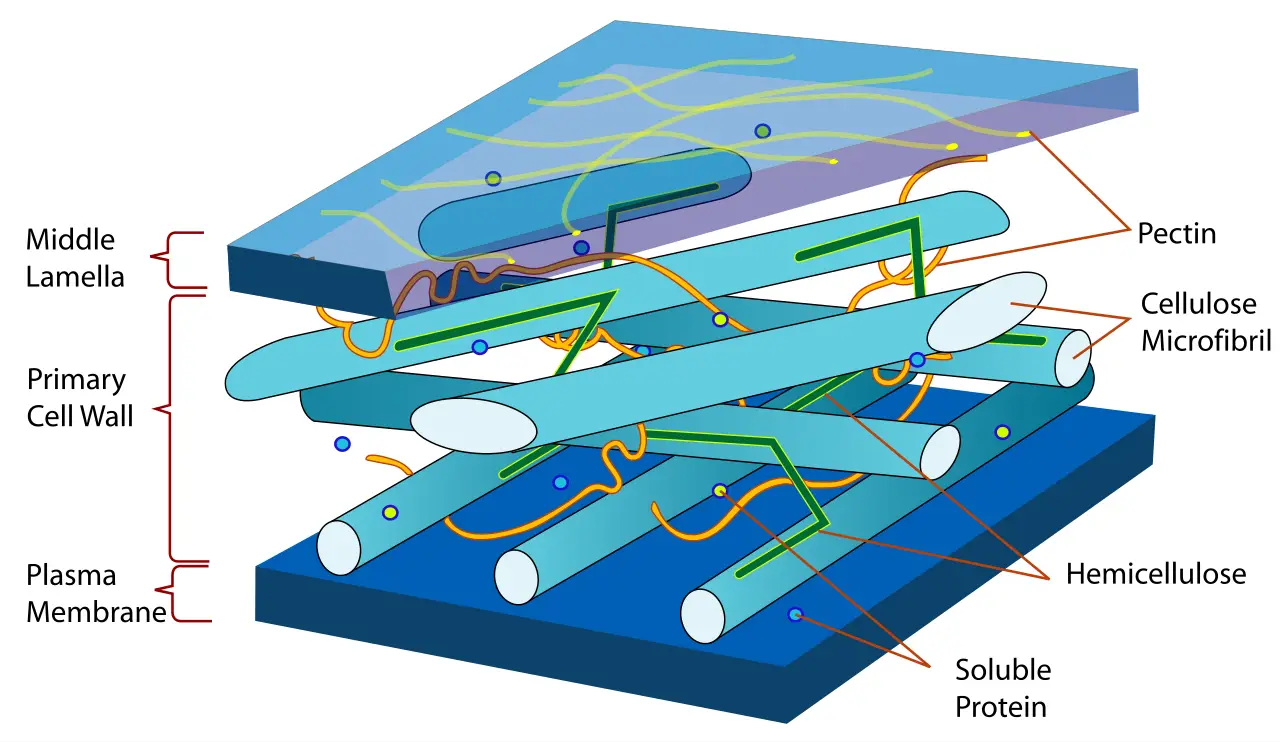
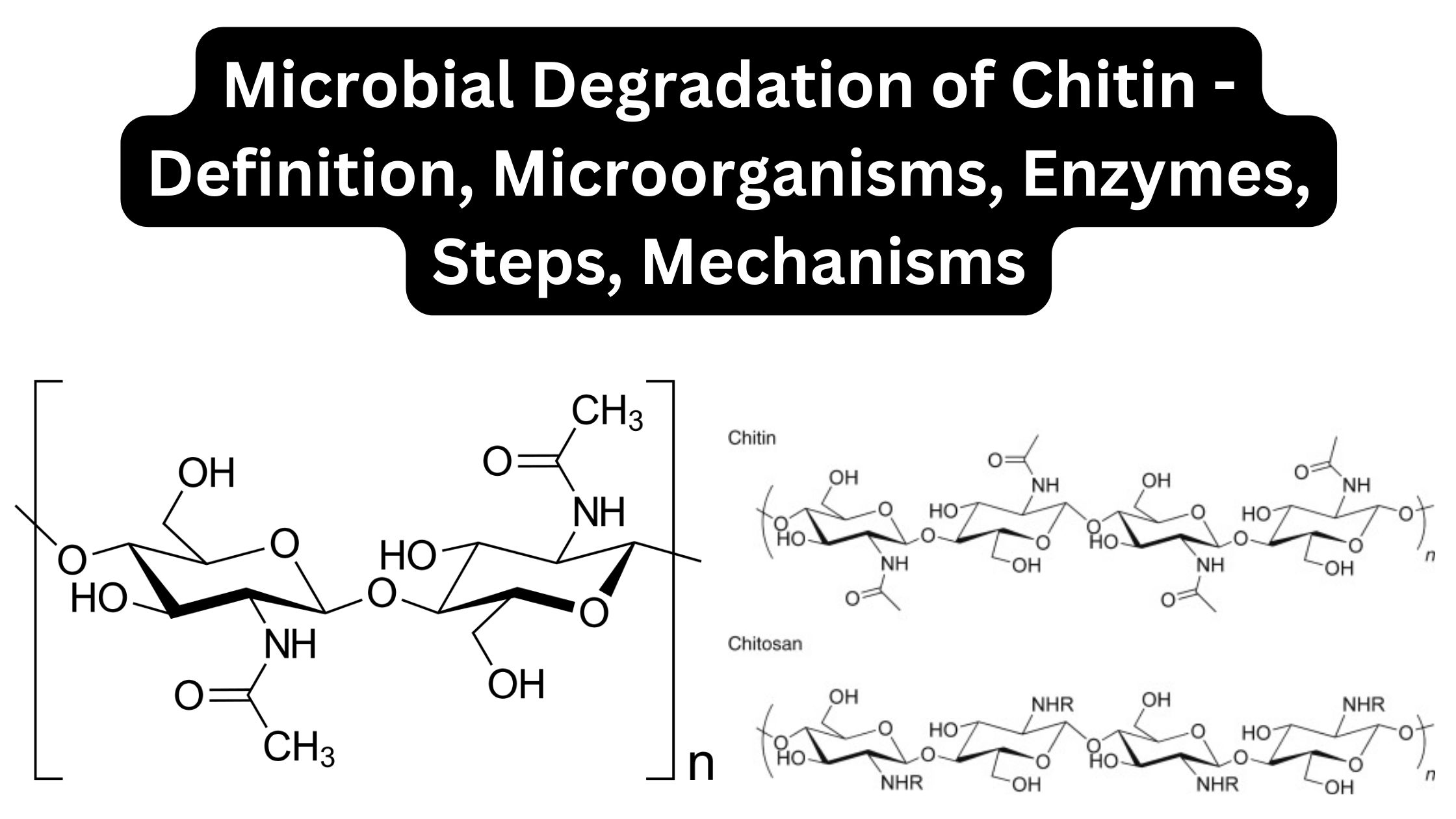
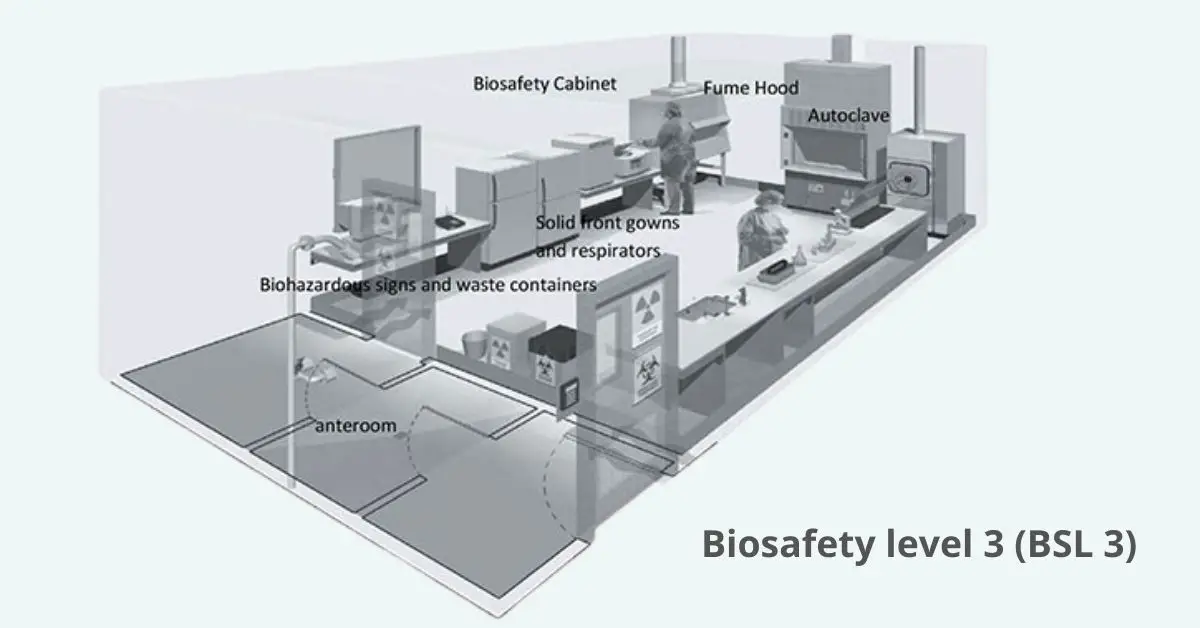
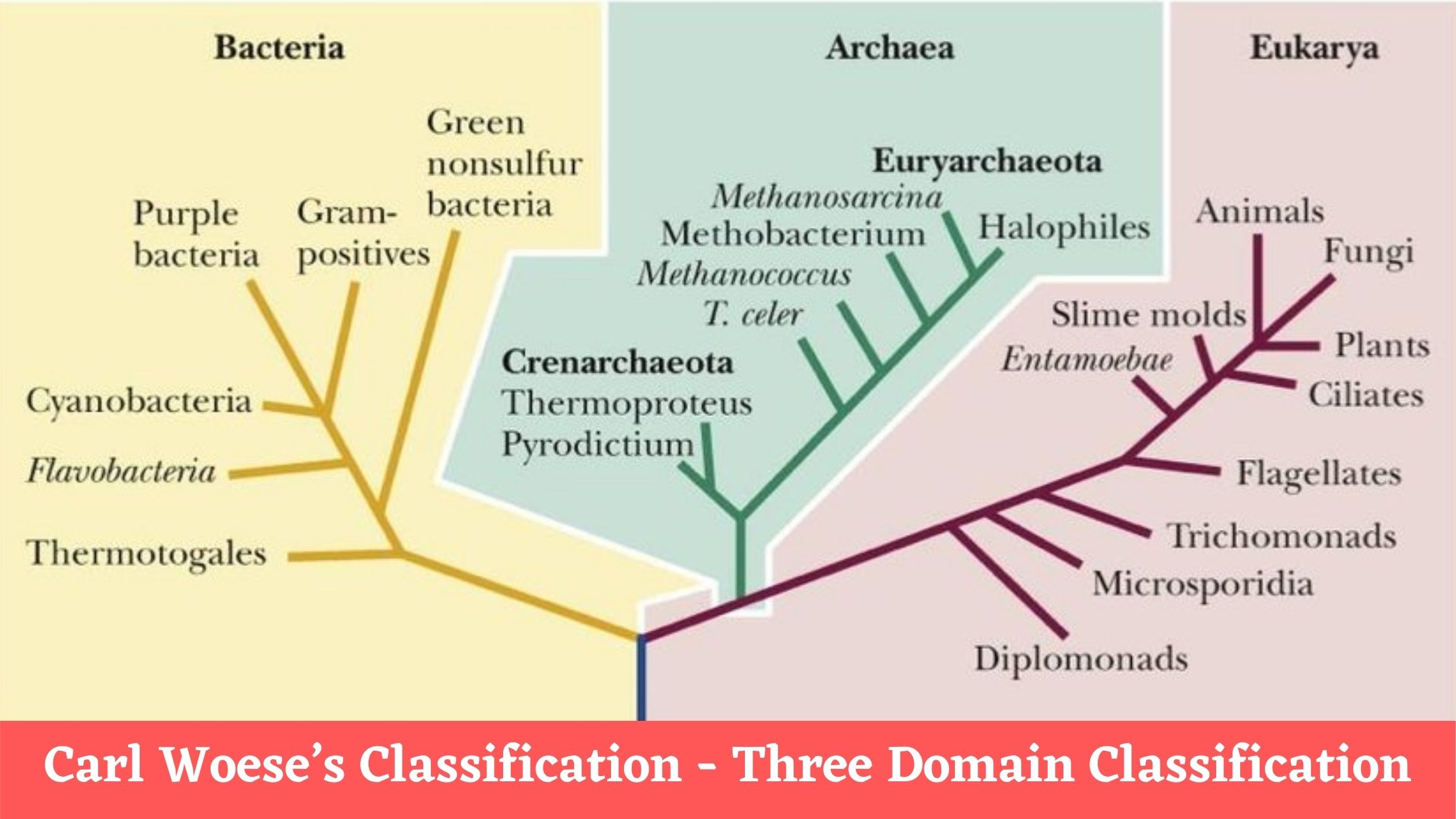
Staphylococcus aureus – Habitat, Morphology, Characteristics, Infection
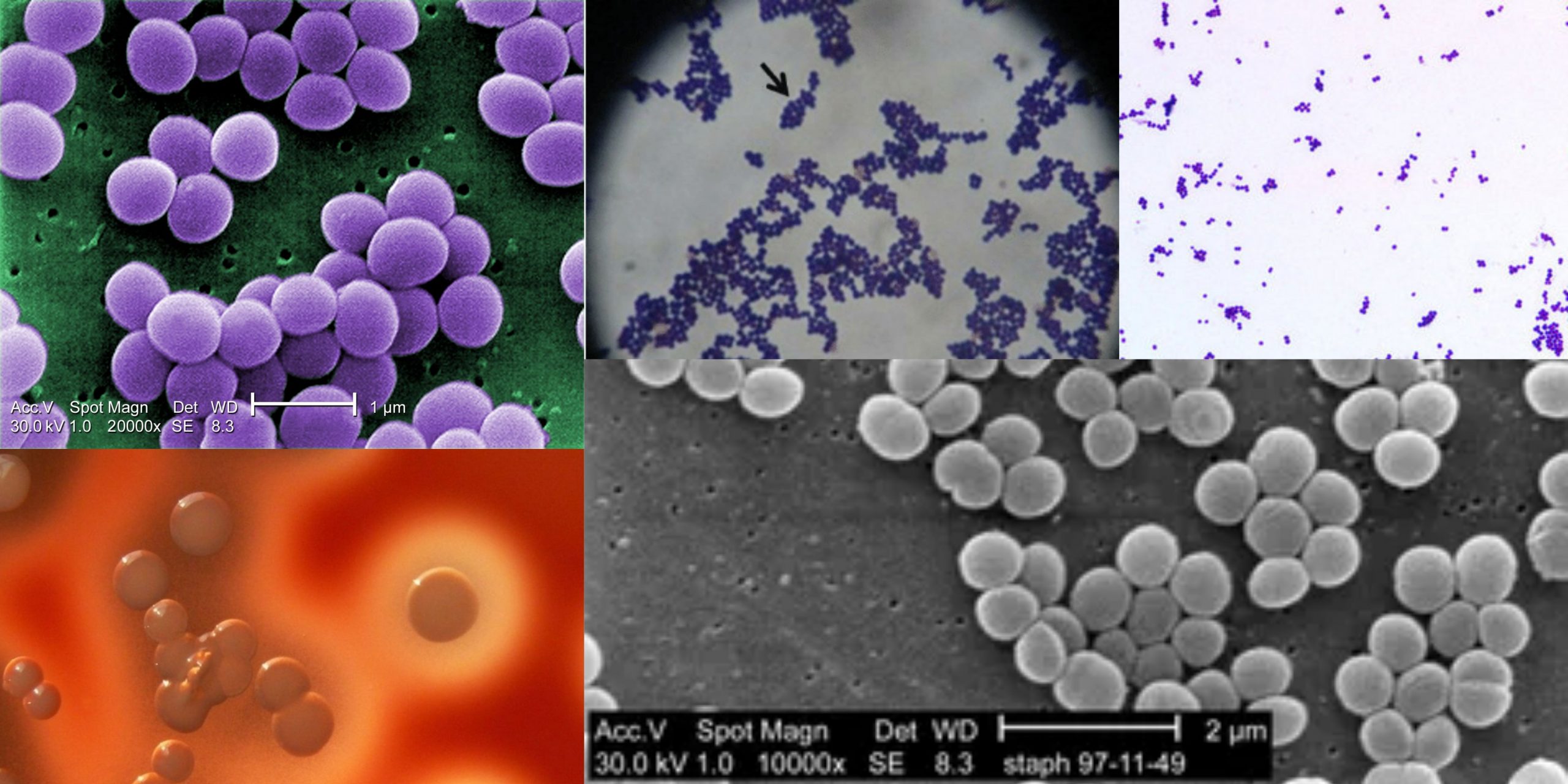
Staphylococcus aureus is a Gram‑positive, facultative anaerobic bacterium, usually found in clusters that resemble grapes and typically 0.5–1µm in diameter. Harbor, as a commensal organism, in the human nasal passages, skin, and mucous membranes of 20–30% of people without causing disease It is an opportunistic pathogen that can cause a wide range of infections—from simple … Read more