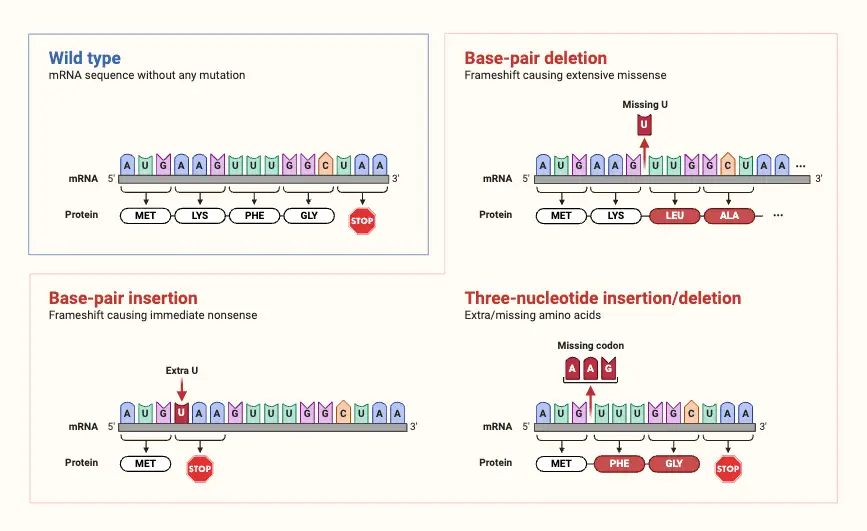
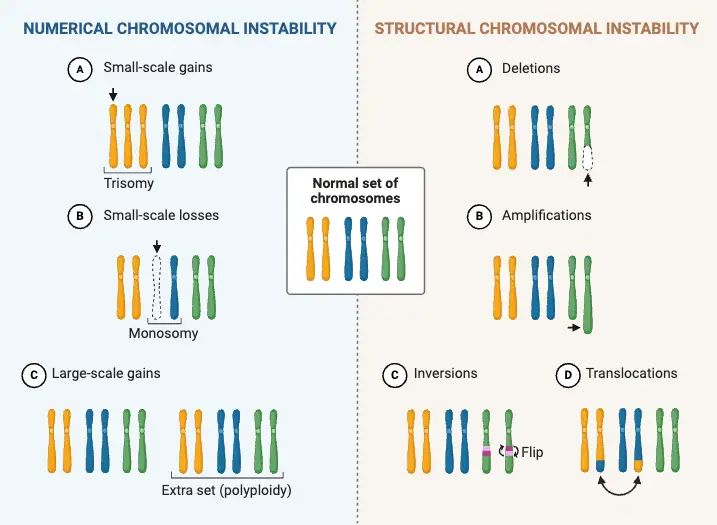
Protection of Traditional Knowledge – Objective, Significance, Issues
What is Traditional Knowledge (TK)? Significance of Traditional Knowledge (TK) The significance of Traditional Knowledge (TK) is deeply rooted in both cultural identity and practical utility for many indigenous and local communities. It forms a fundamental part of their daily lives and is essential for their continued development and sustainability. The following points outline the … Read more