History of Microbiology
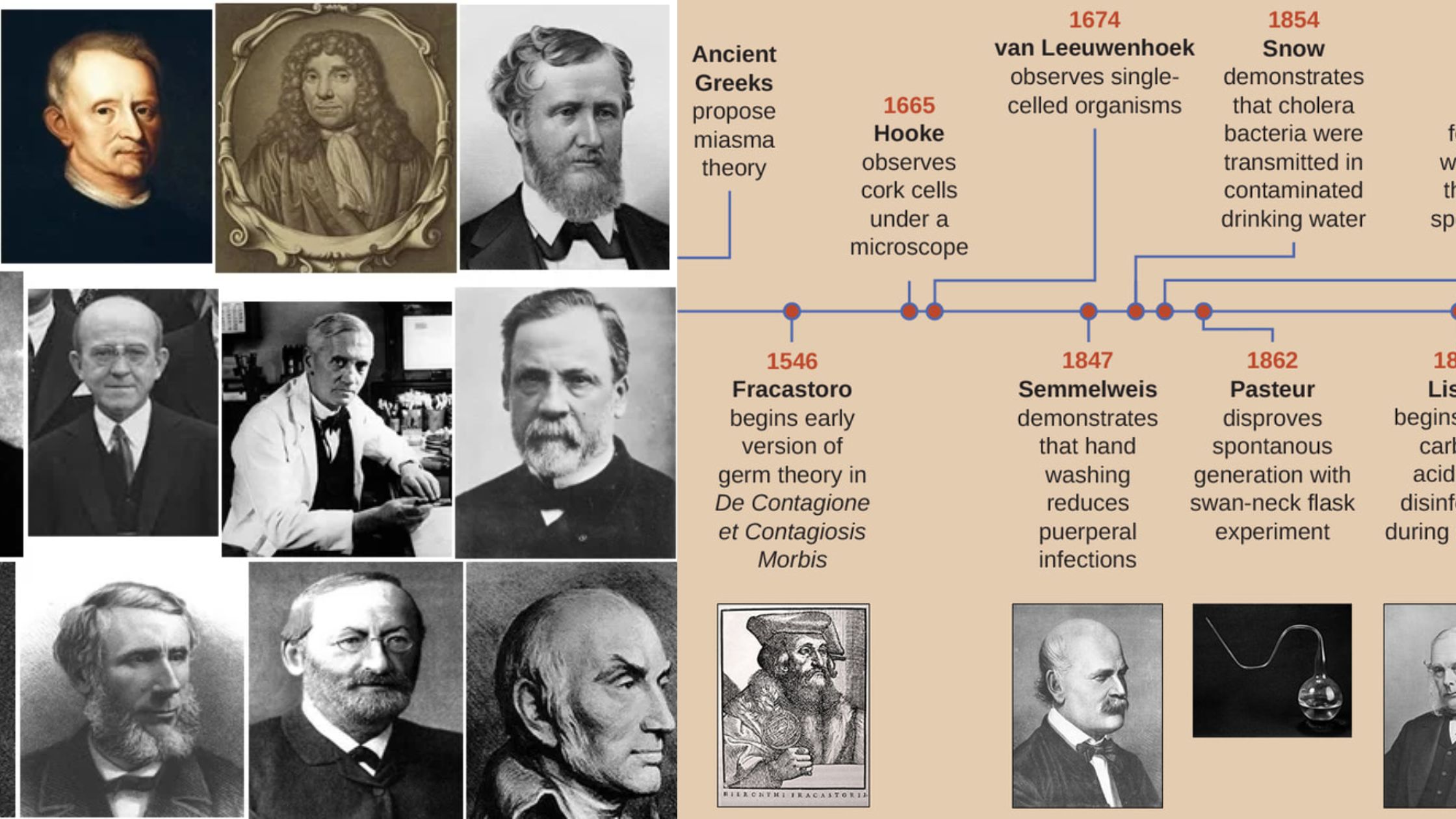
The Emergence of Microbiology: Uncovering Microbes Microbiology, the study of microscopic living organisms, is a relatively recent scientific field that has significantly advanced our understanding of biology and disease. The foundation of microbiology can be traced back to the mid-19th century, during a period of considerable growth and development in the biological sciences. Key Developments … Read more