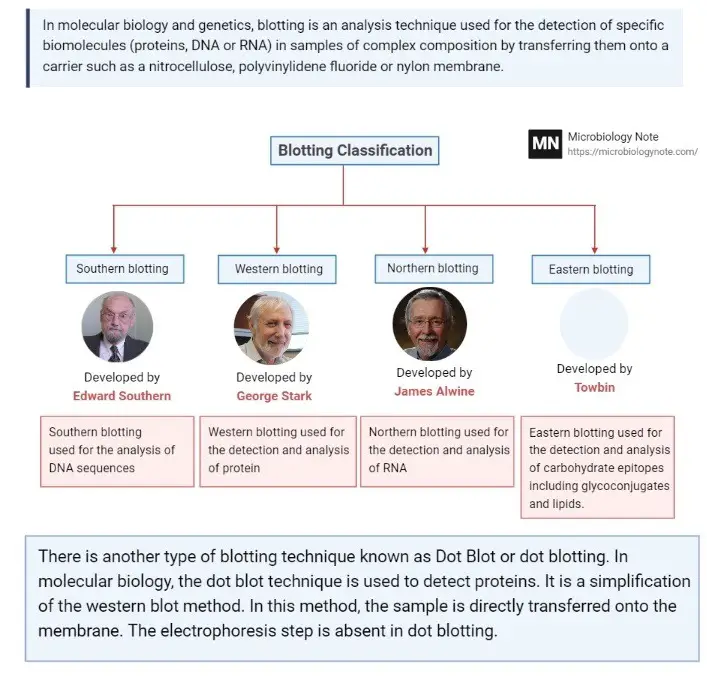
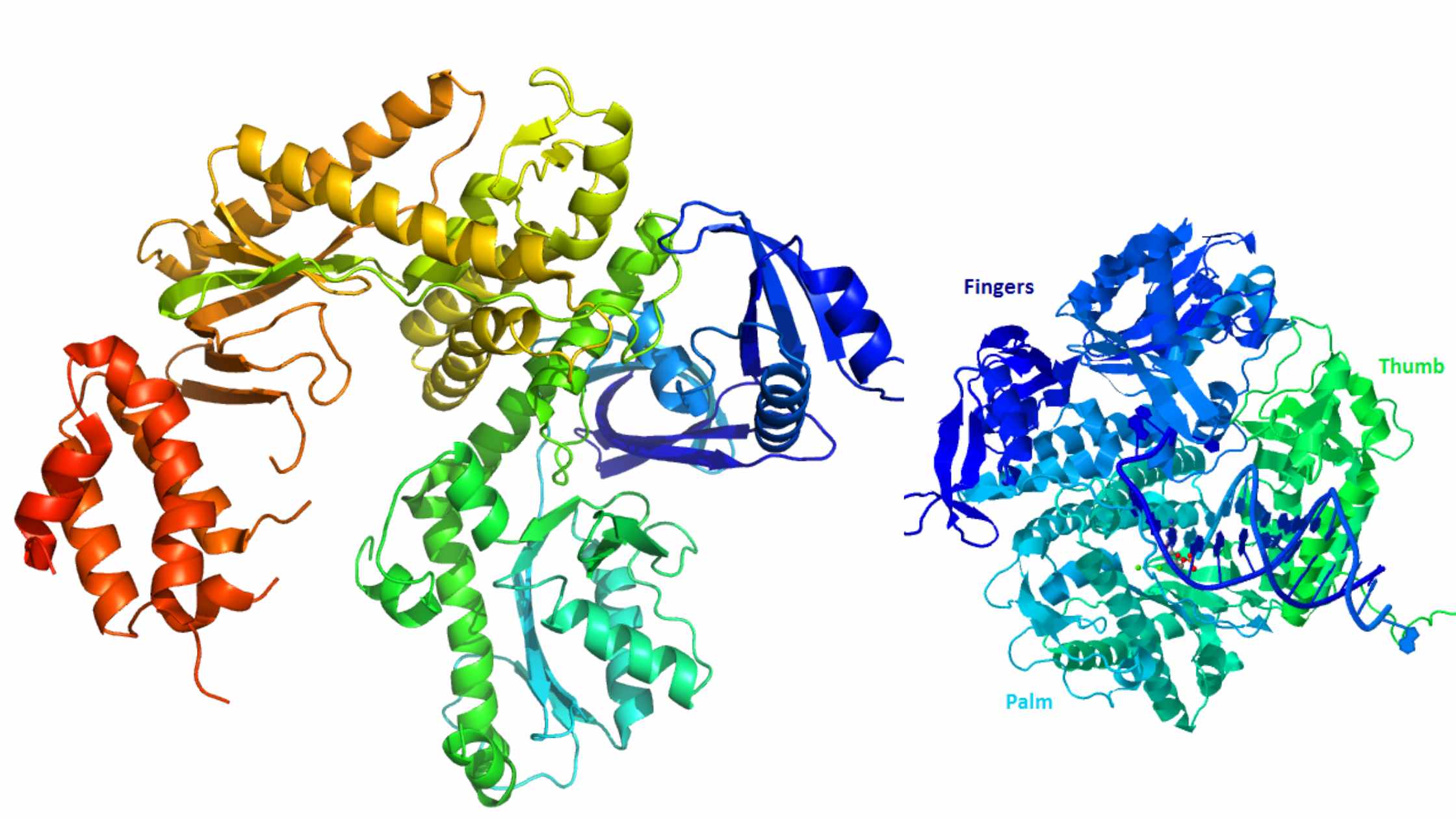
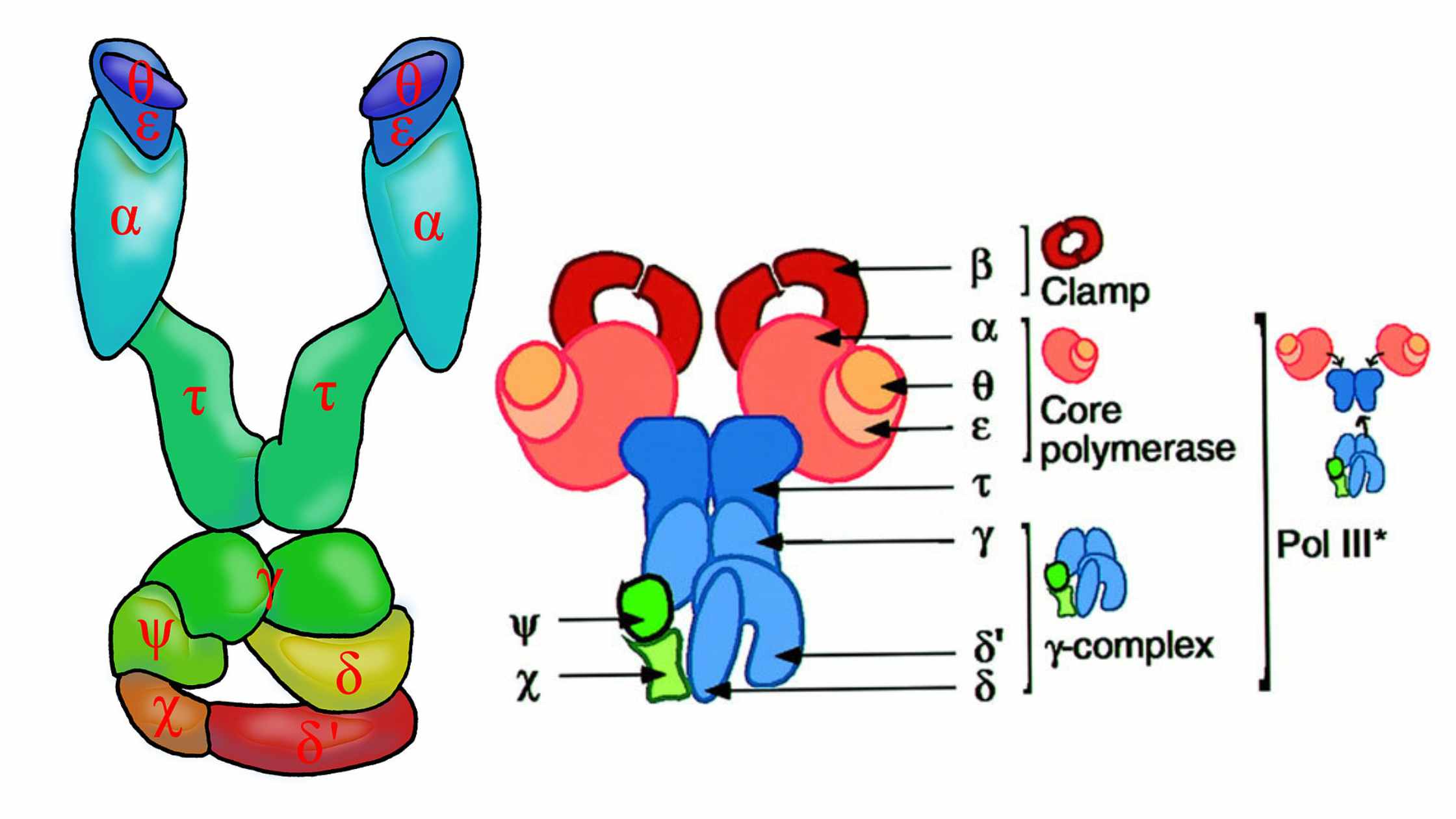
Transcription In Prokaryotes – Definition, Stages, Significance
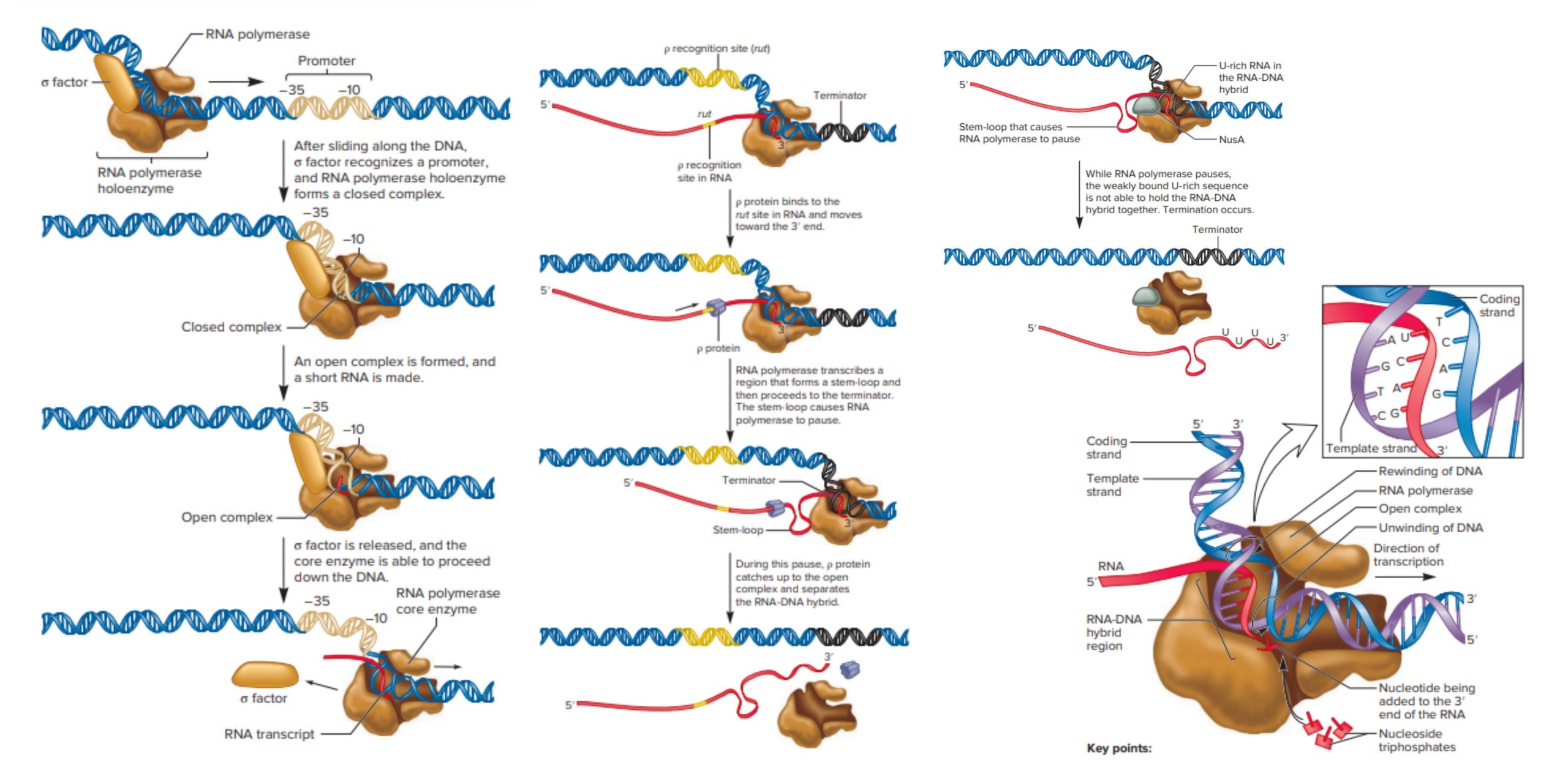
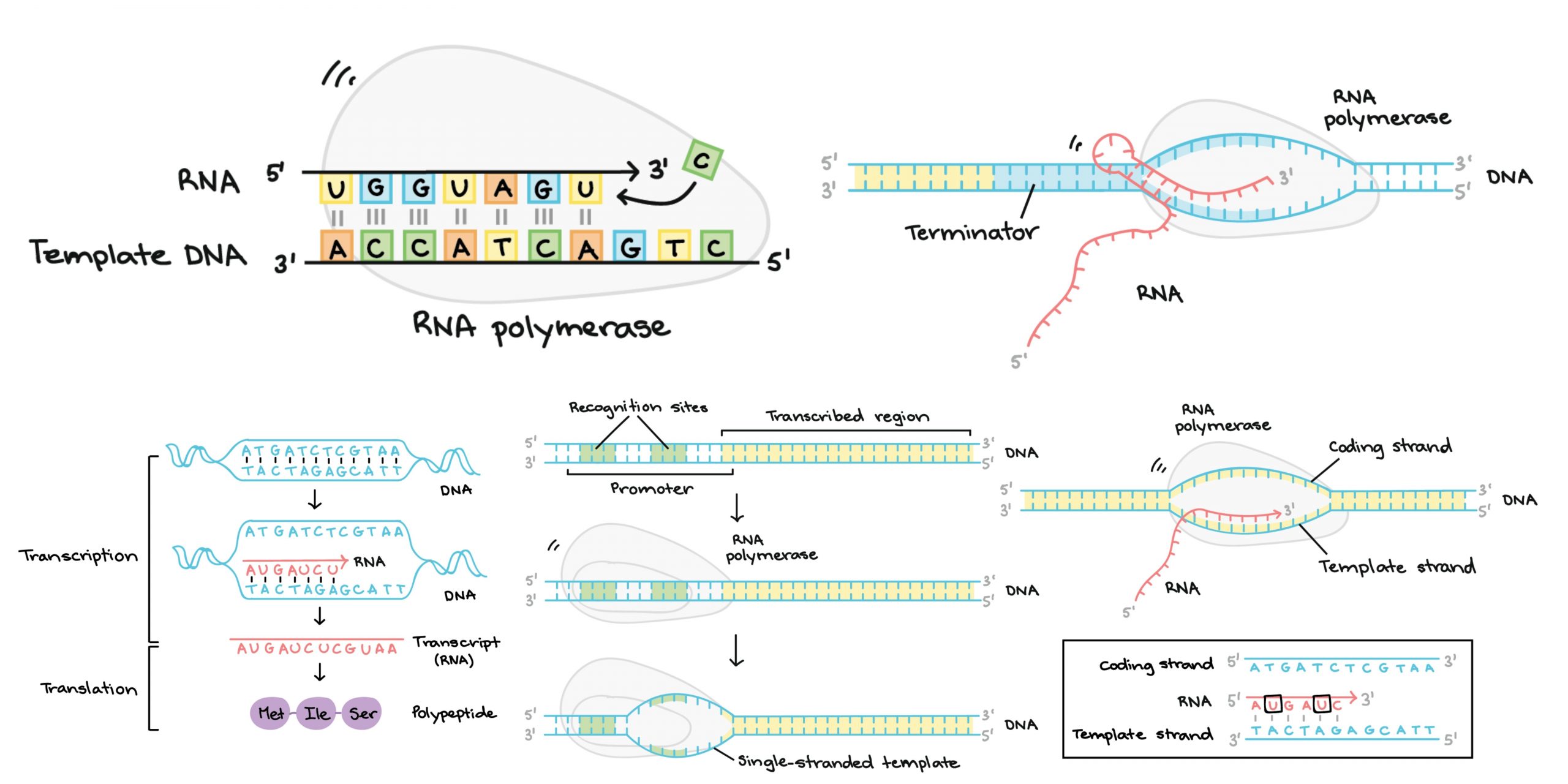
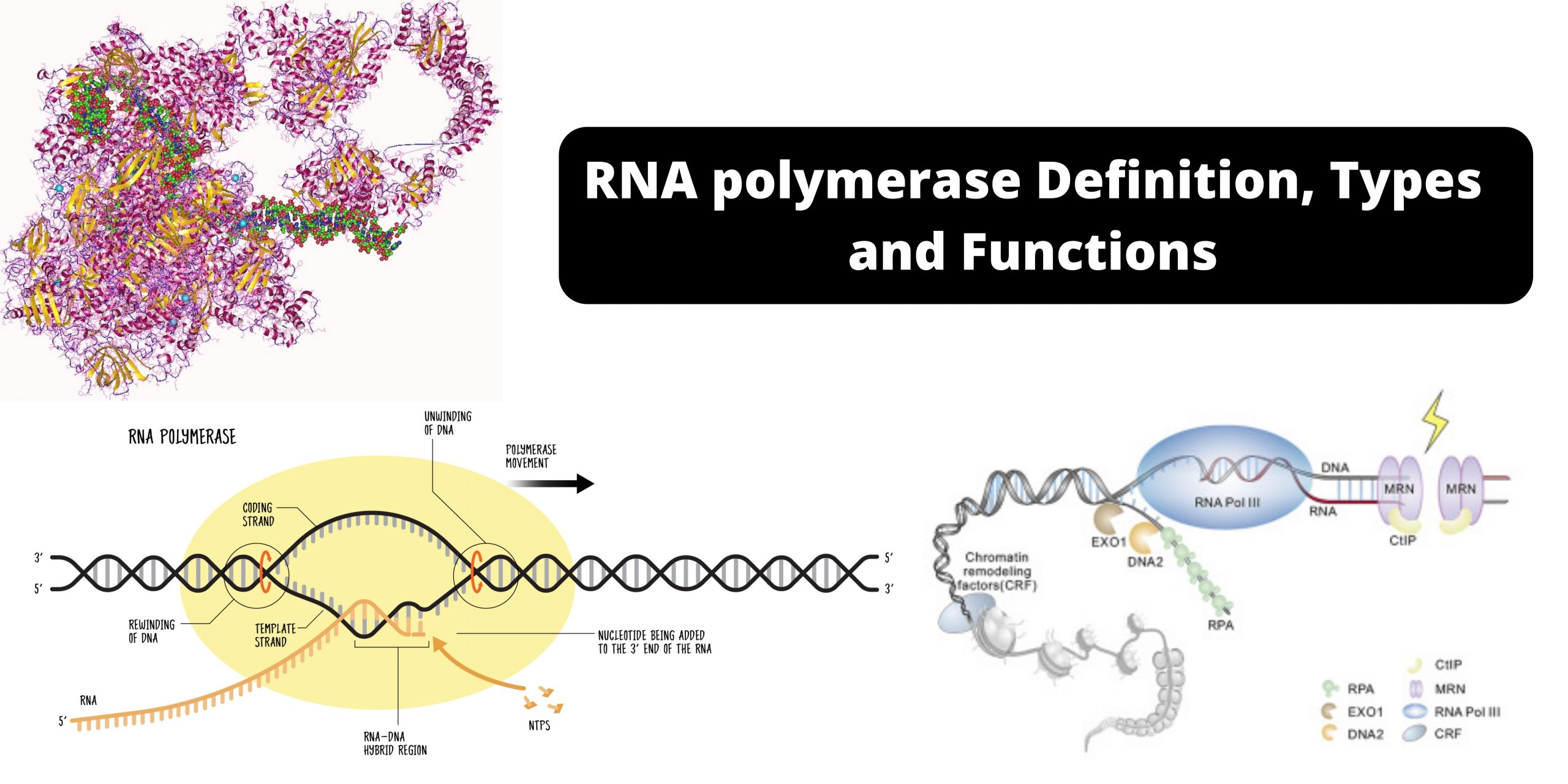
Transcription refers to the process in which the information contained in the DNA strand is transformed into a new messenger RNA molecule (mRNA). In prokaryotic cells, transcription occurs in three stages called the initiation, the elongation, and the termination.