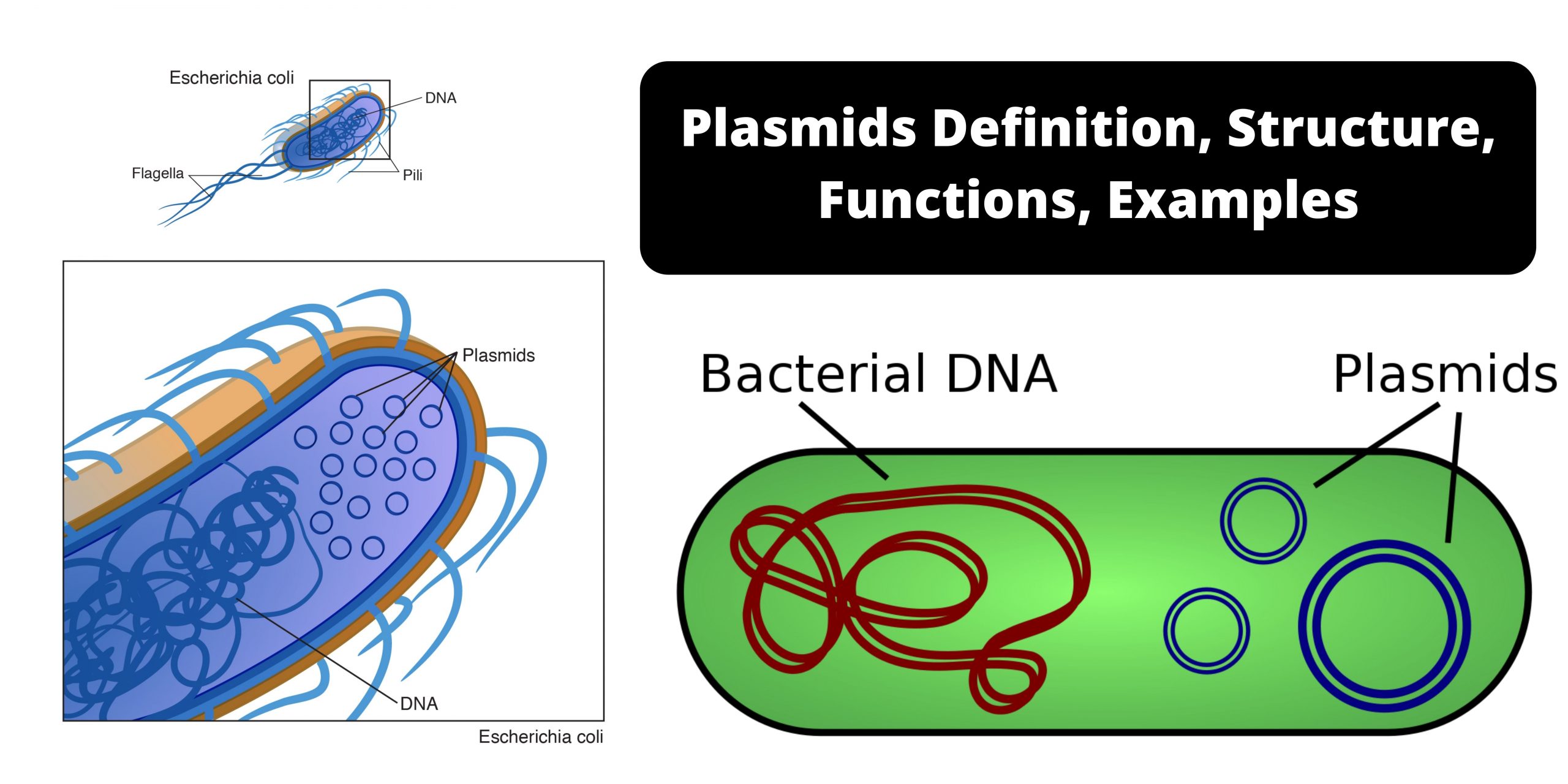
Cell Growth – Definition, Types, Mechanisms
Growth Definition Levels of Growth There are two distinct stages of growth in living organisms: A. Cell growth B. Growth of multicellular organisms The growth of multicellular animals and plants in connection to the growth and multiplication of their individual cells can be divided into three distinct categories: (1) Auxetic growth (Auxesis = growth resulting … Read more