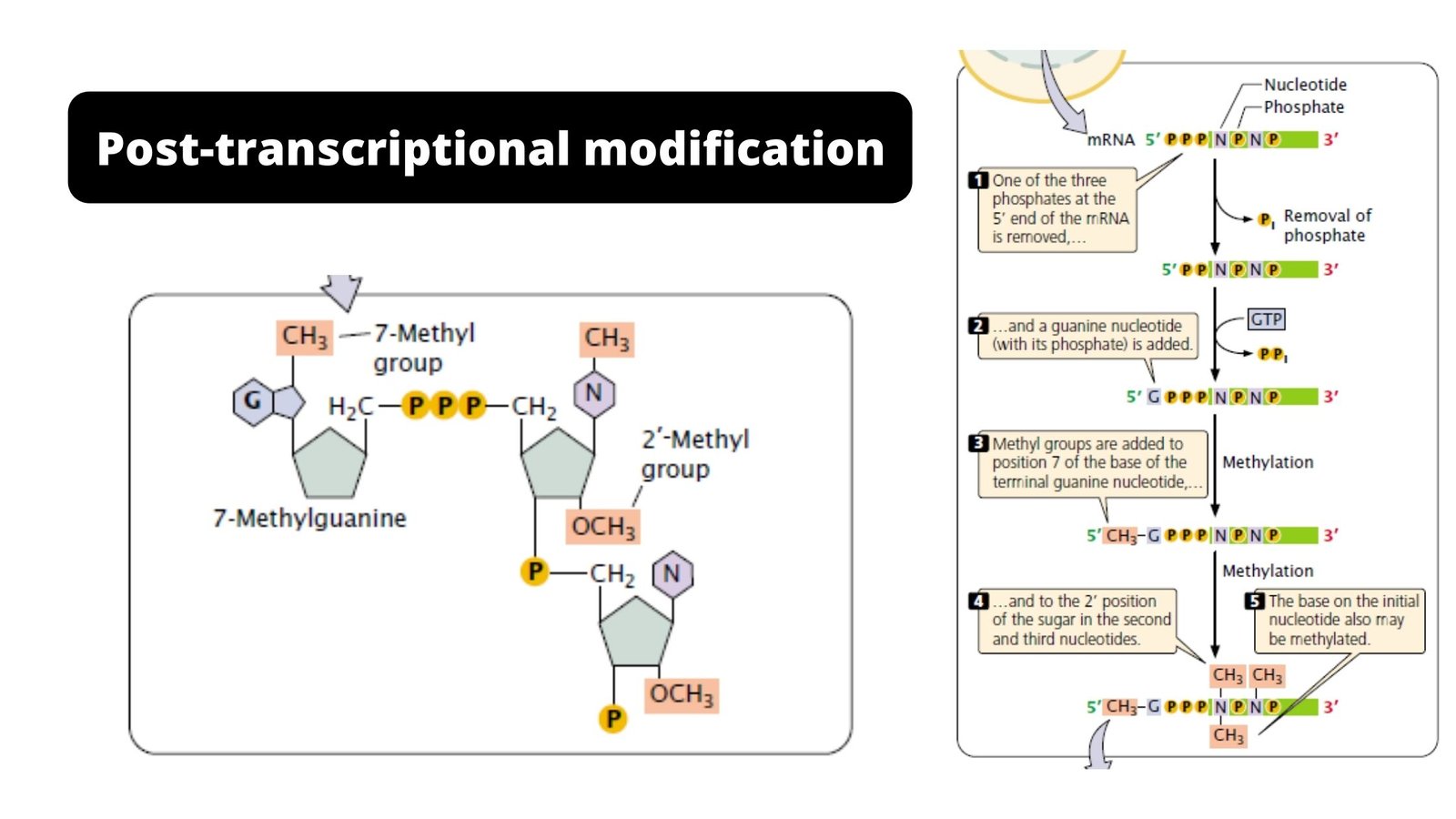
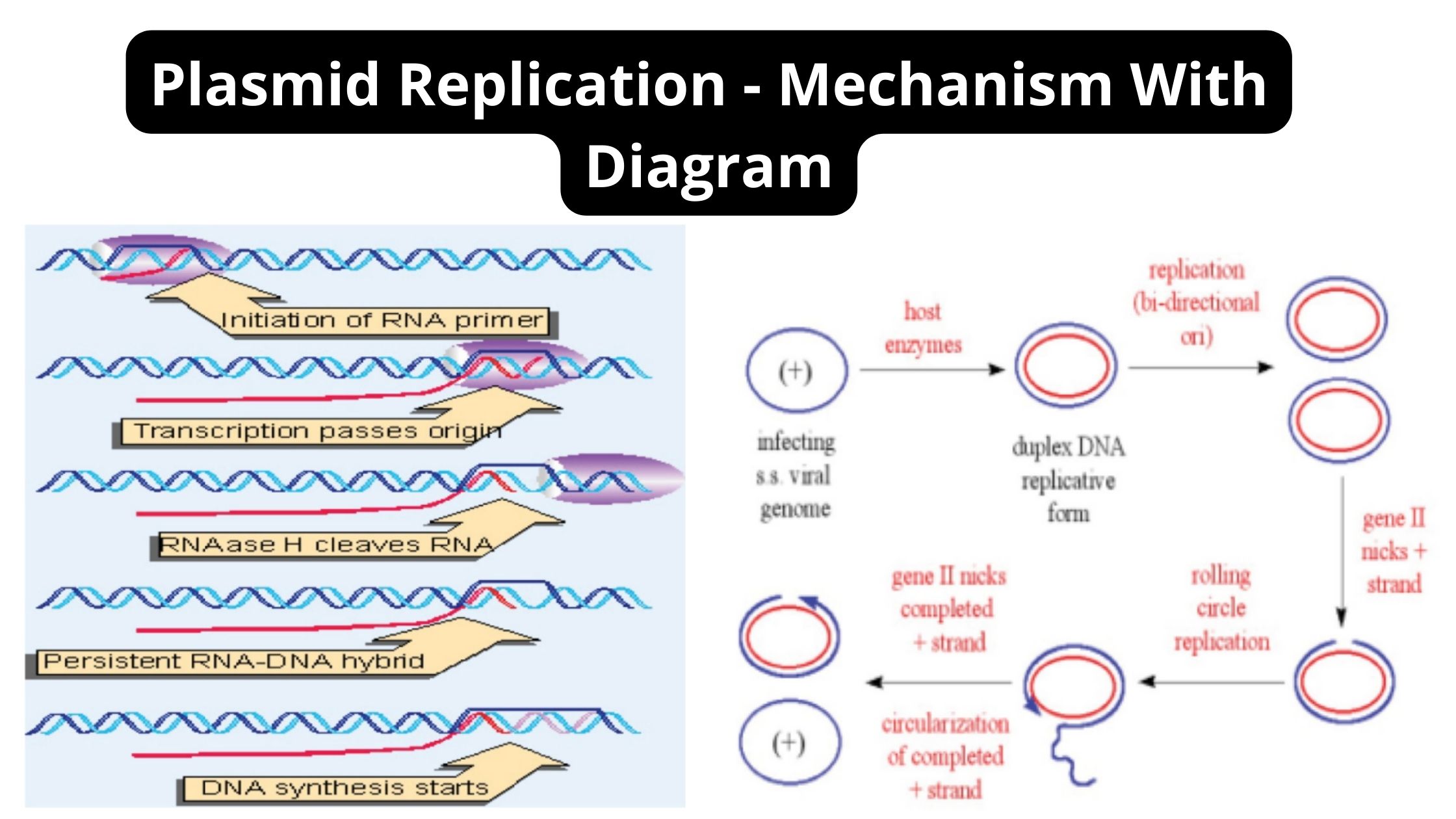
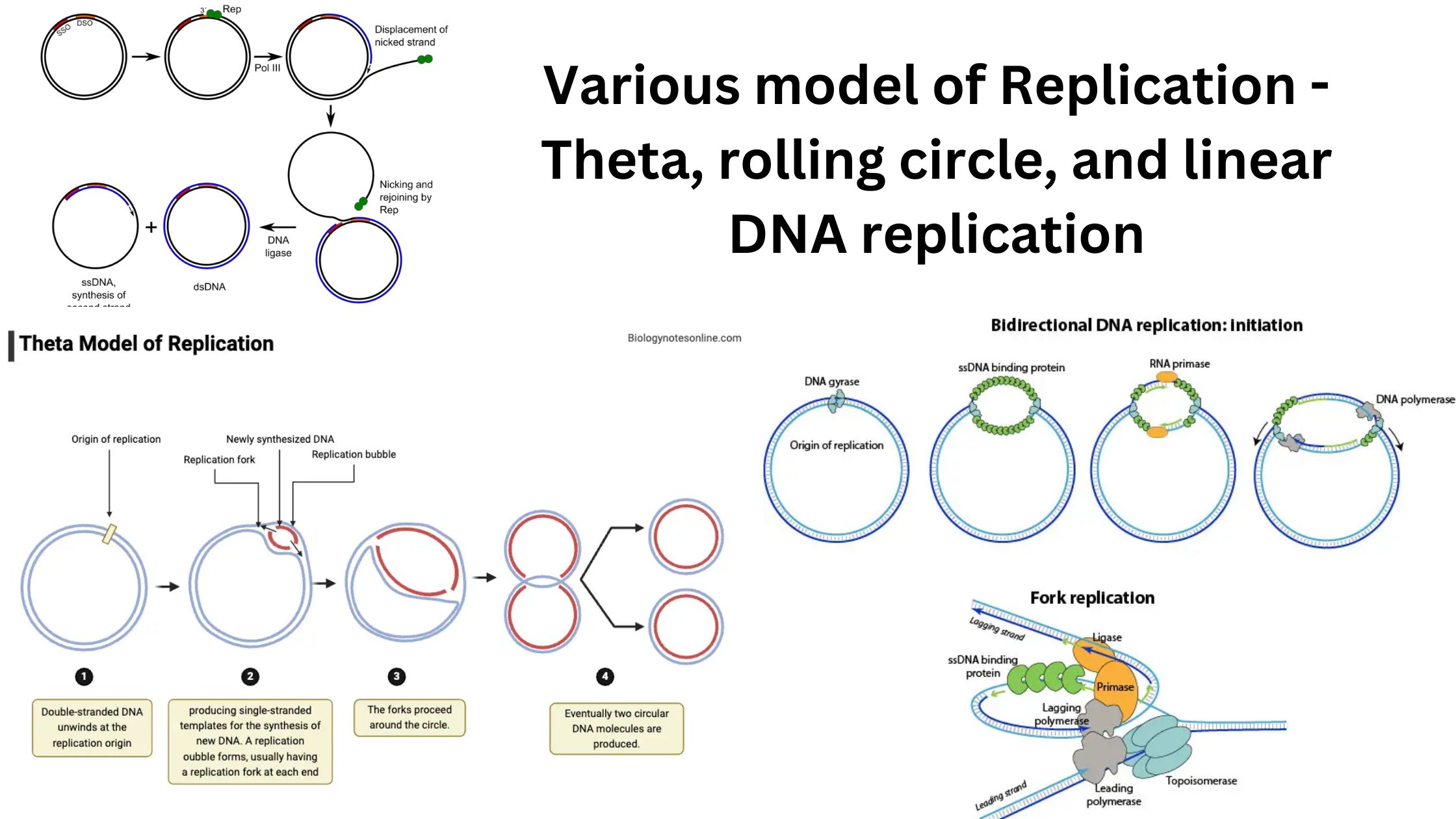
Post-transcriptional Modification – Definition, Types, Process, Importance
Post-transcriptional modification is a set of biological processes common to most eukaryotic cells by which an primary RNA transcript is chemically altered following transcription from a gene to produce a mature, functional RNA molecule that can then leave the nucleus and perform any of a variety of different functions in the cell.