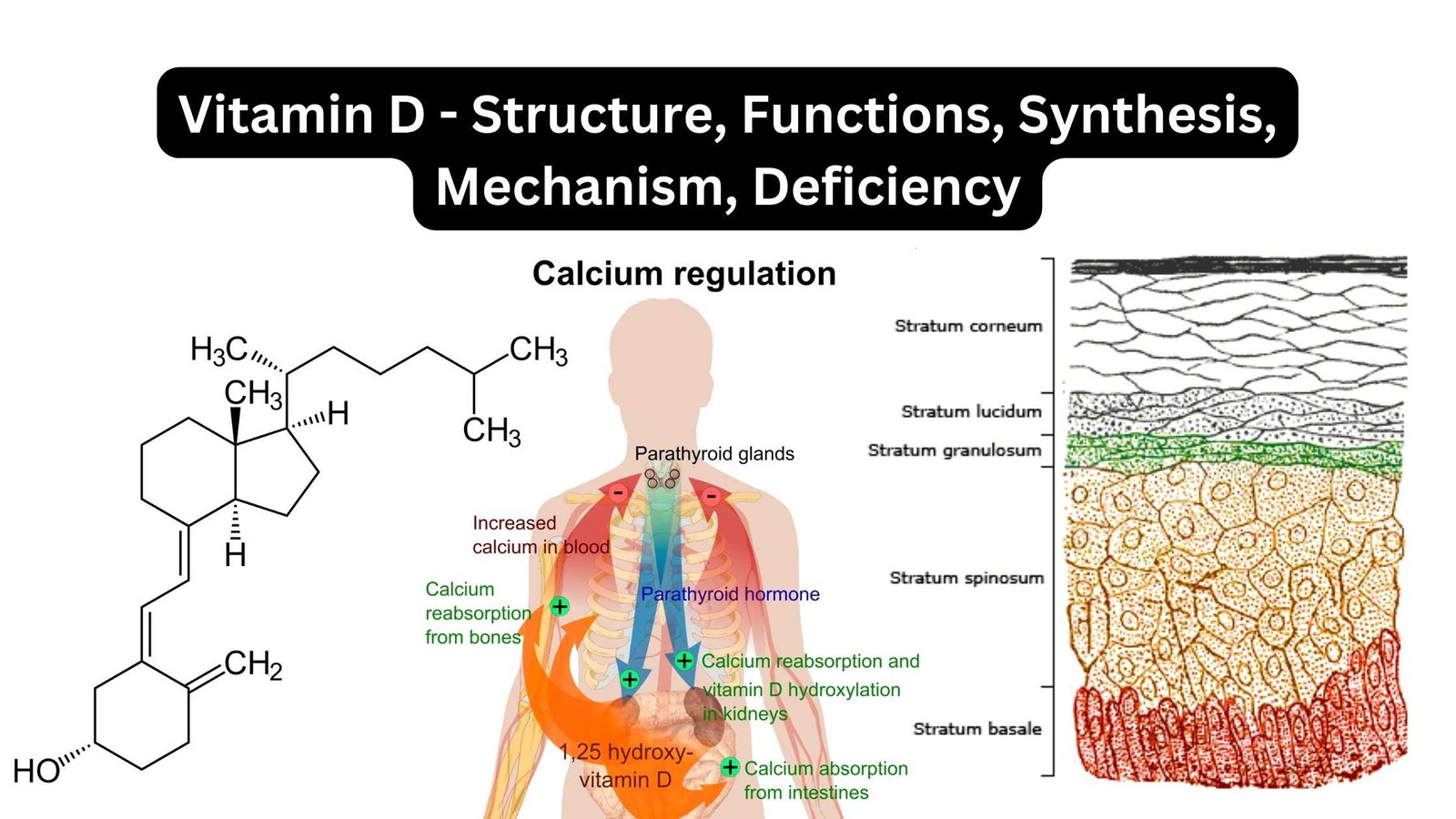
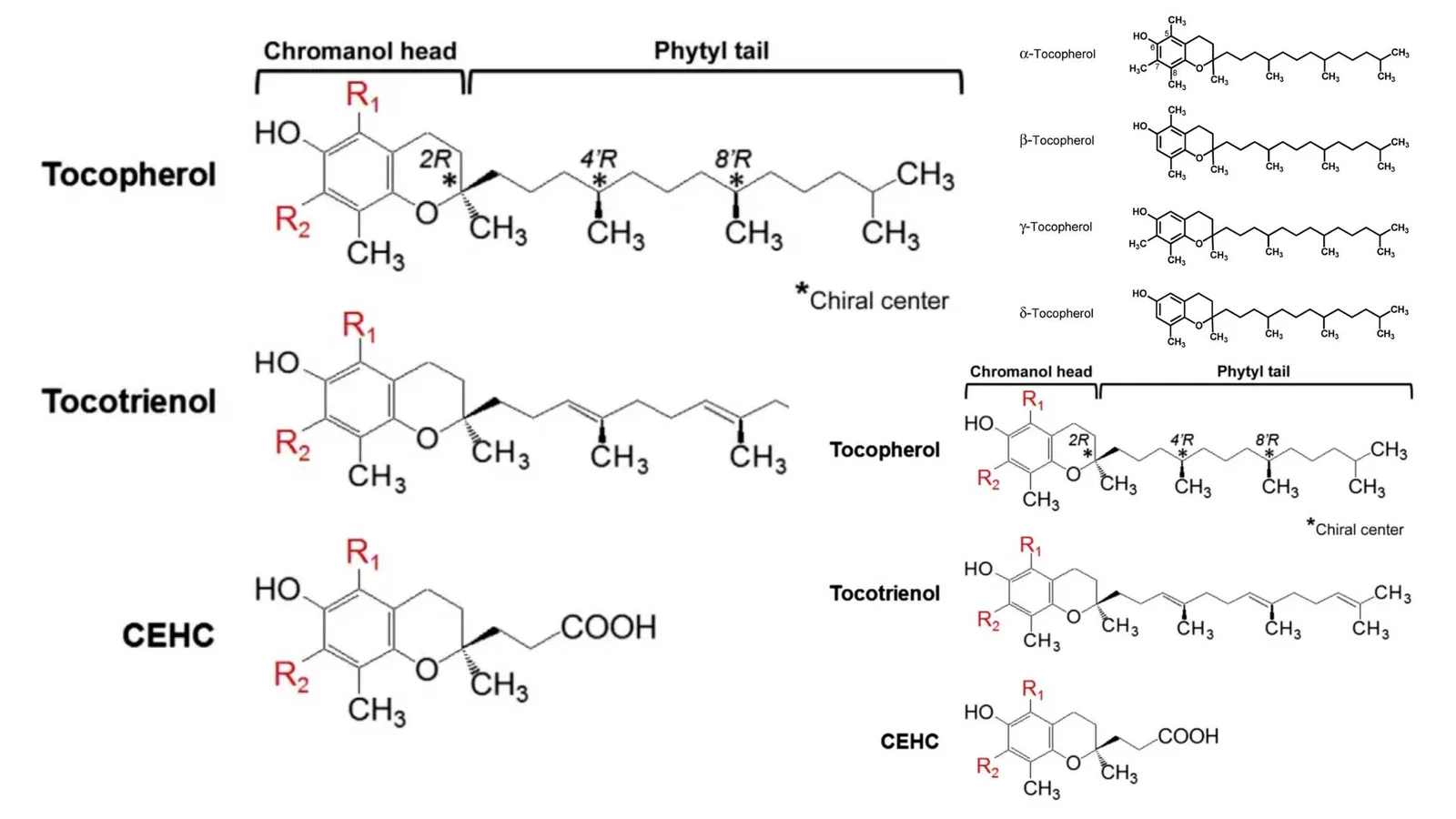
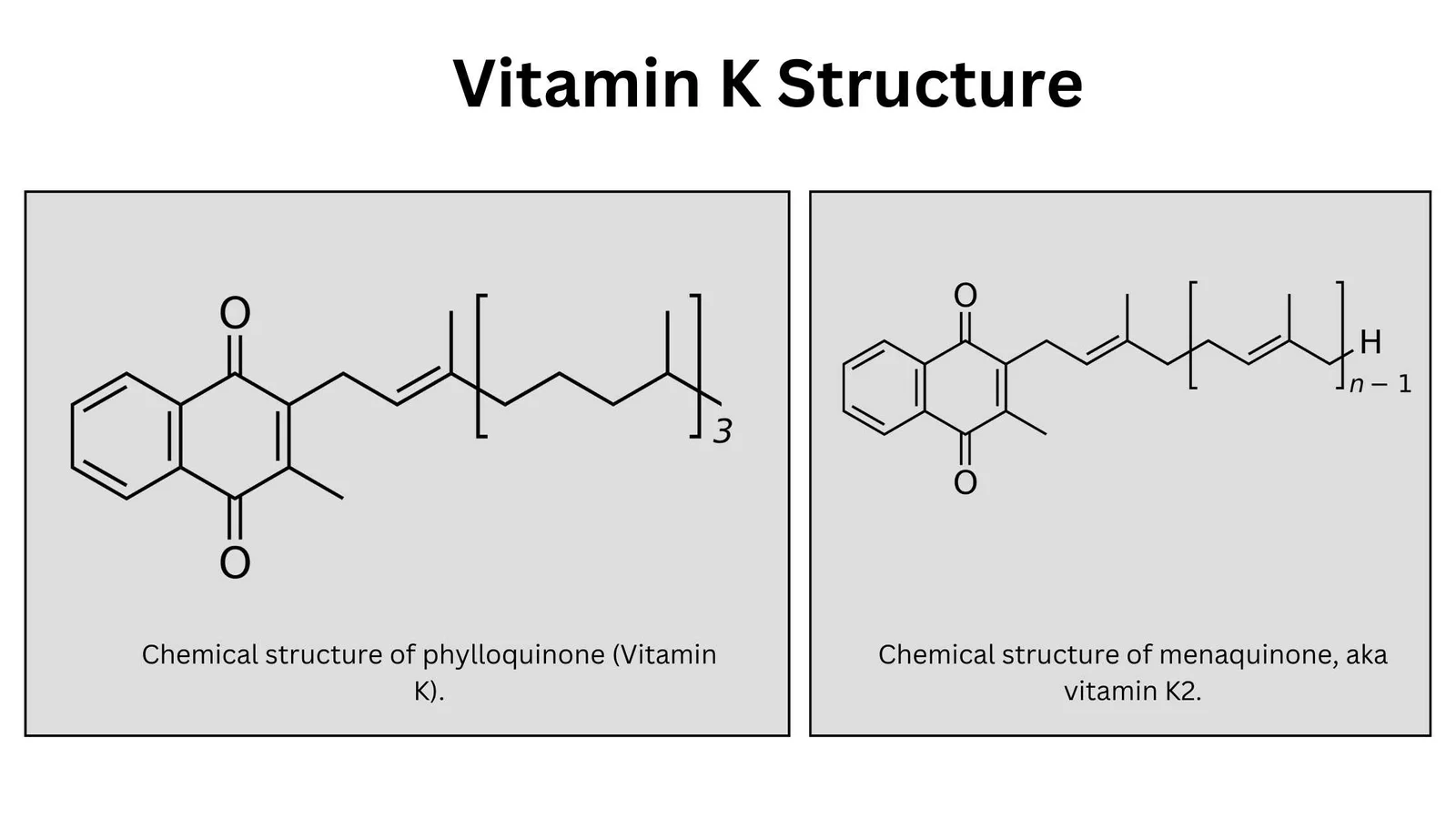
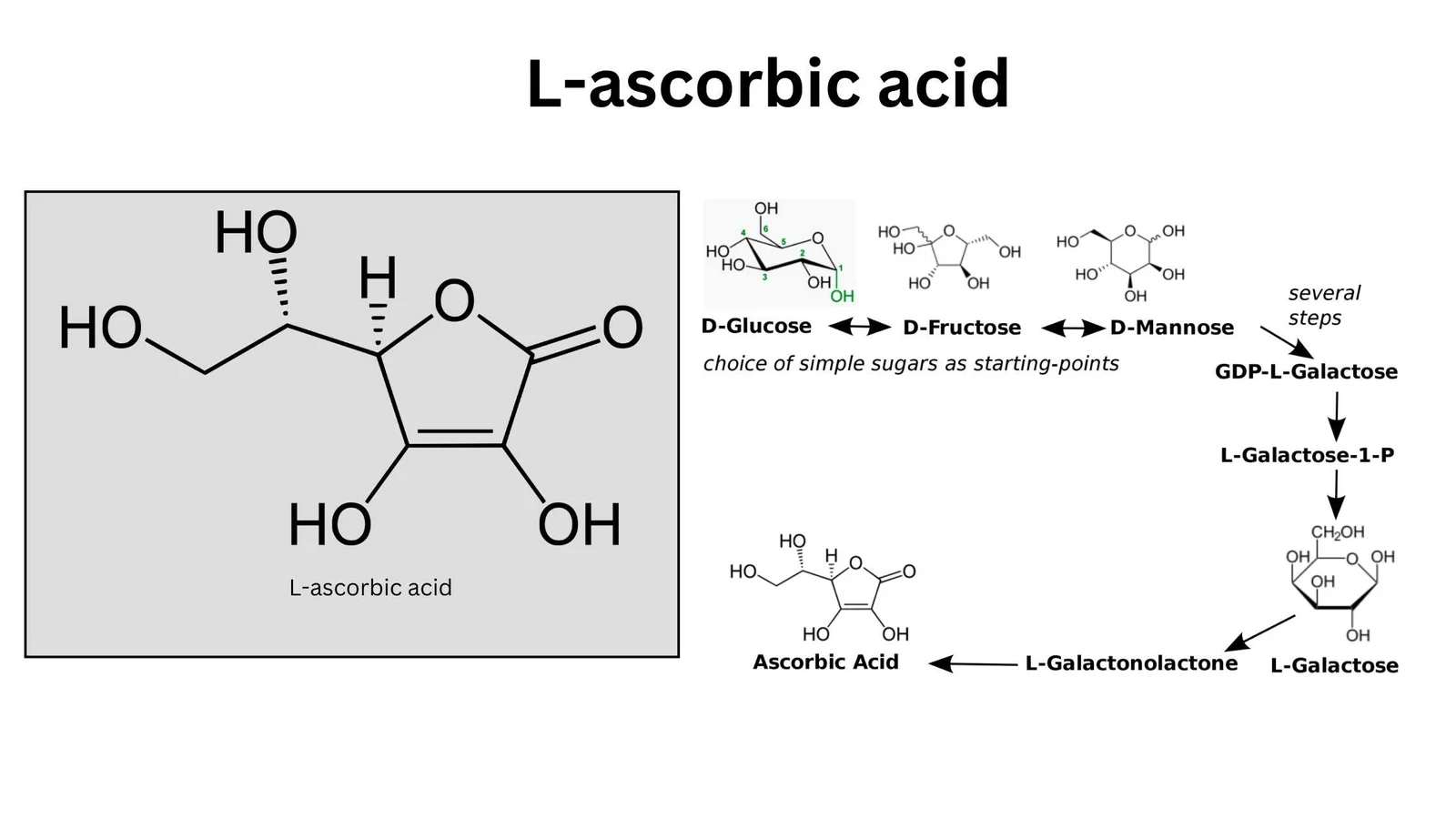
What is Induced Fit Model? – Mechanism, Advantages, Limitations
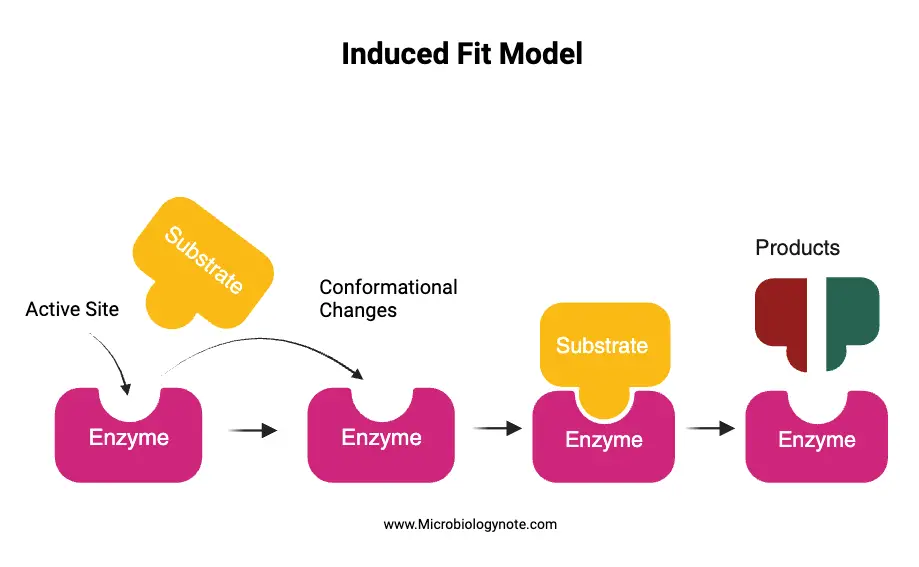
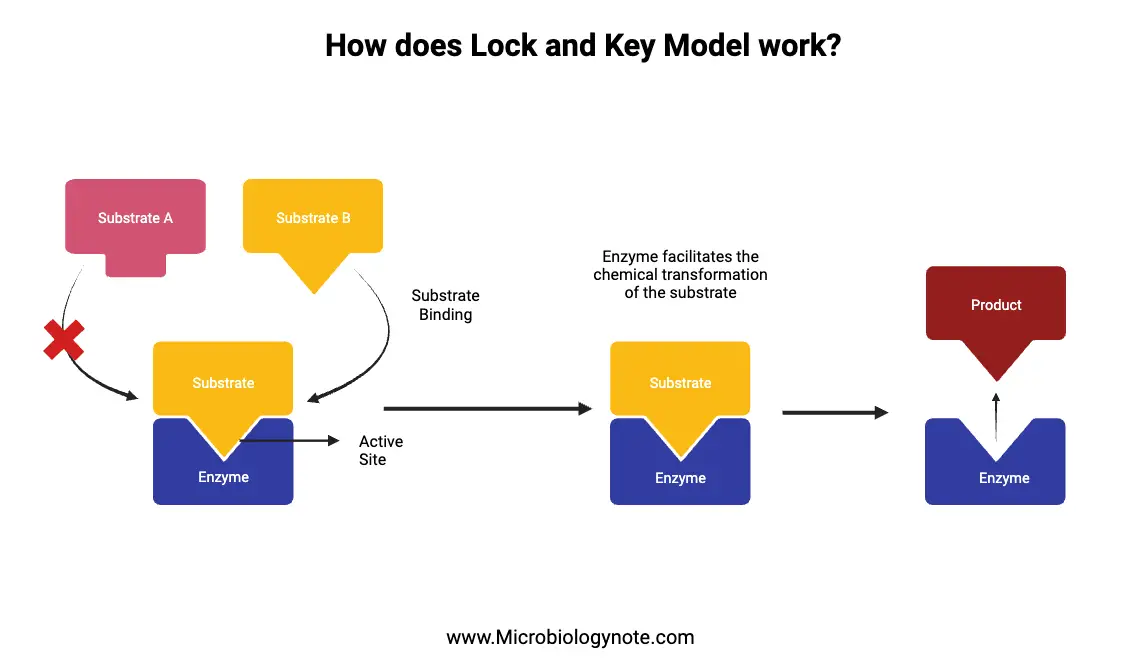
What is Induced Fit Model? Evidences Supporting Induced Fit Model The Induced Fit Model has garnered significant attention in the realm of biochemistry, and various pieces of evidence support its validity. This model posits that proteins, including enzymes, are not static or rigid structures. Instead, they exhibit dynamic properties, allowing them to adapt and change … Read more