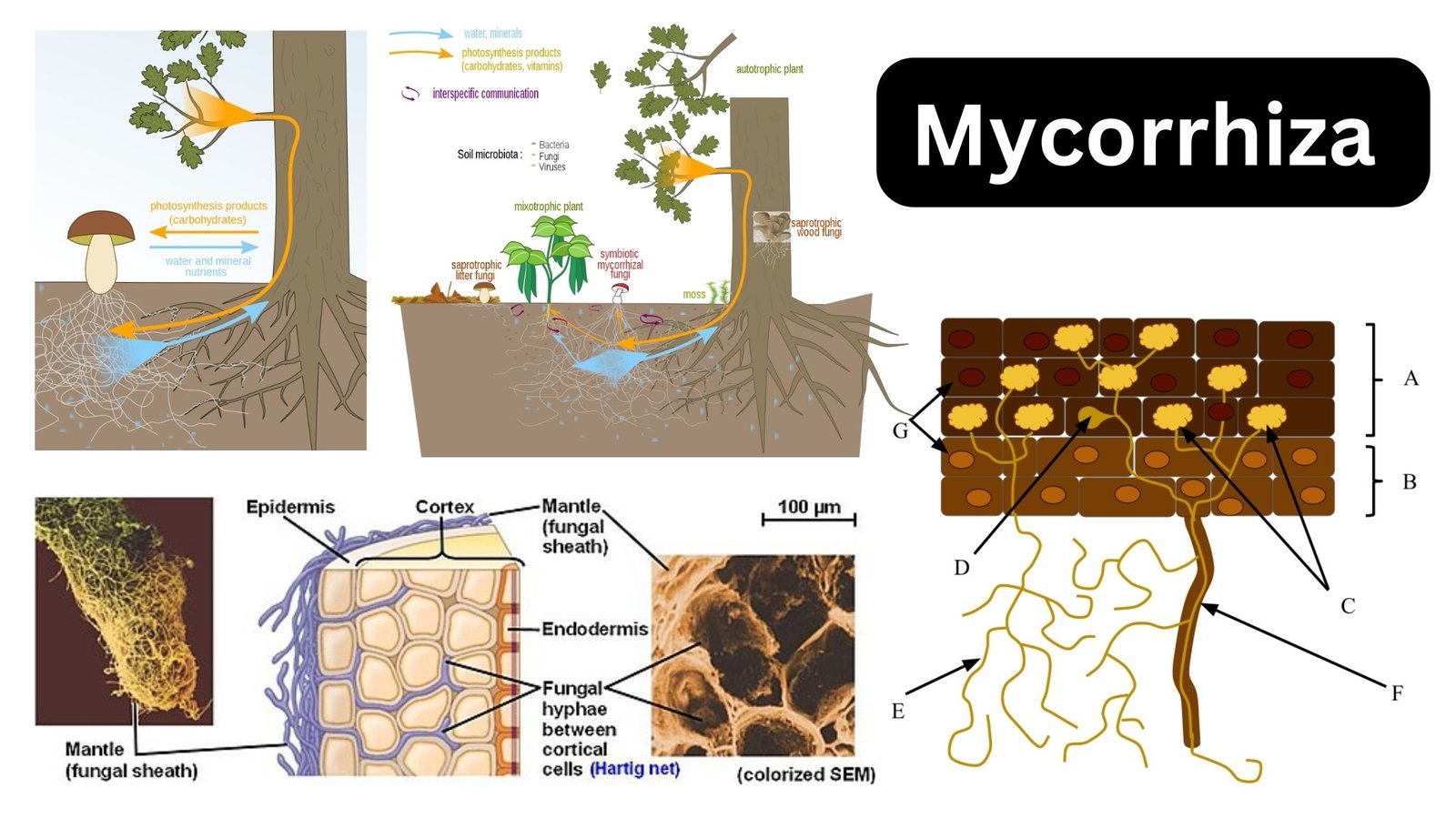
Mycorrhiza – Definition, Types, Examples, Importance
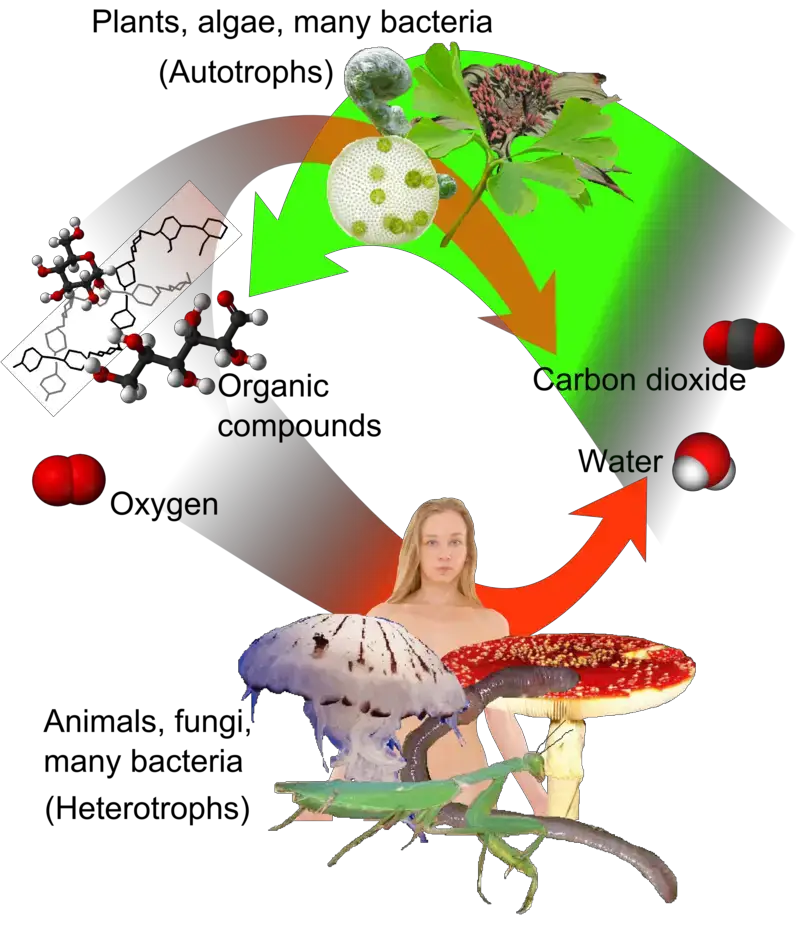
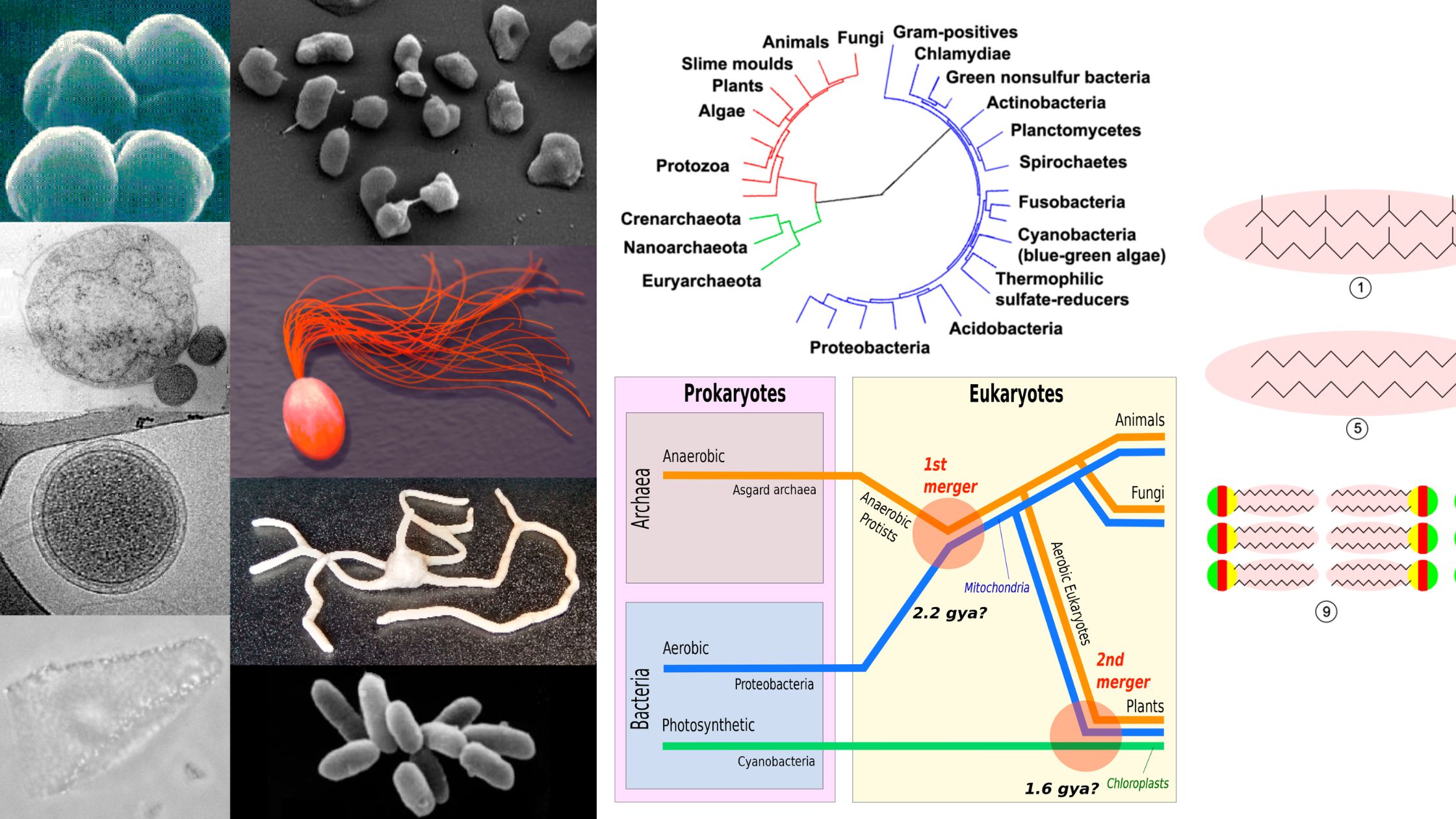
What is Mycorrhiza? Definition of Mycorrhiza Mycorrhiza refers to the symbiotic association between specific fungi and plant roots, where the fungus aids in nutrient and water uptake for the plant, and in return, the plant provides the fungus with essential nutrients produced through photosynthesis. Types of Mycorrhizae Mycorrhizae represent diverse symbiotic associations between fungi and … Read more