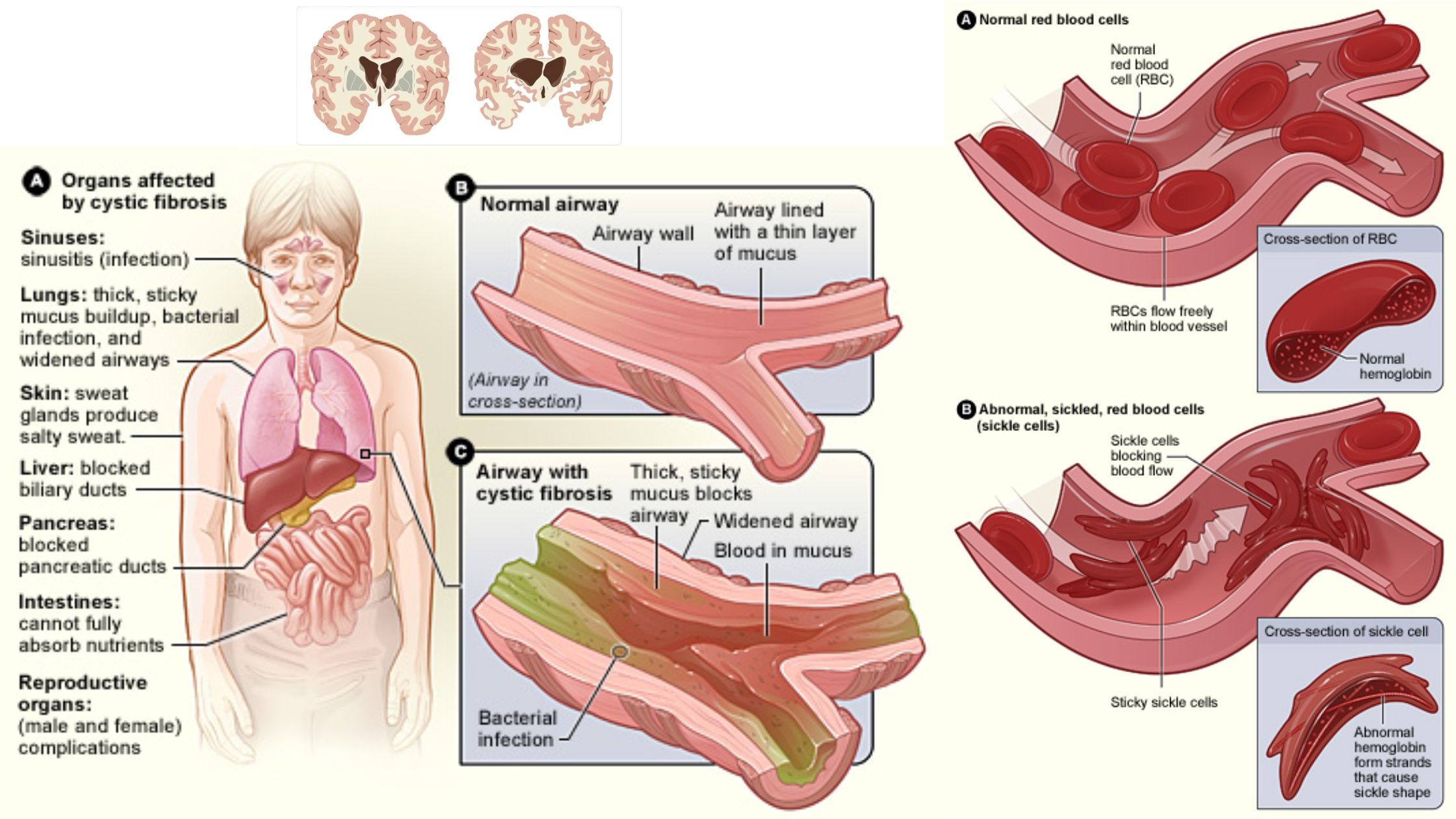
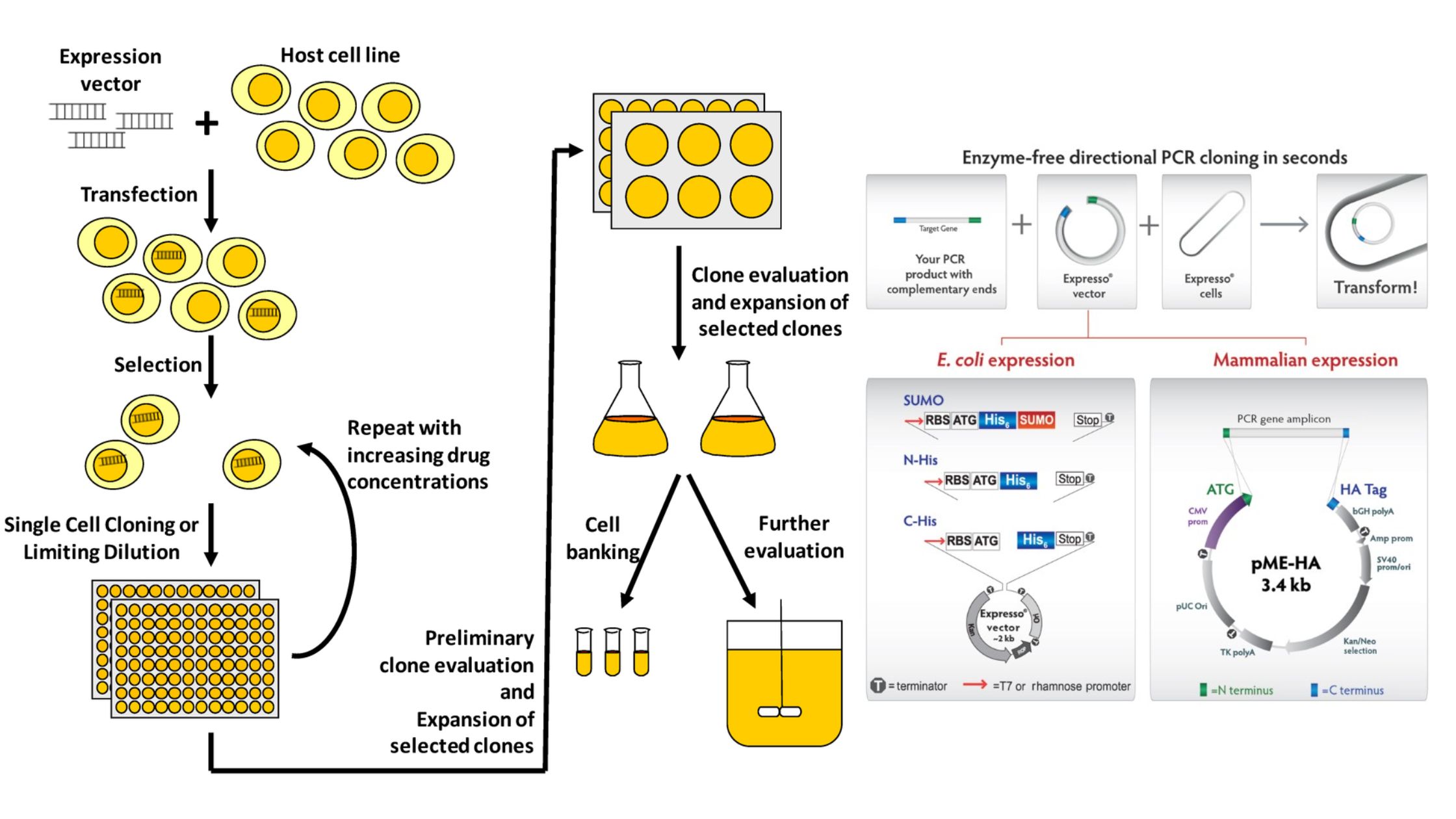
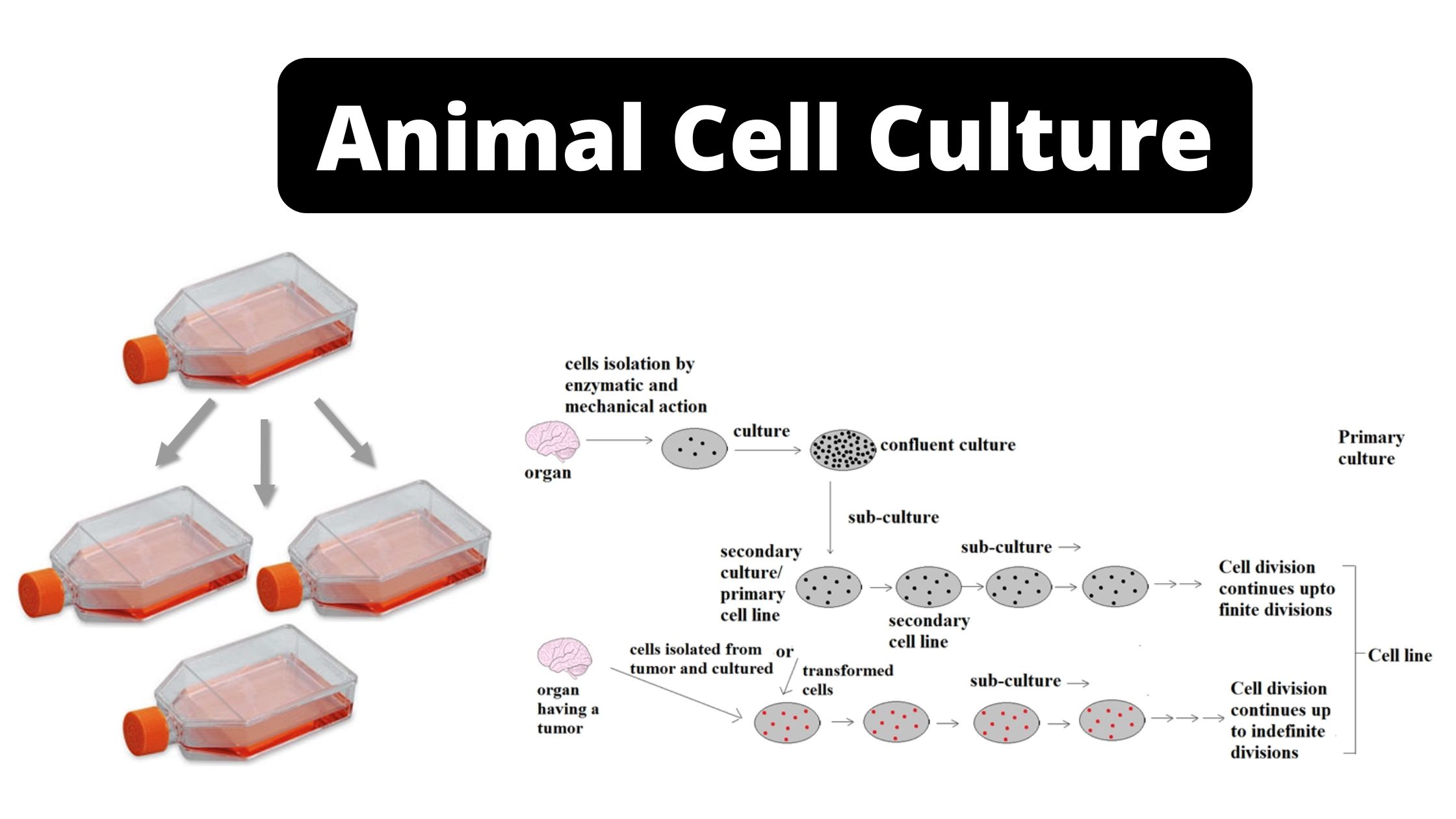
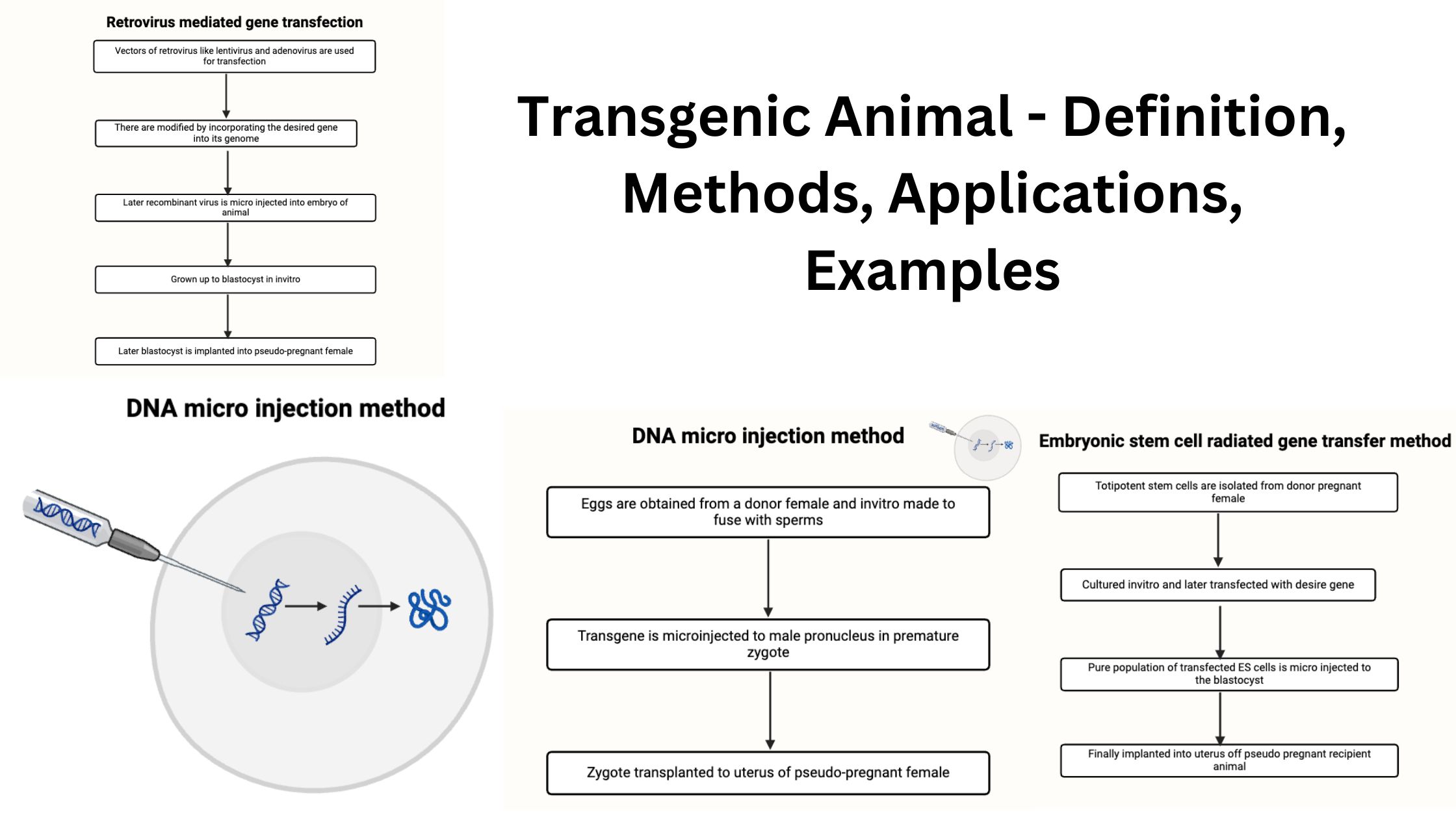
Hormones – Definition, Structure, Types, Functions, Examples
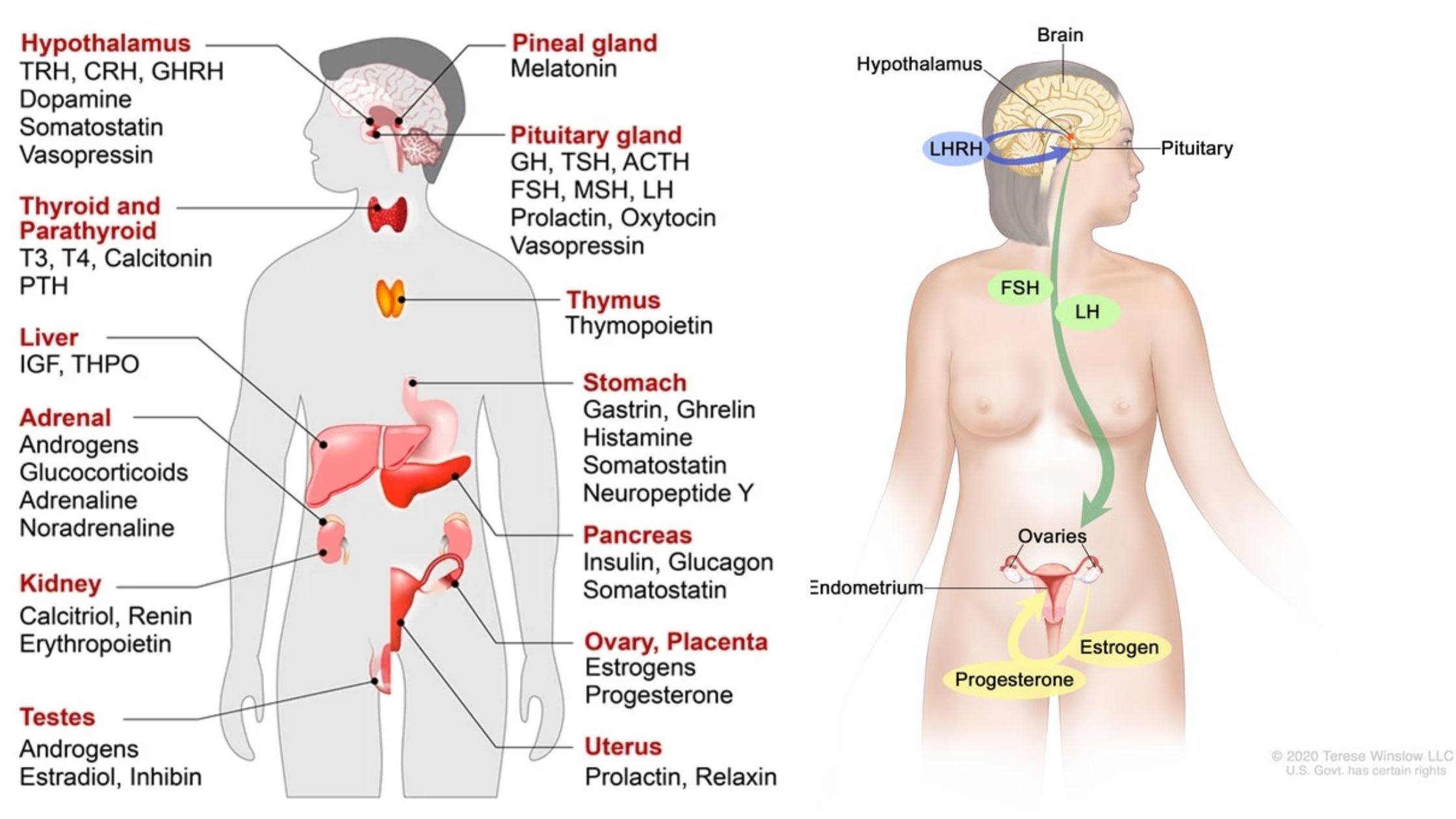
What are Hormones? Definition of Hormones Hormones are chemical messengers produced by endocrine glands that travel through the bloodstream to regulate various bodily functions by interacting with specific target cells or organs. Characteristics or properties of hormone Below are some key characteristics of hormones: Endocrine Glands and Their Major Hormones Endocrine Gland Associated Hormones Chemical … Read more