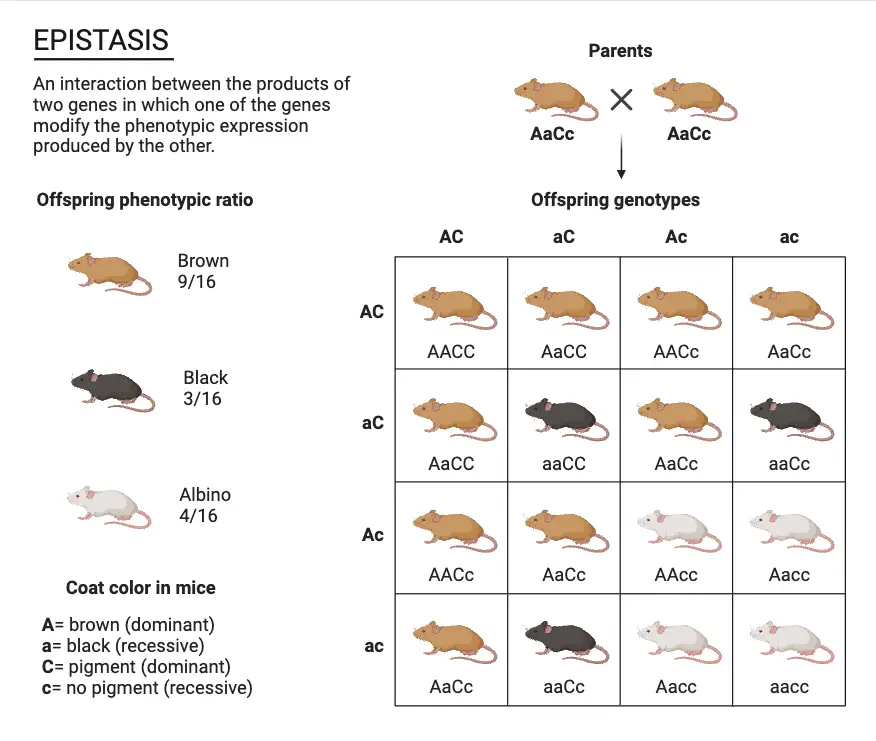
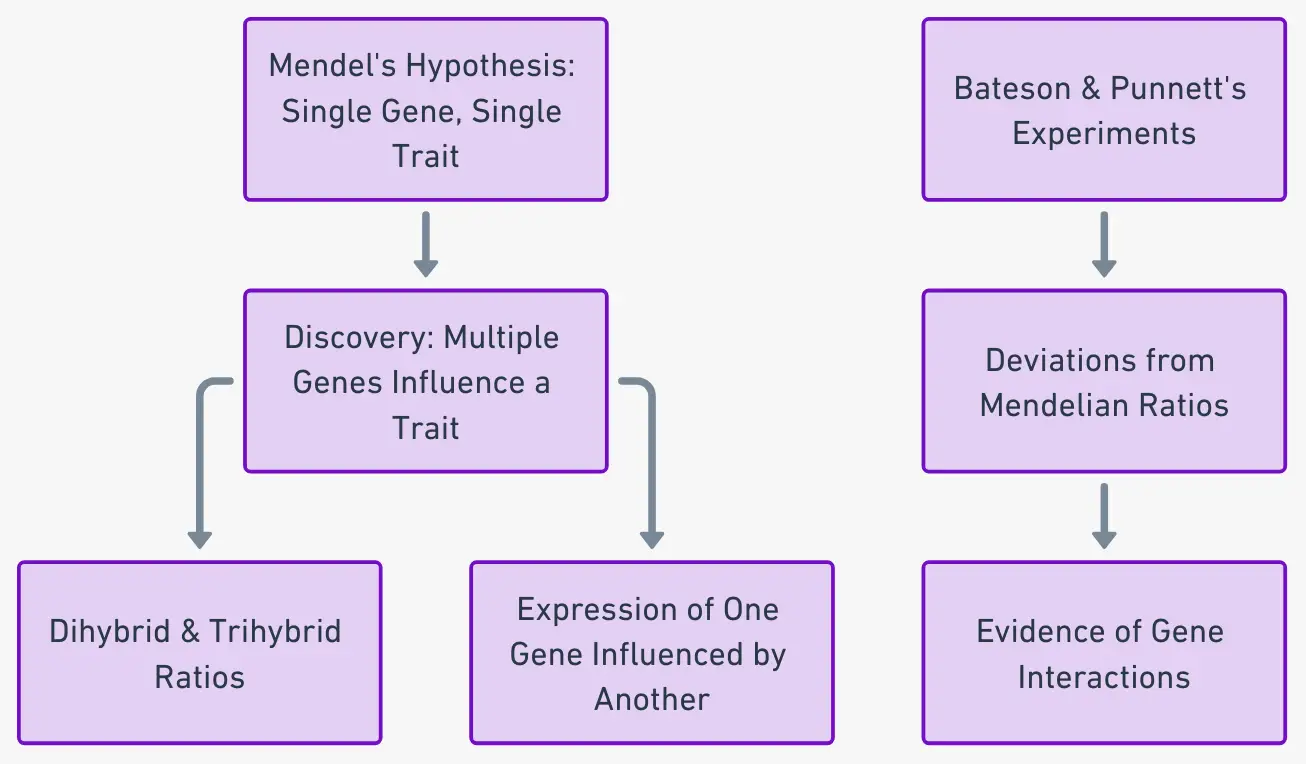
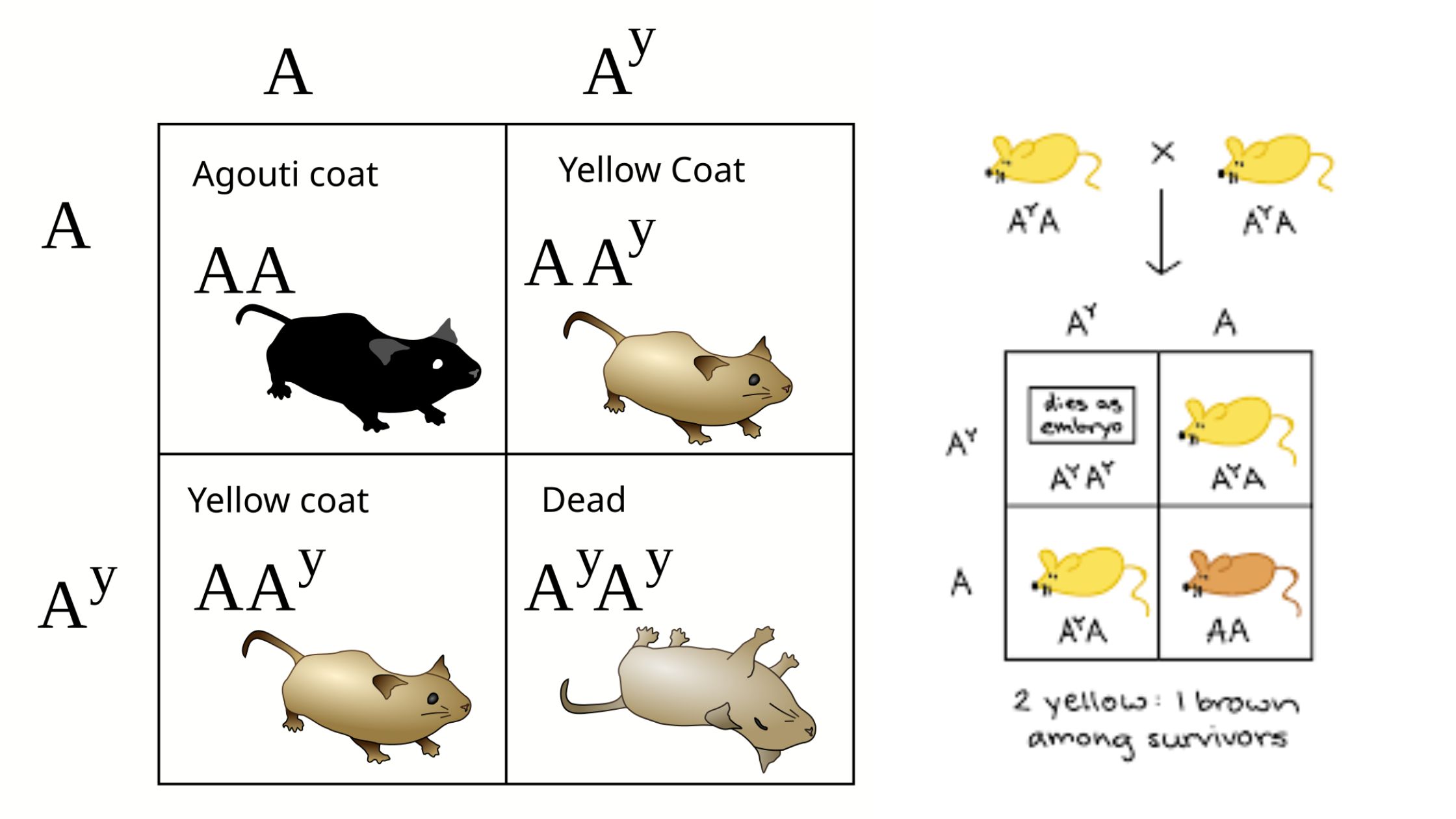
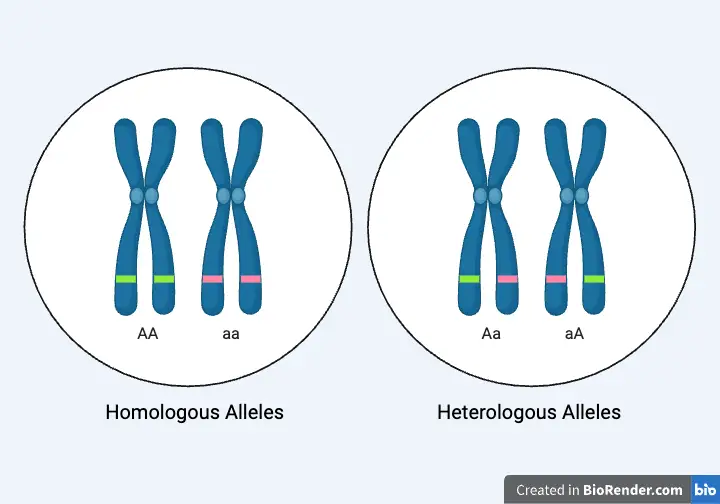
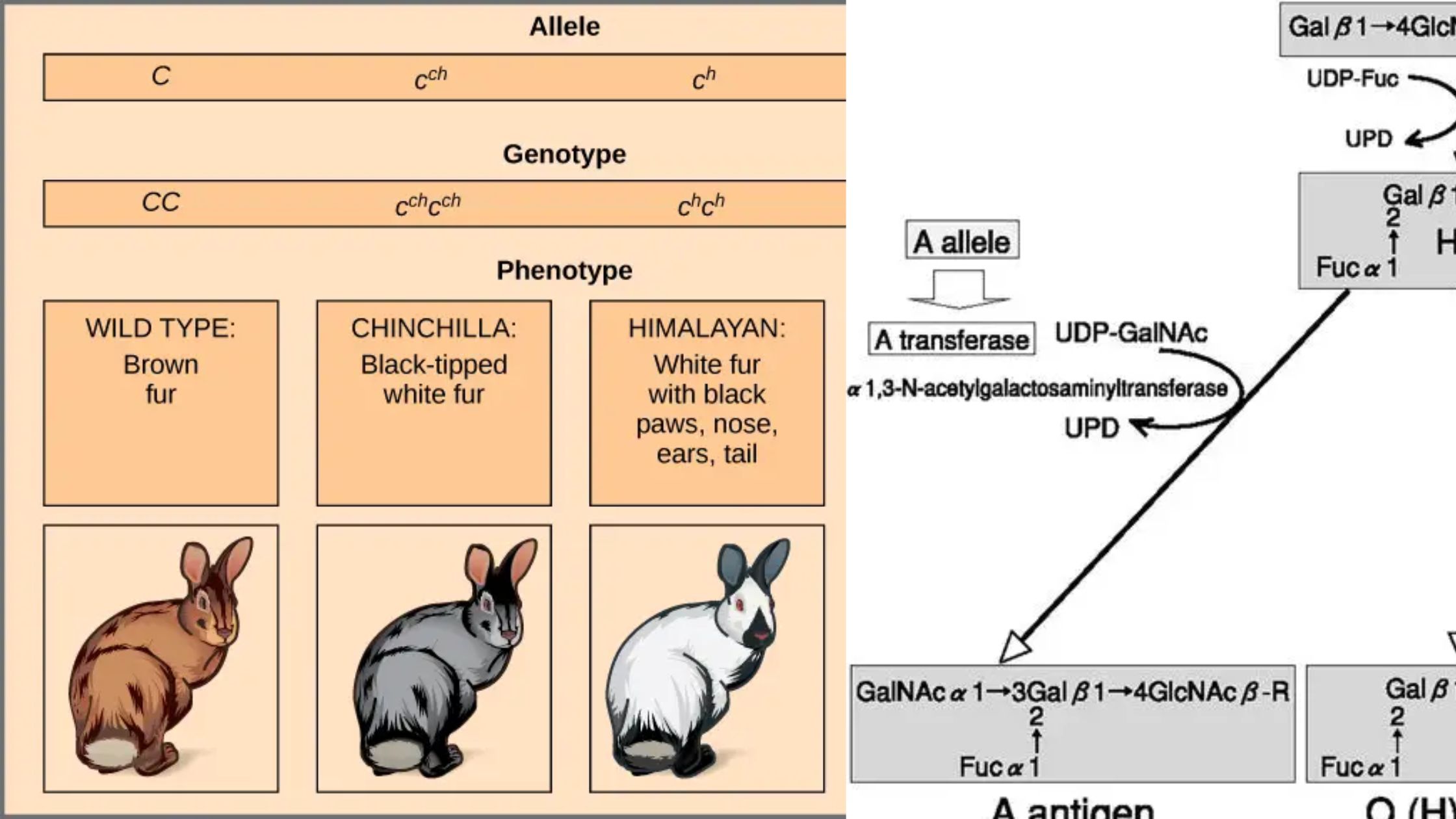
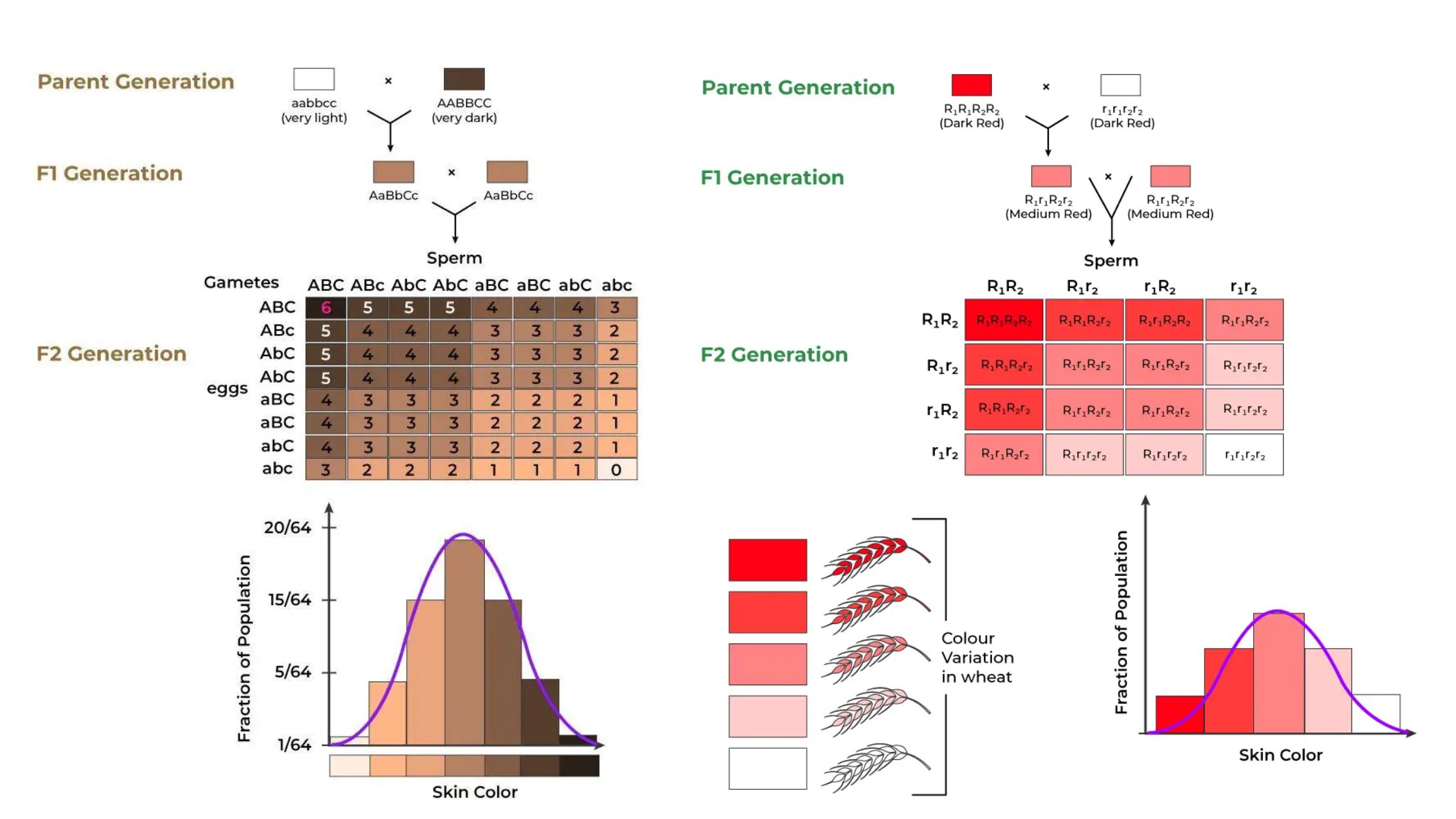
Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance
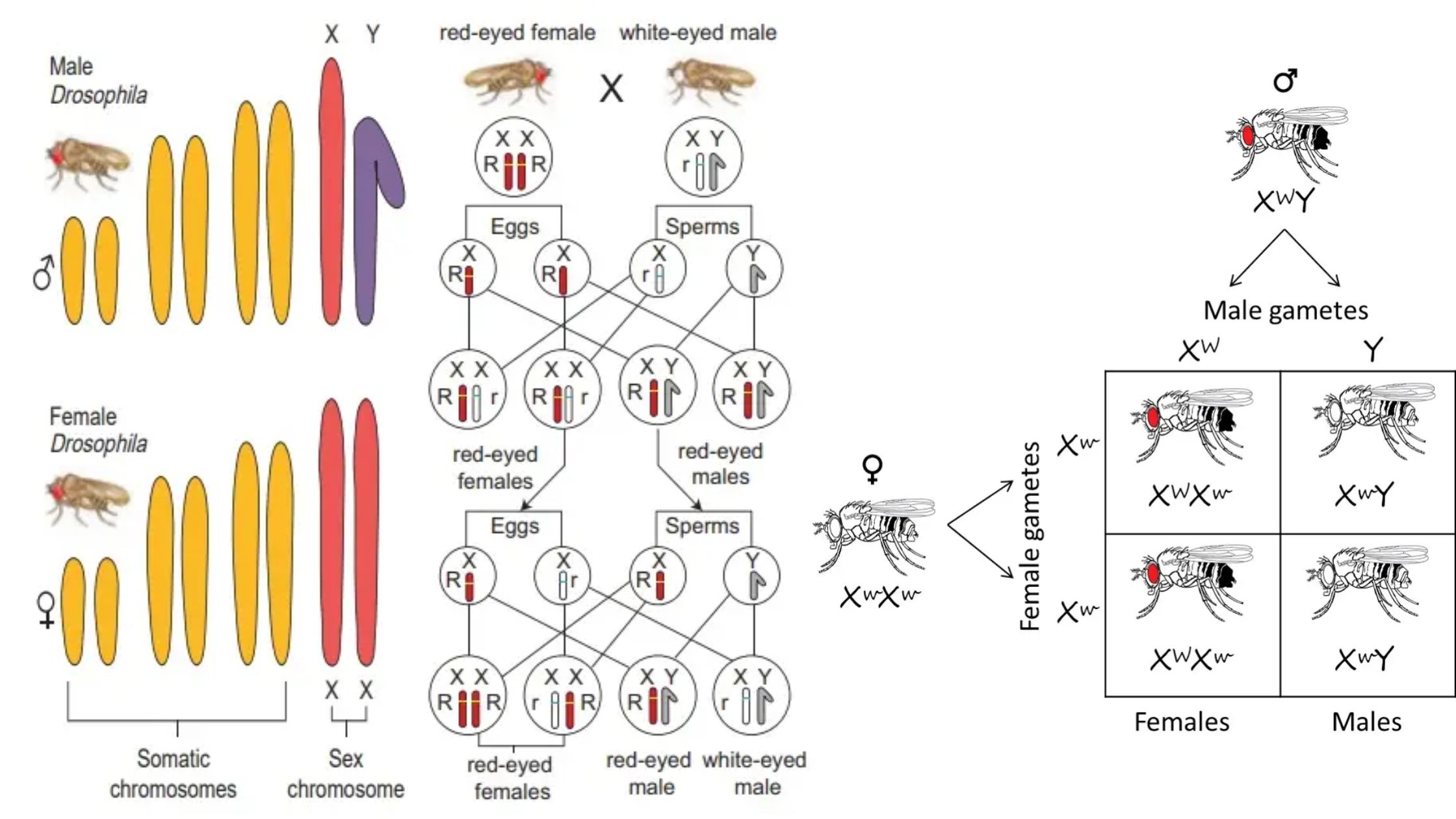
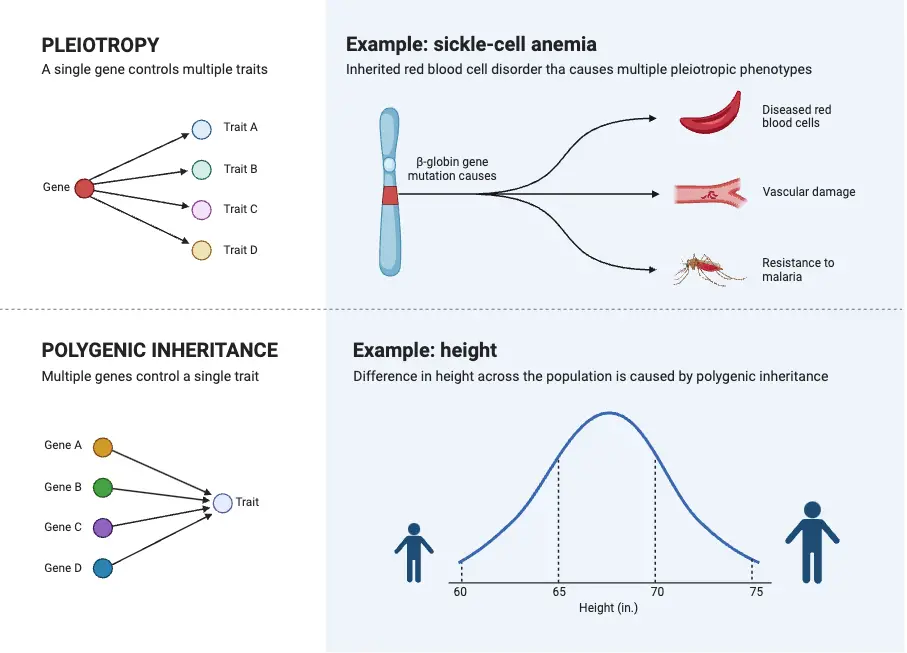
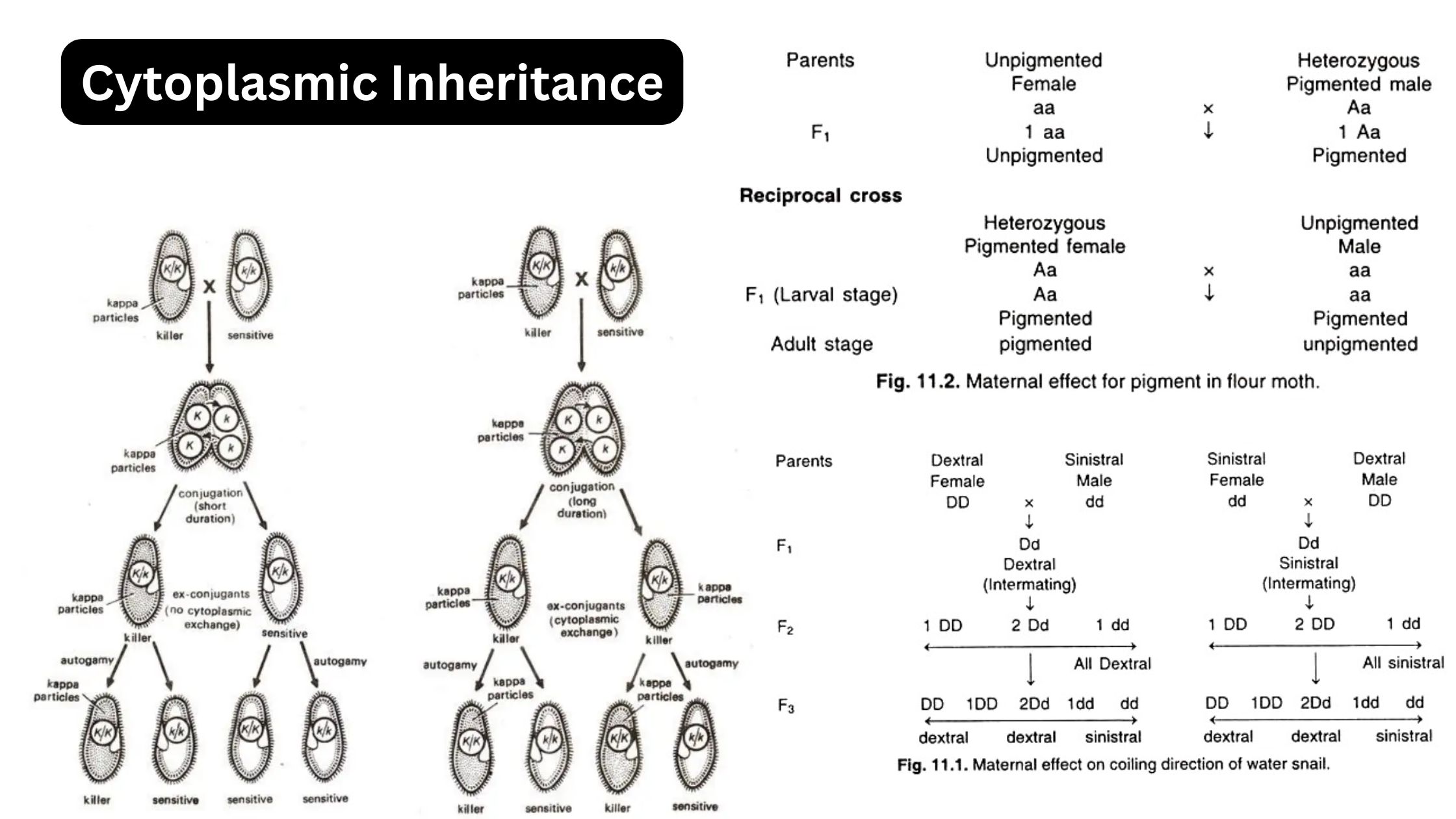
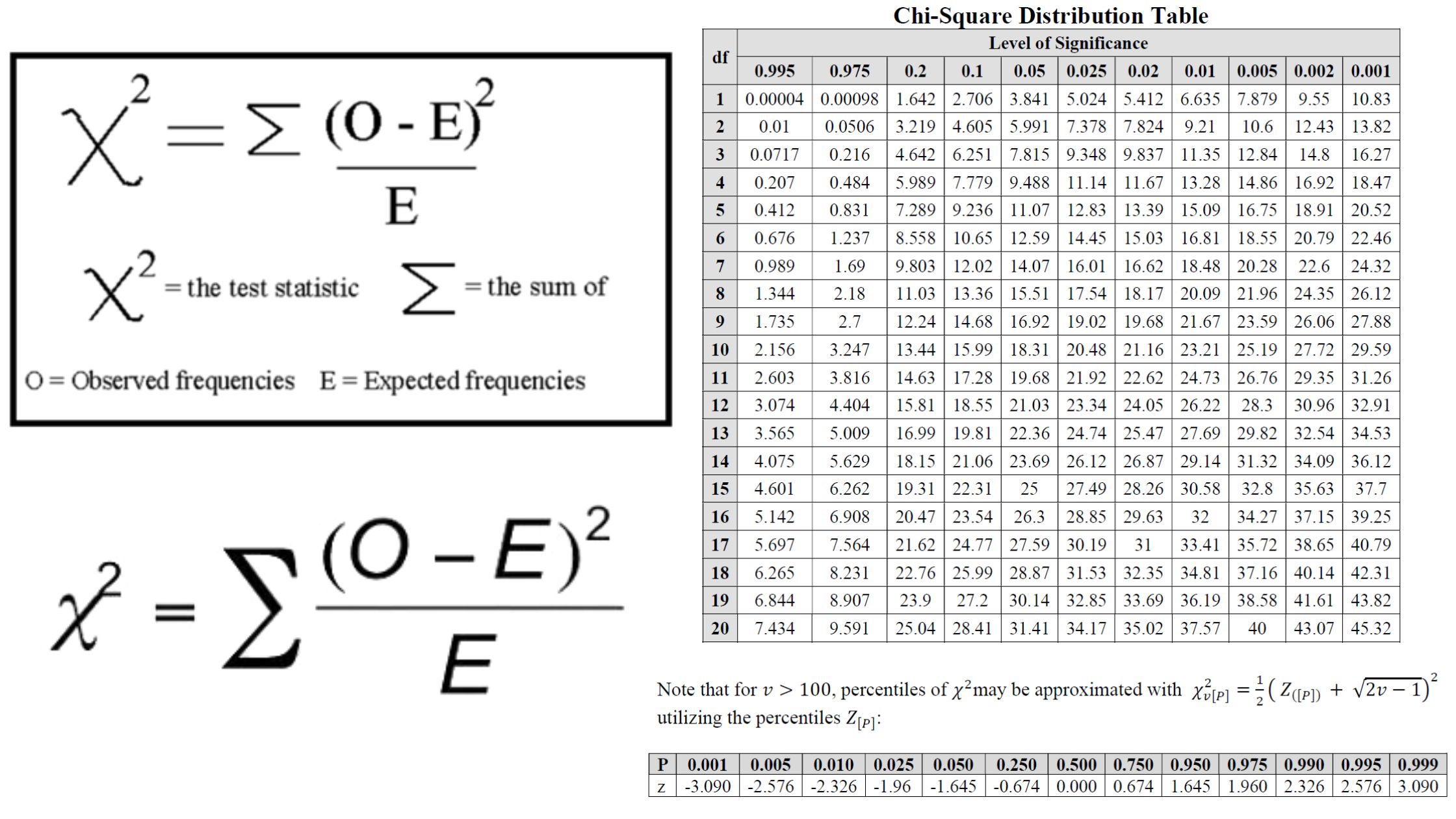
What is Chromosome? What is Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance? Observations of Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance The Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance provided a clear link between the behavior of chromosomes and Mendel’s laws of inheritance. It was supported by a series of critical observations that connected chromosomal behavior during meiosis with the inheritance patterns Mendel described. … Read more