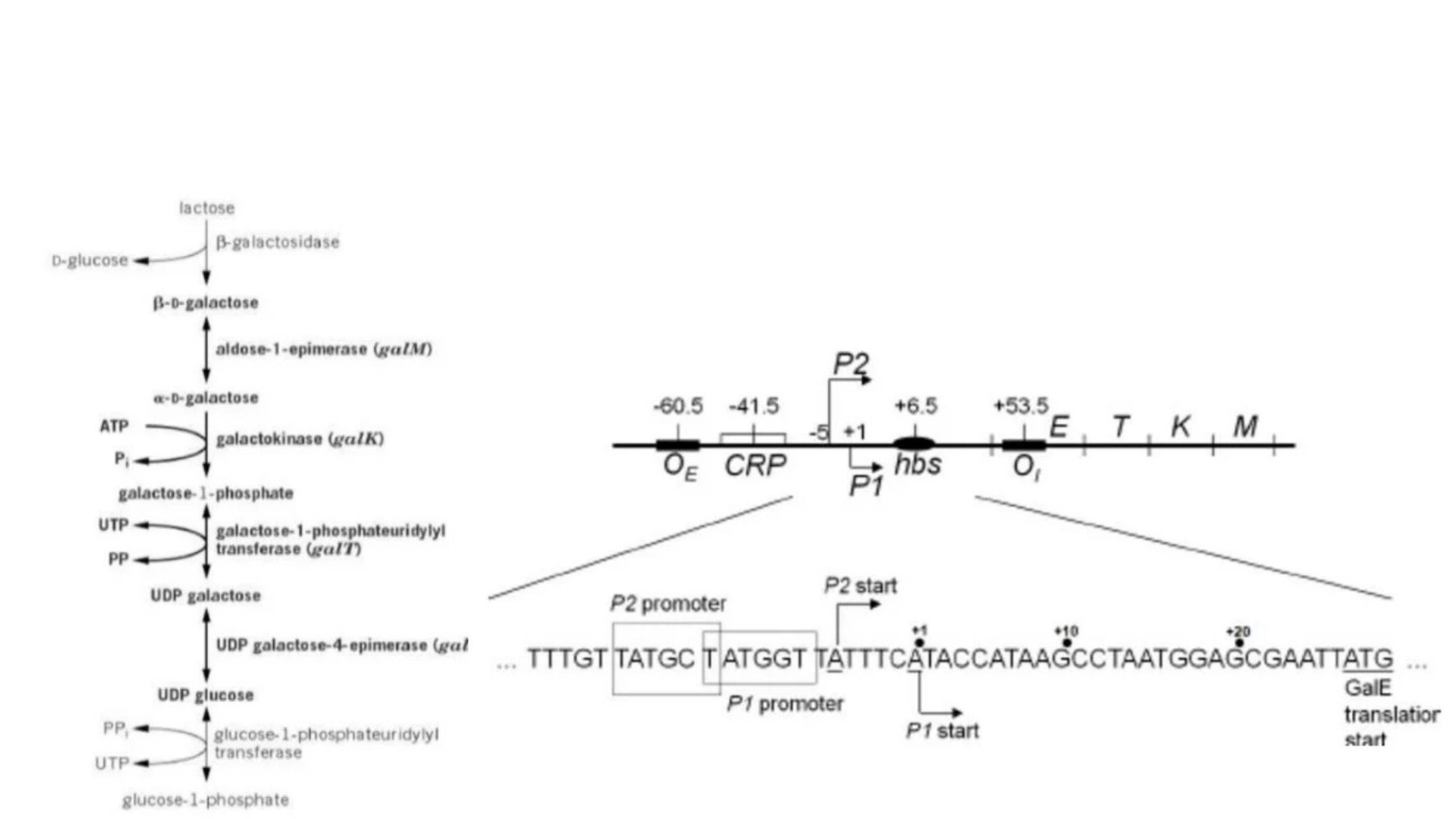
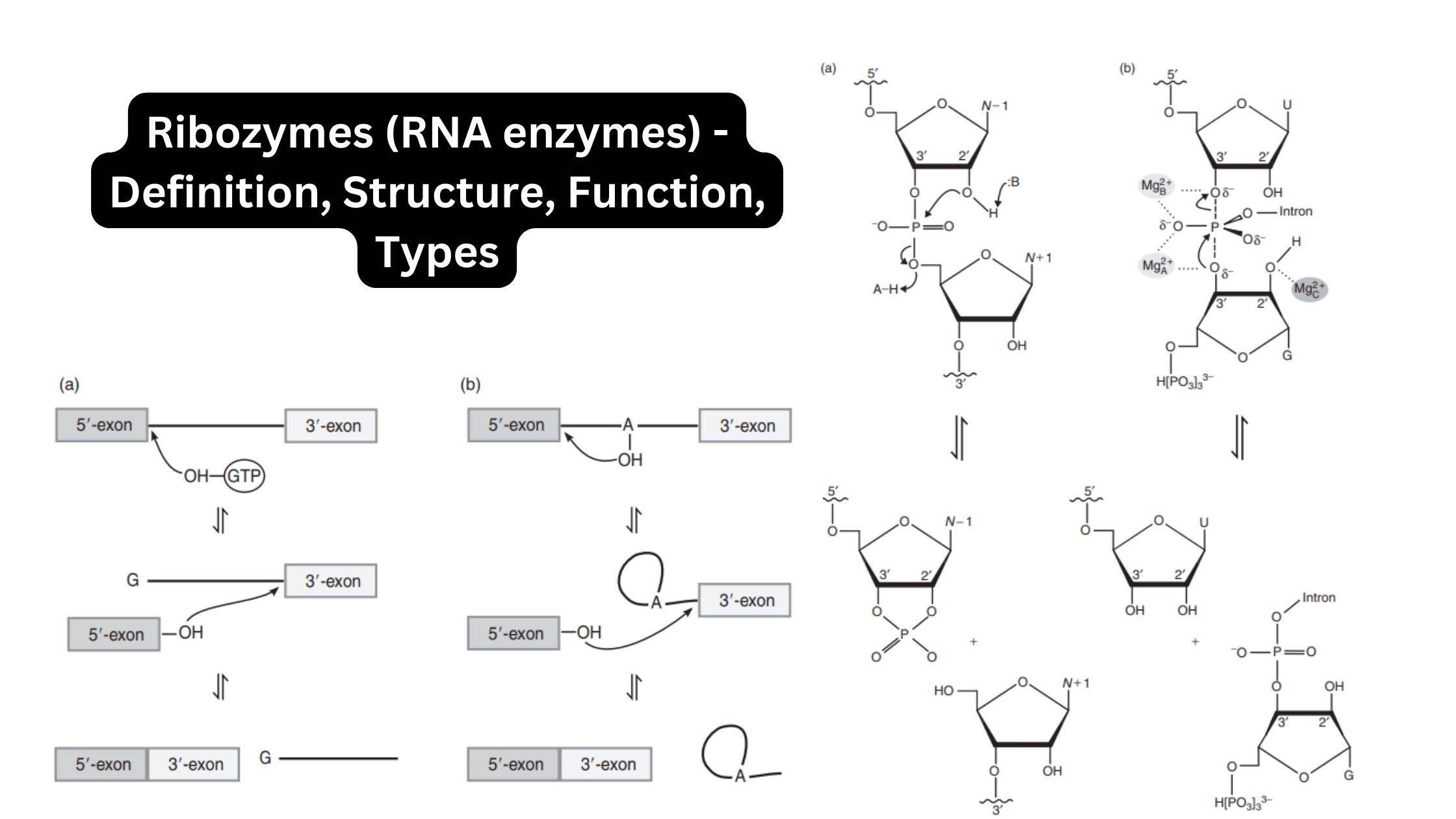
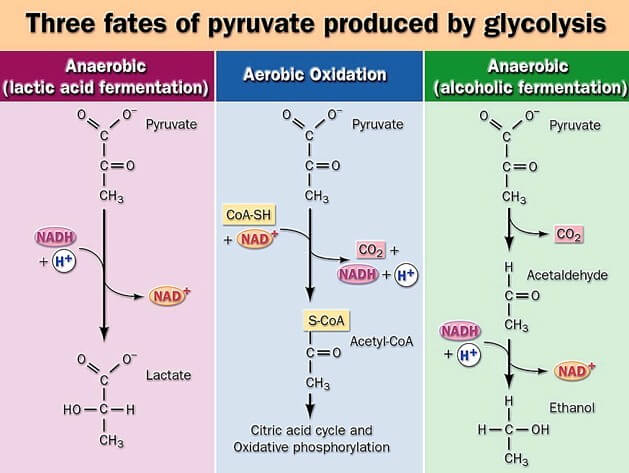
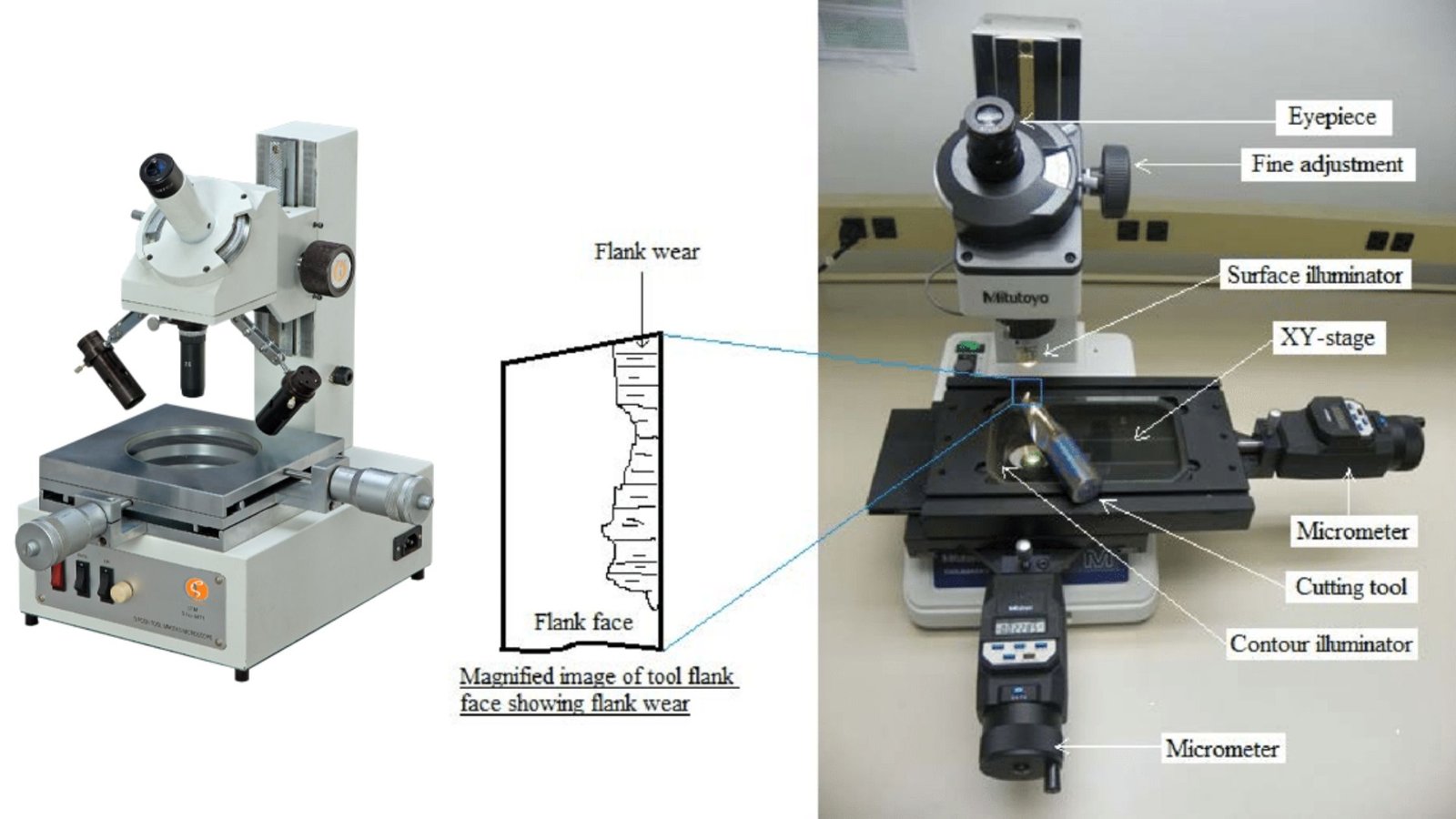
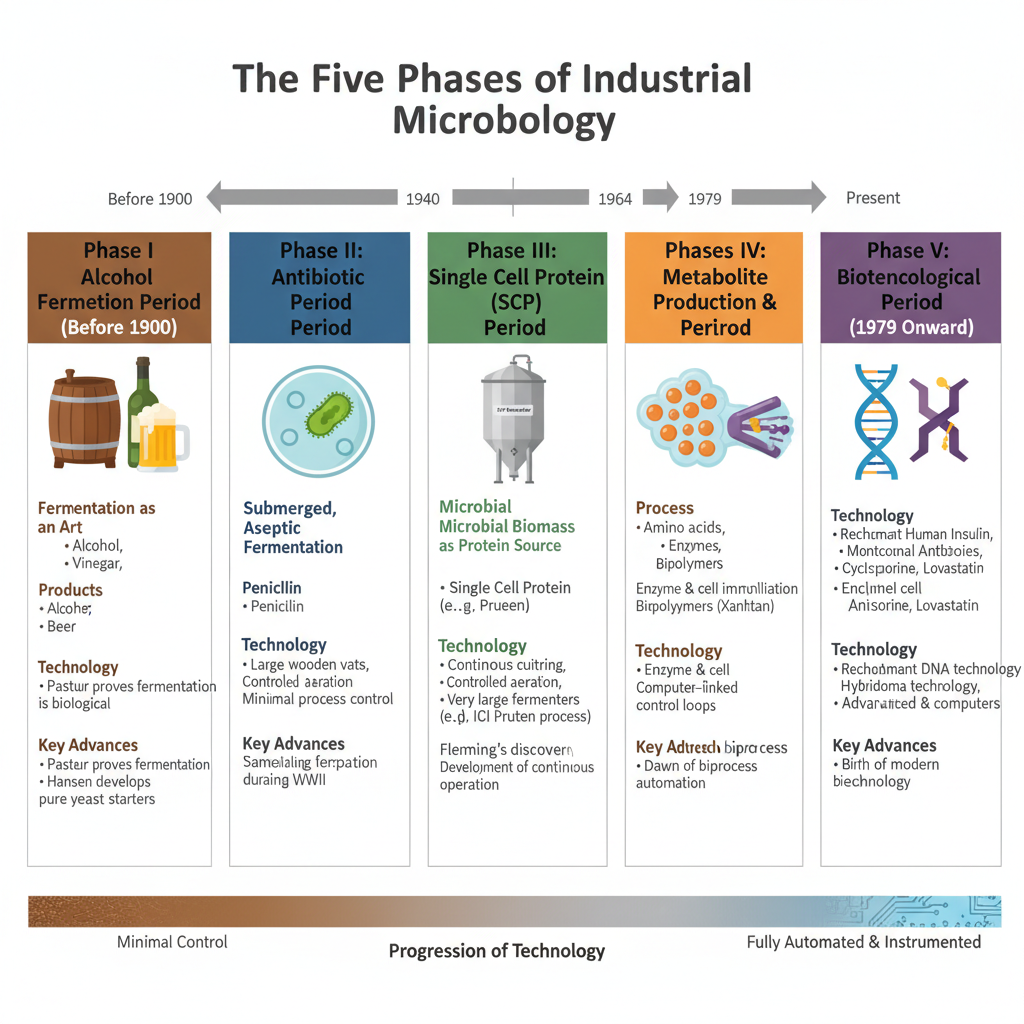
Production Media – Types, Characteristics, Examples, Uses
What is Production Media? Production media is the nutrient-rich medium used to support the large-scale growth of microorganisms or cell cultures for the purpose of producing useful biological substances. It is designed in such a way that optimum growth conditions is maintained, and the metabolic activities of the organisms is supported for yielding products like … Read more