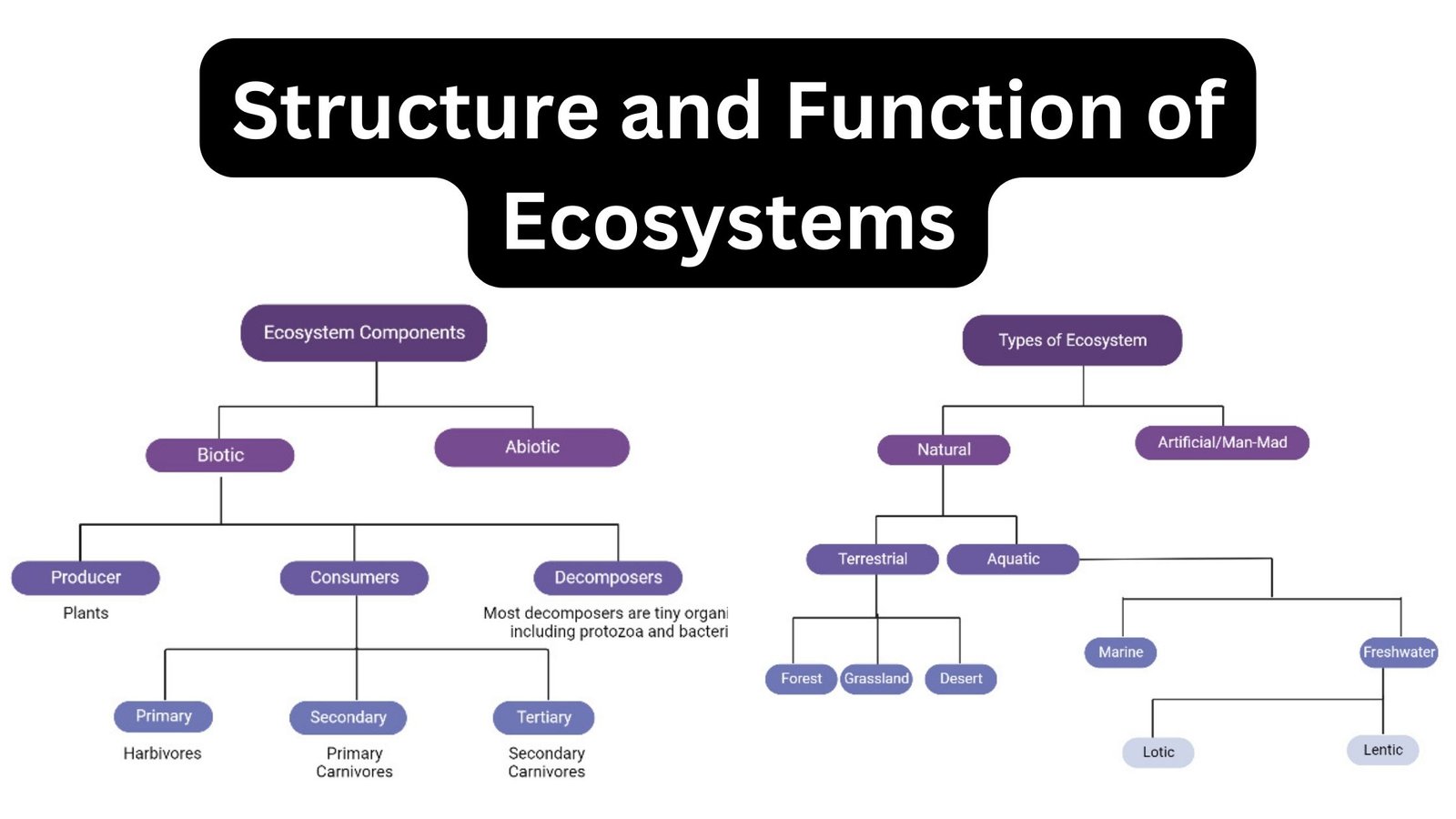
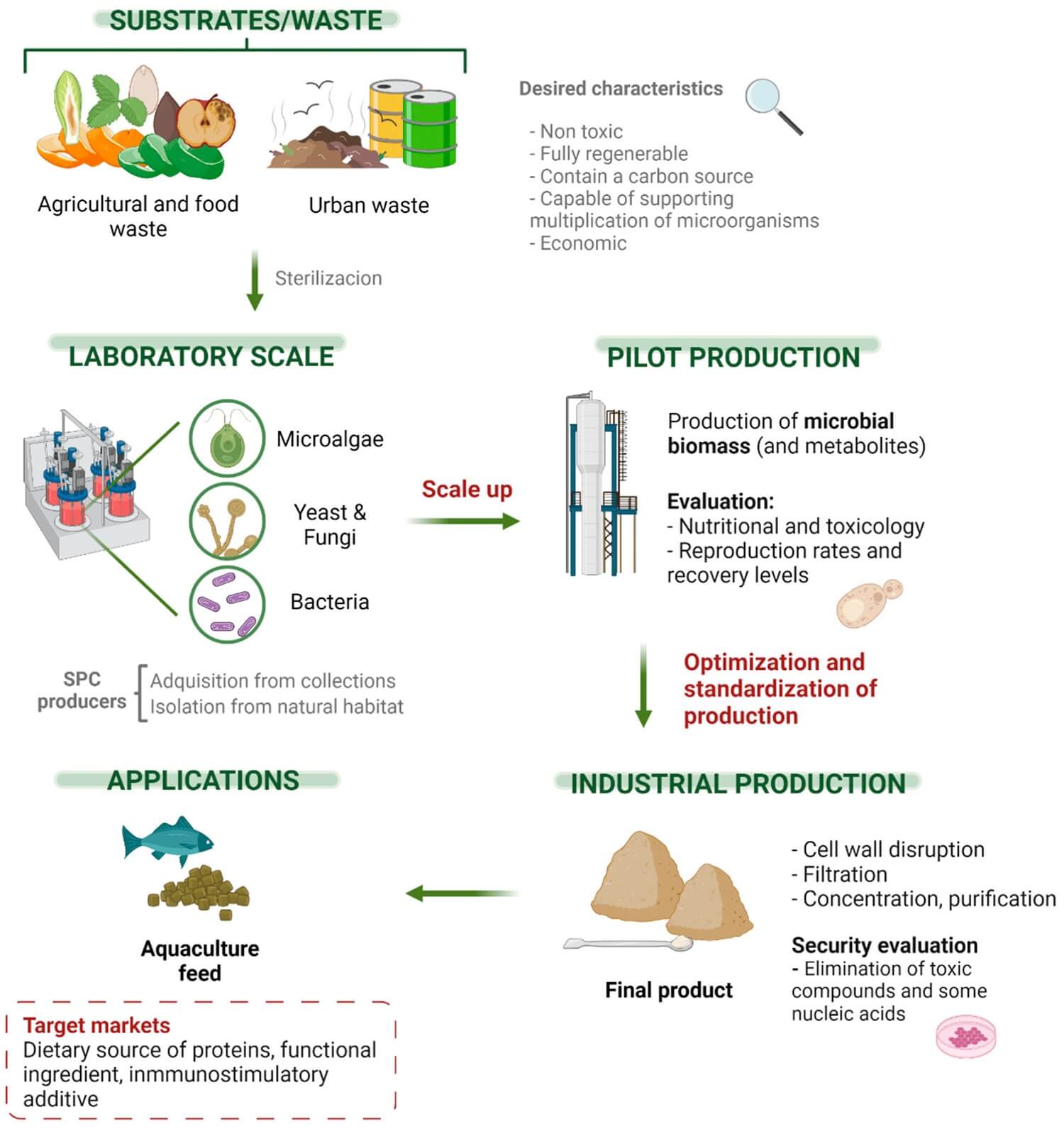
Interactions In communities – Types, Definition, Examples
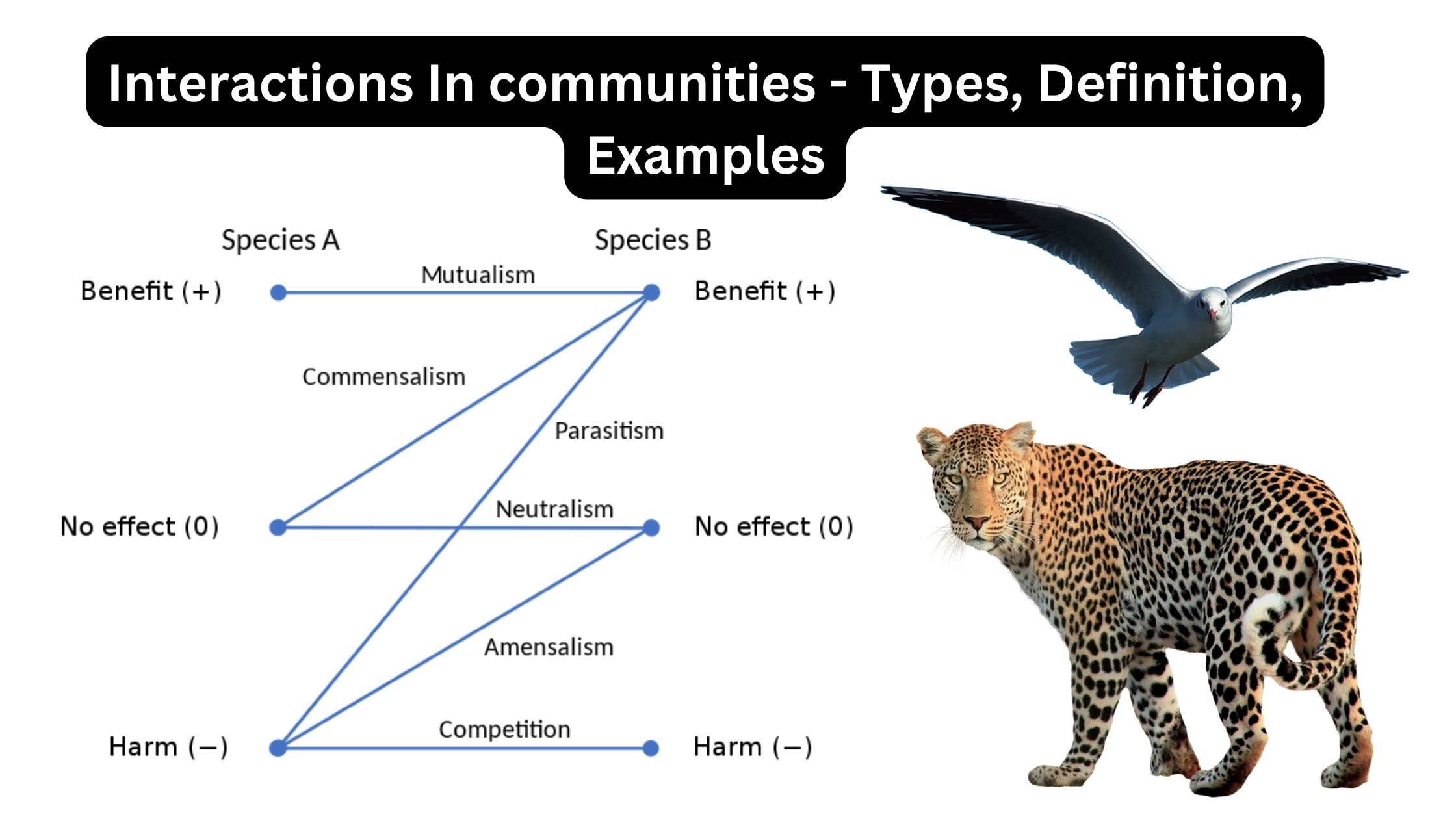
Short-term interactions 1. Predation Example of Predation 2. Pollination Example of Pollination 3. Seed dispersal Example of Seed dispersal Symbiosis: long-term interactions Mutualism, commensalism, parasitism, neutralism, amensalism, and competition are the six forms of symbiosis. These are distinguished by the extent to which they benefit or hurt each partner. 1. Competition Example of Competition 2. … Read more