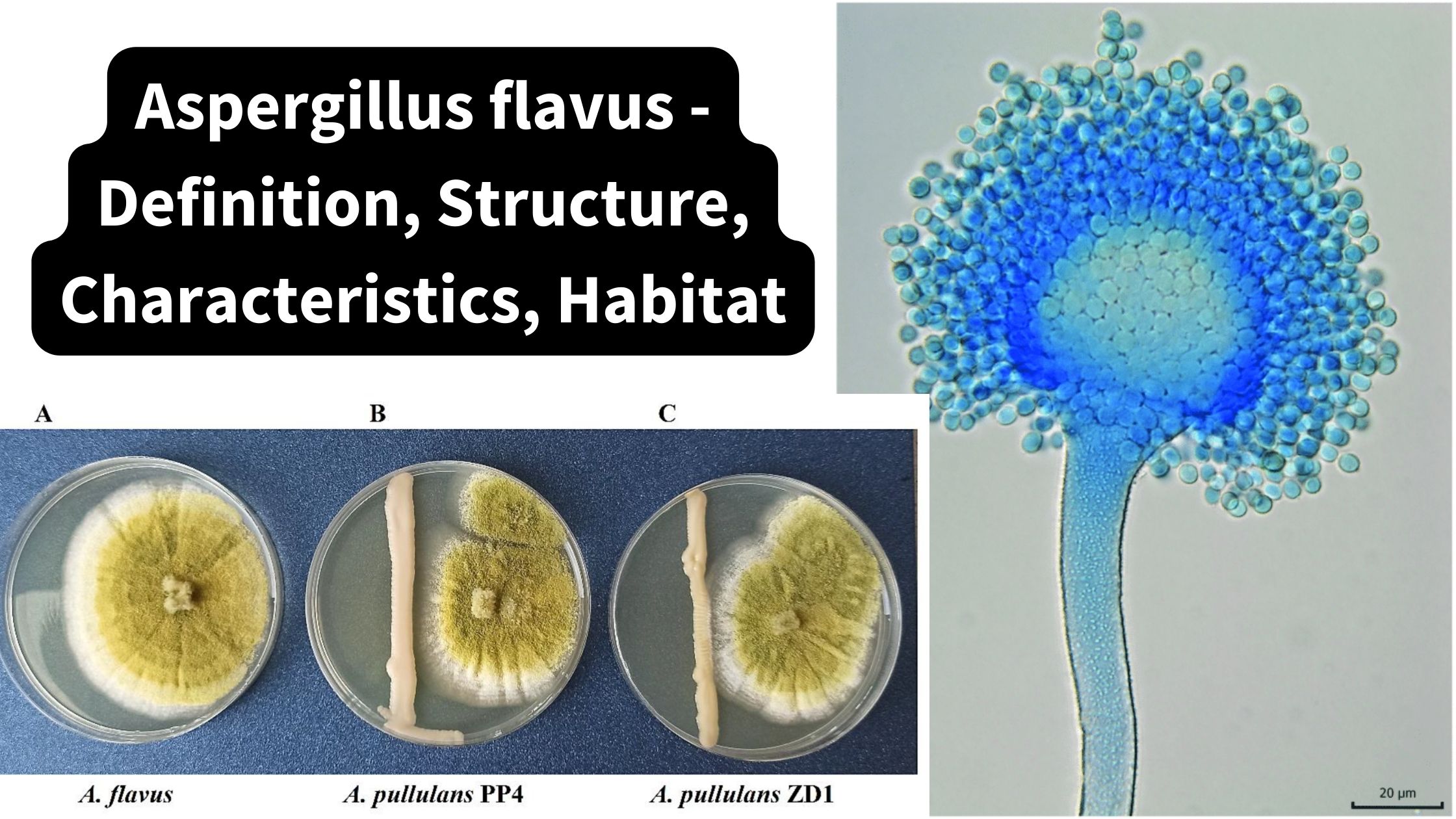
Geographical Indications – Definition, Process, Benefits, Examples
What is Geographical Indication? A Geographical Indication (GI) is basically a sign / mark used on products that come from a particular location and have qualities or reputation mainly due to that place. It’s considered as one of the forms of Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) which protects names or signs linked with geographic origin rather … Read more