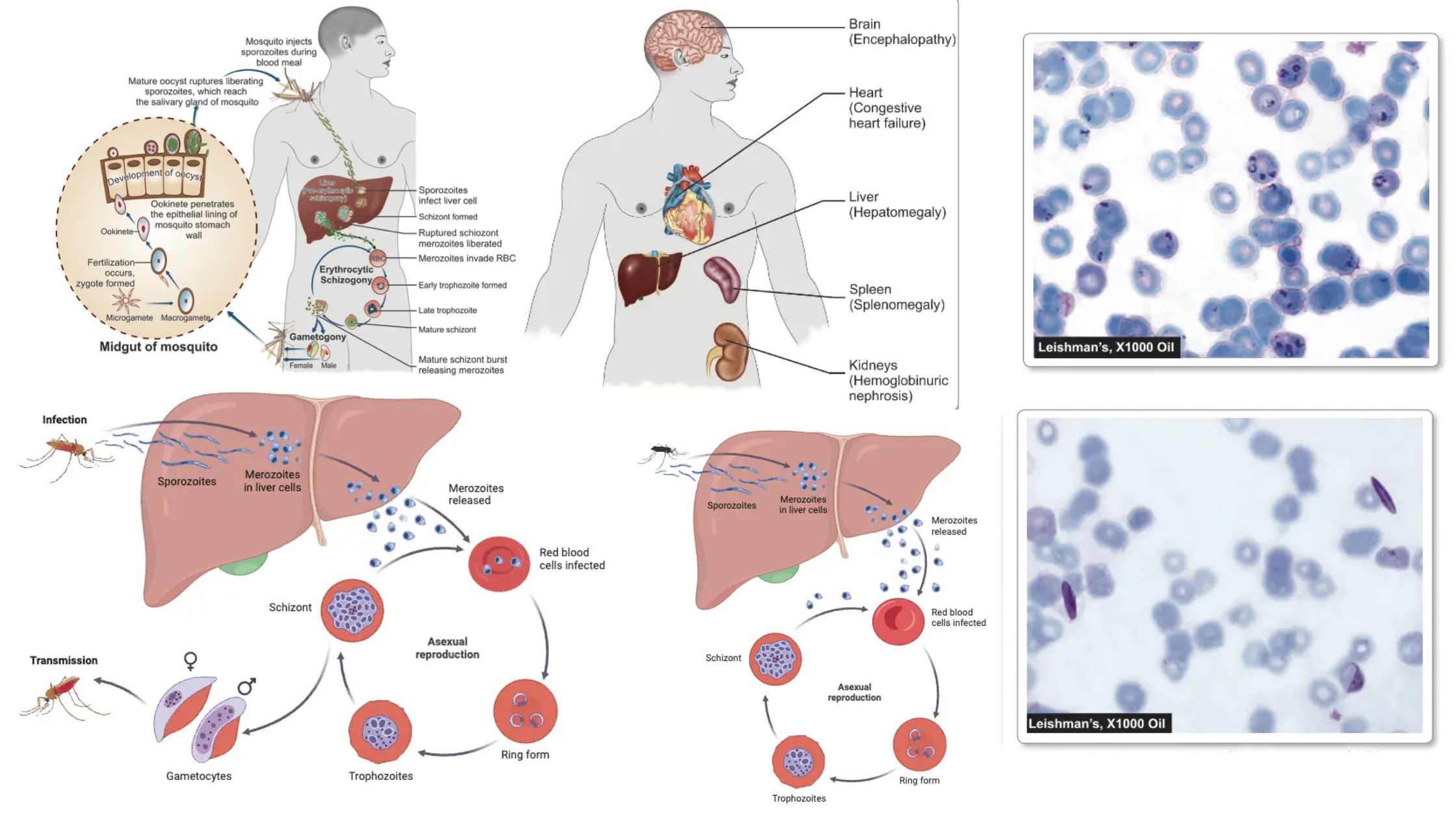
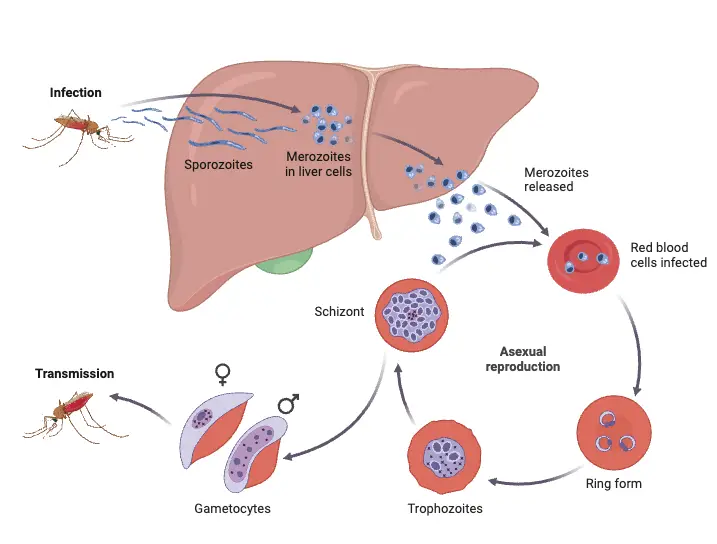
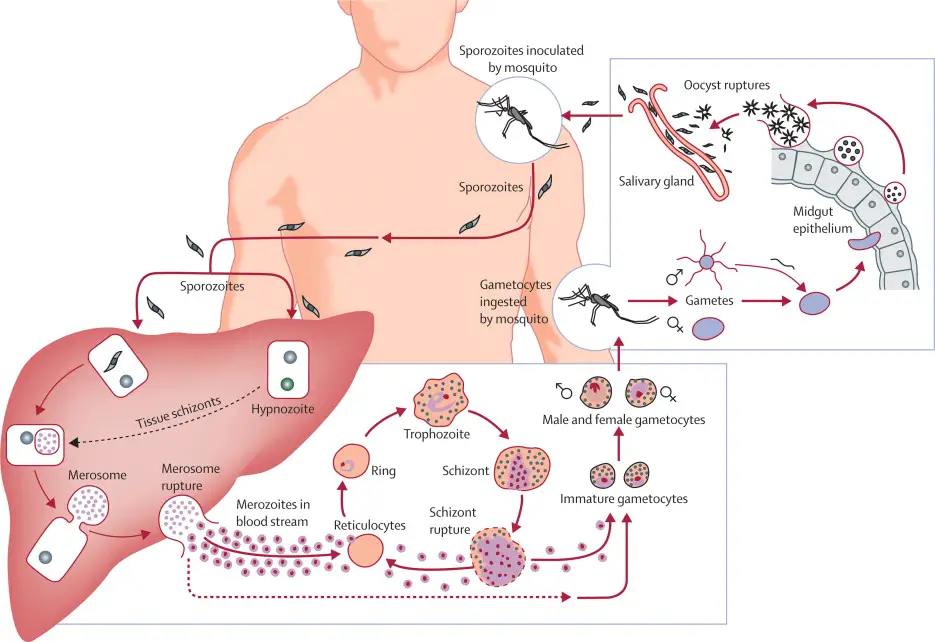
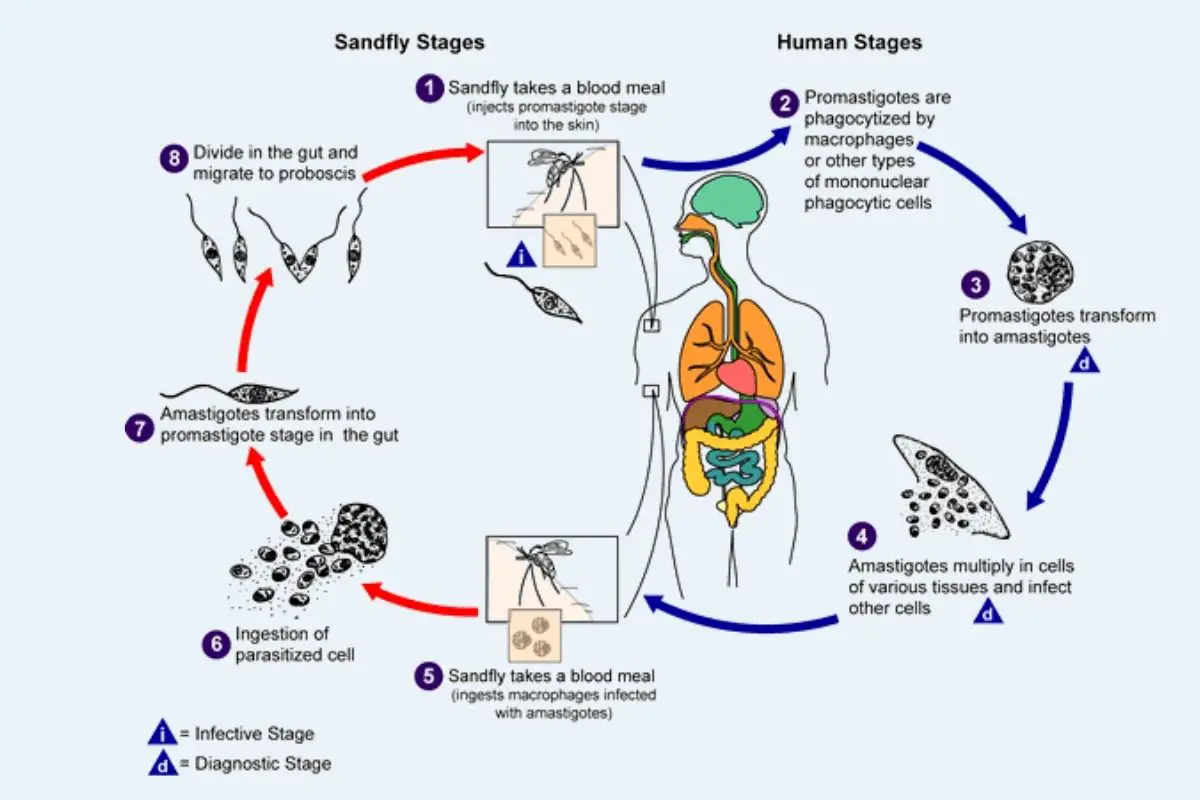
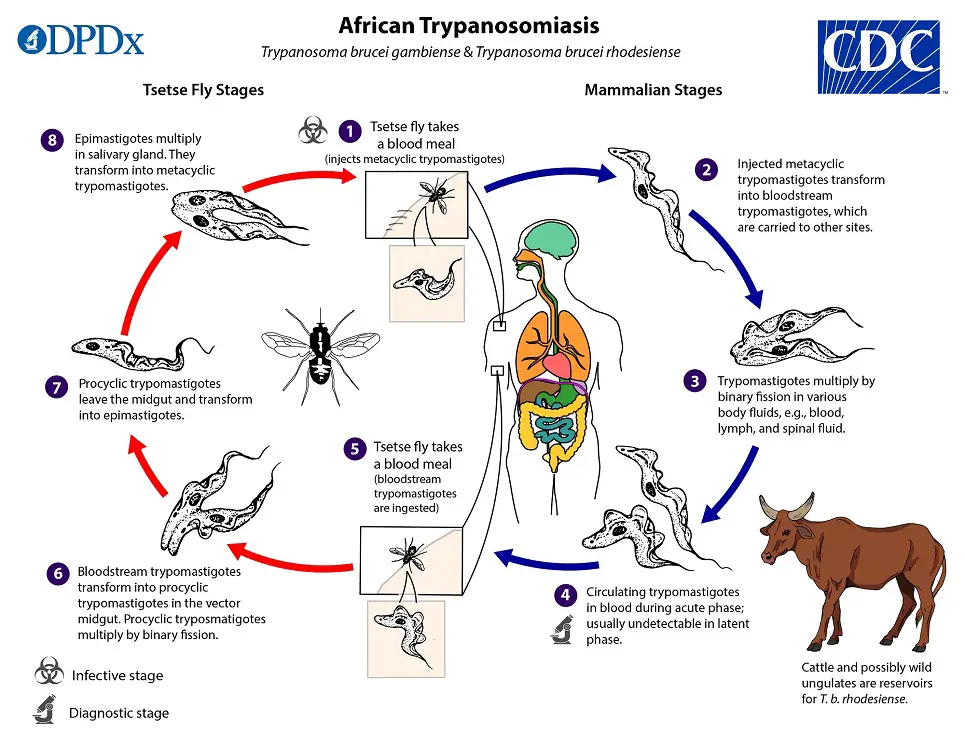
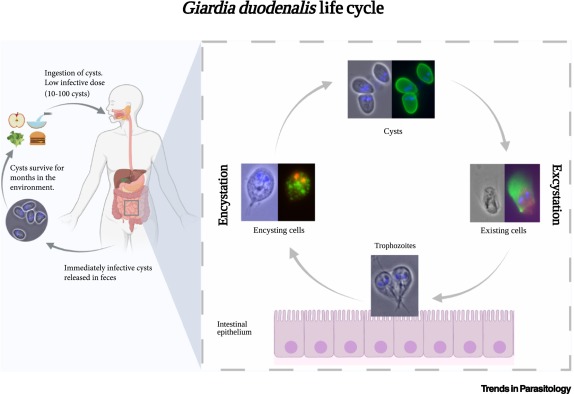
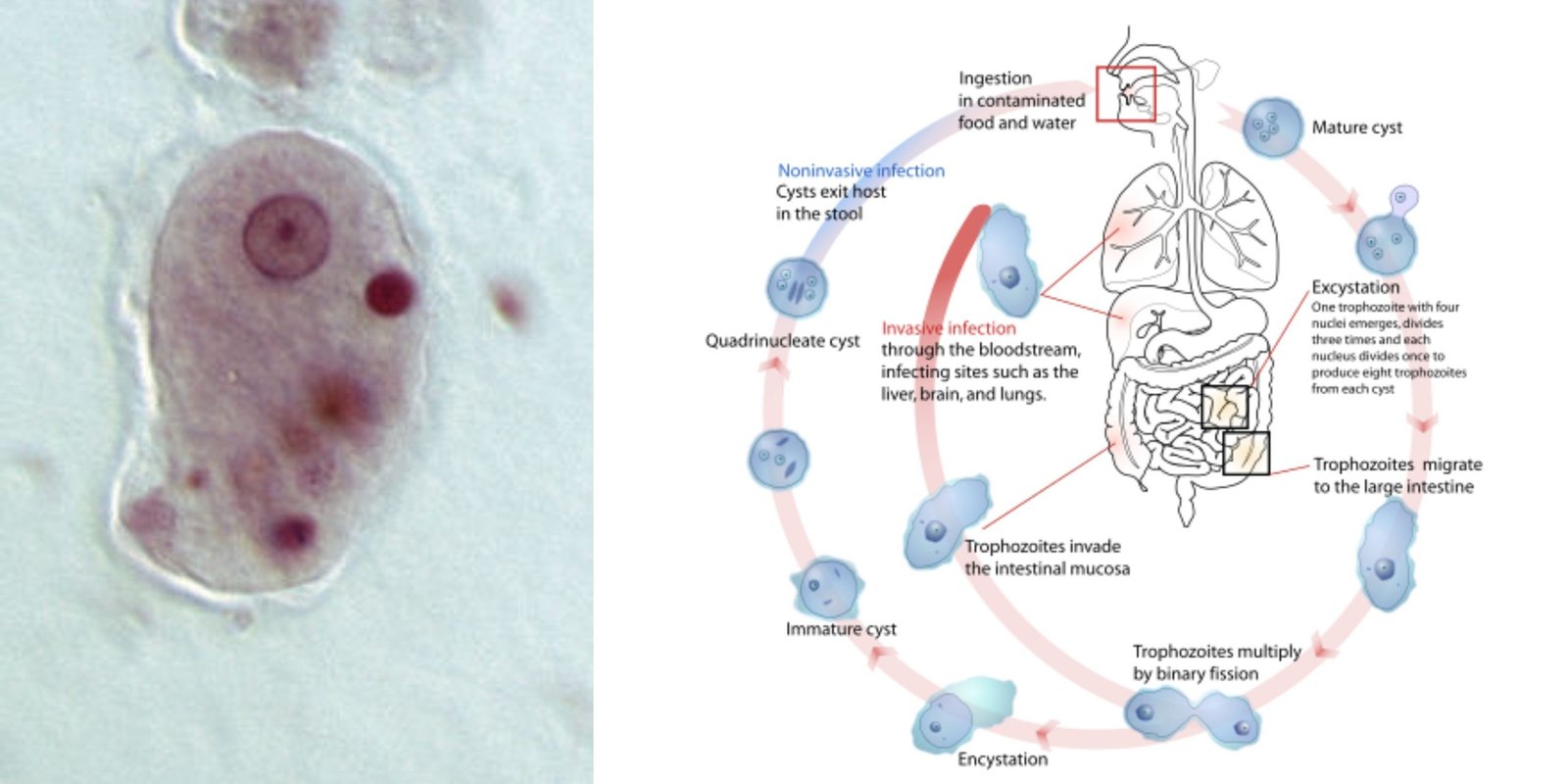
Malaria – Parasite, Life Cycle, Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, Treatment, Prophylaxis
What is Malaria? Classification of Malaria parasite Malaria, a significant global health challenge, is caused by parasitic organisms that belong to the genus Plasmodium. These parasites are classified under the Phylum Apicomplexa, which encompasses various protozoans known for their complex life cycles. A comprehensive understanding of the classification of malaria parasites is essential for educators … Read more