Sphaeroplasts – Definition, Formation, Applications
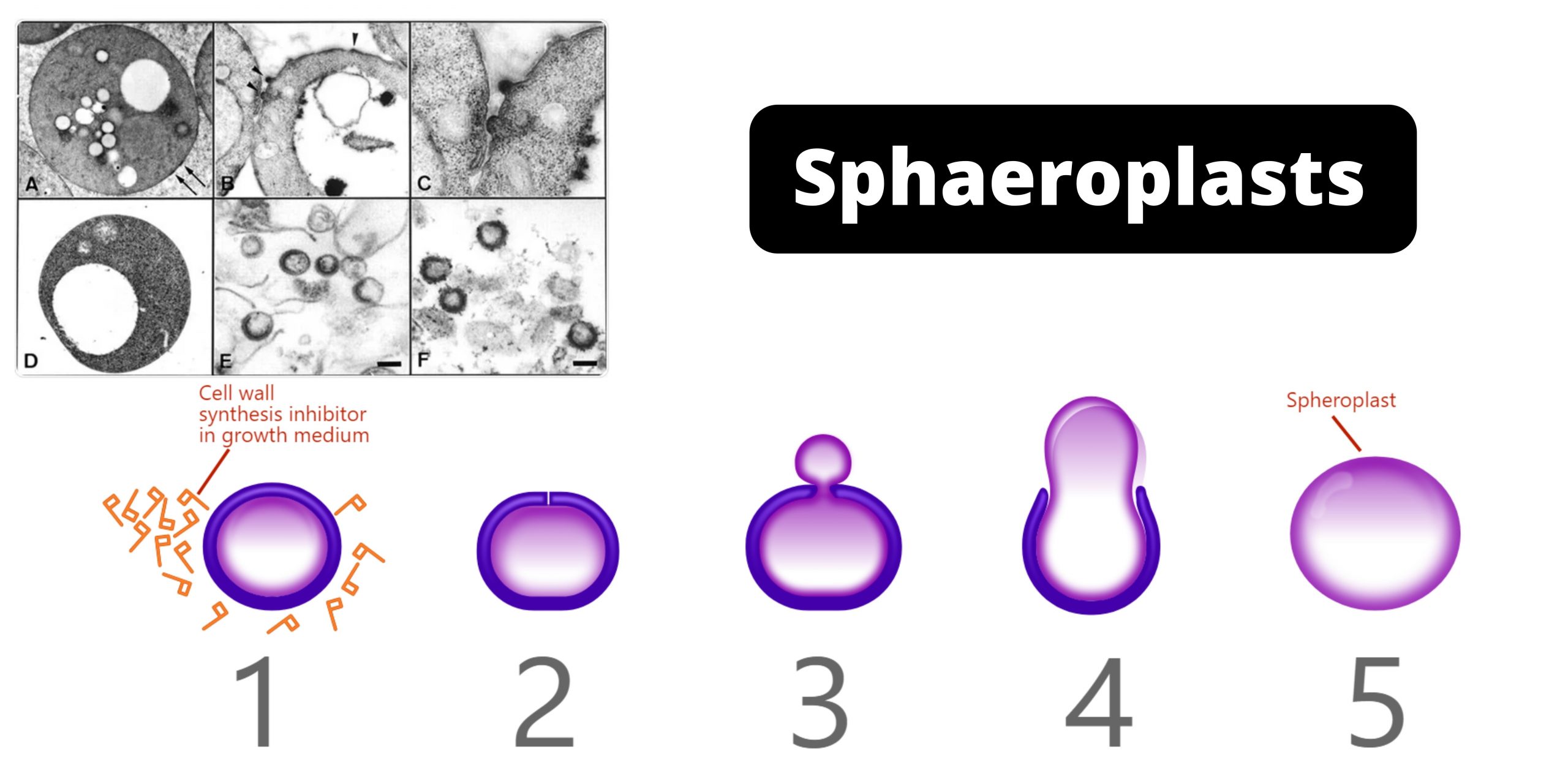
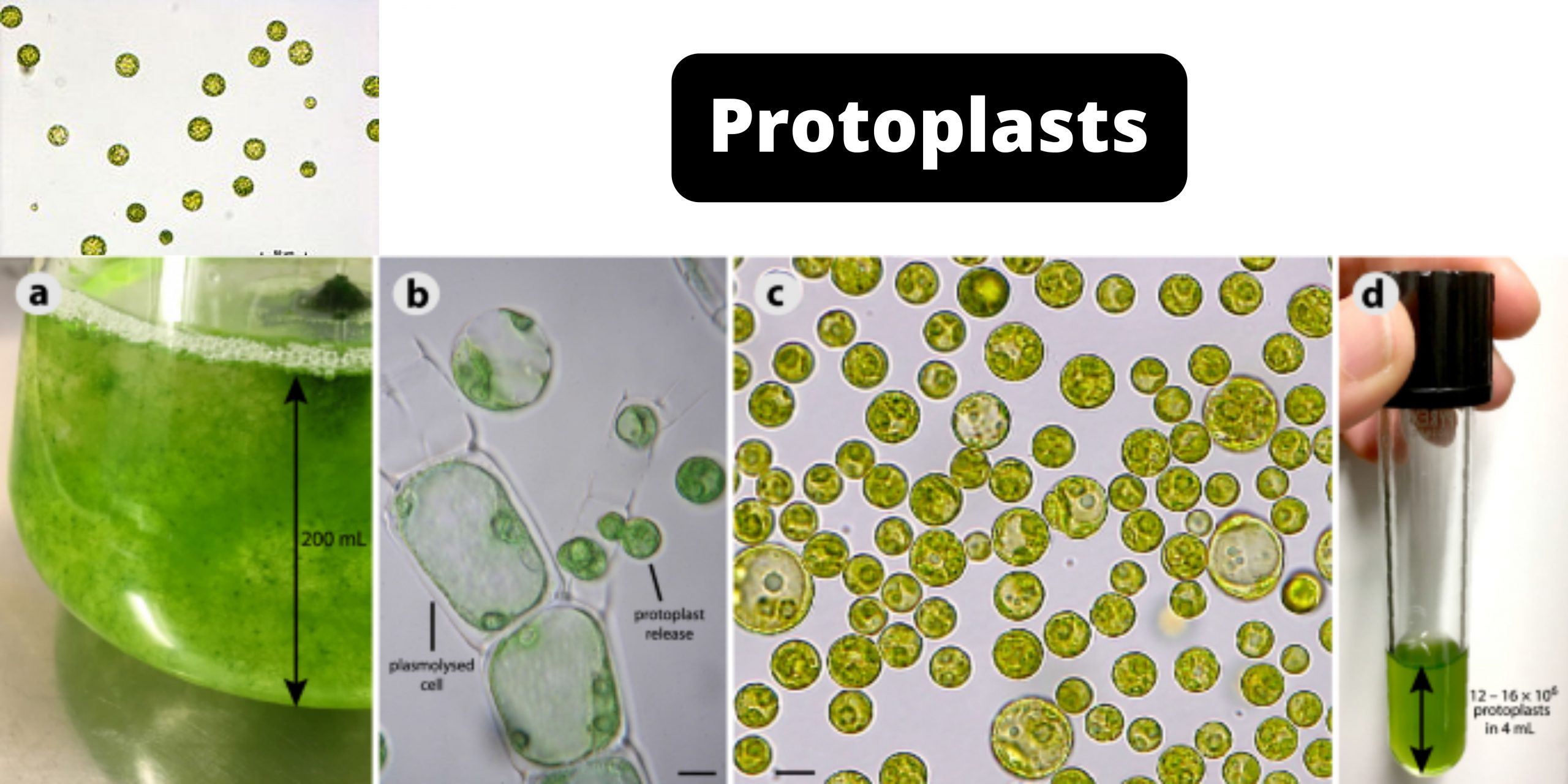
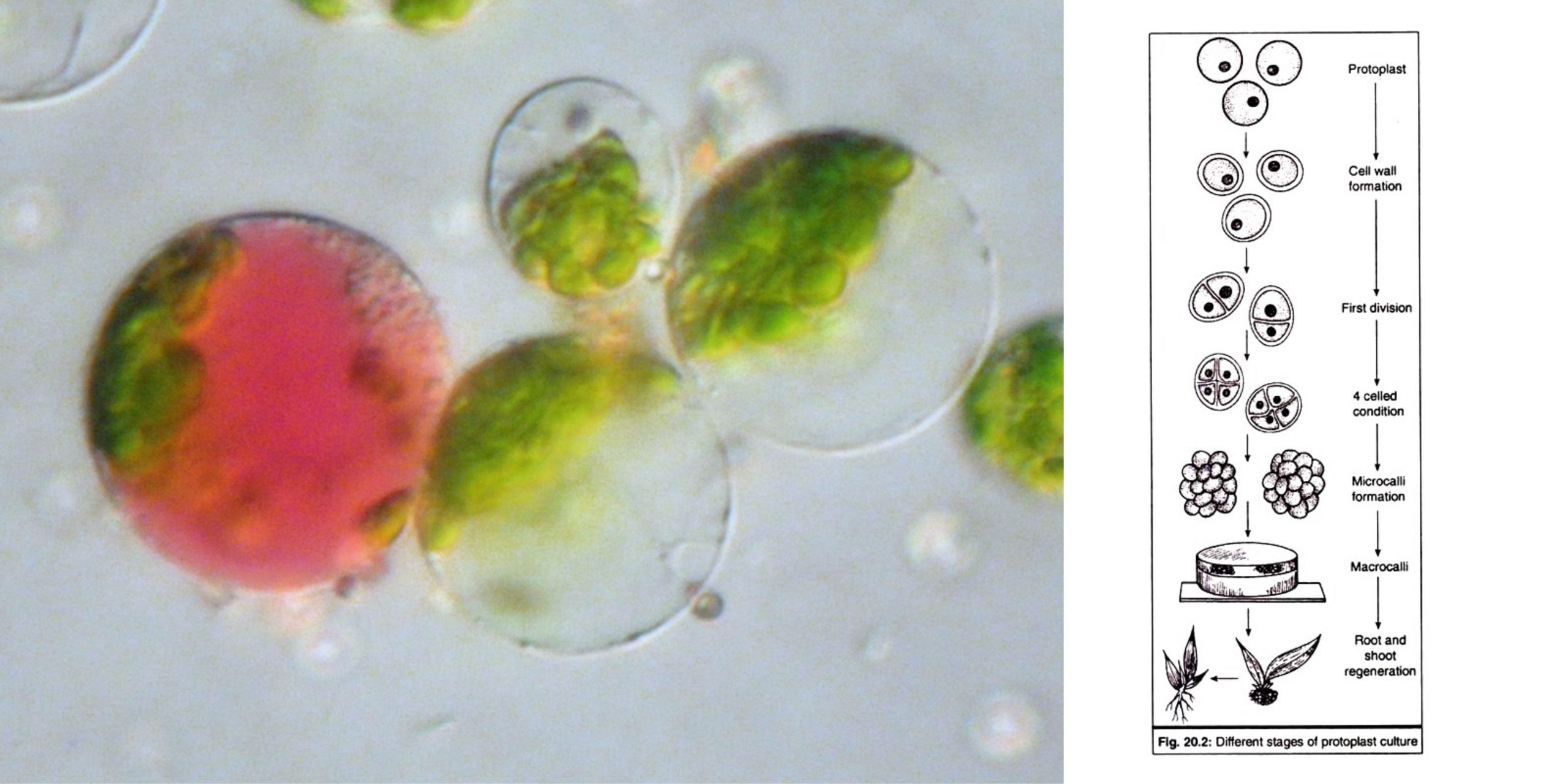
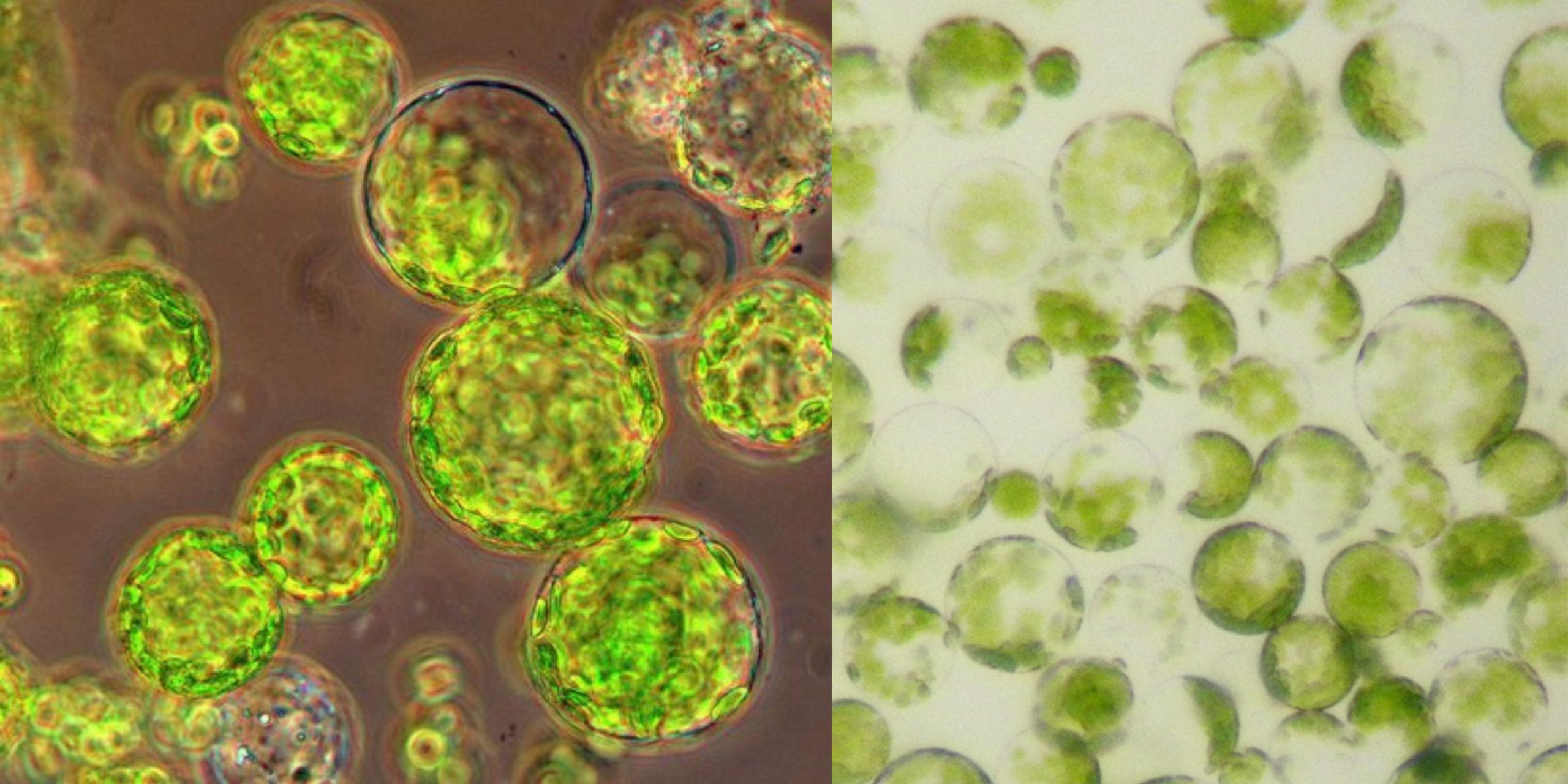
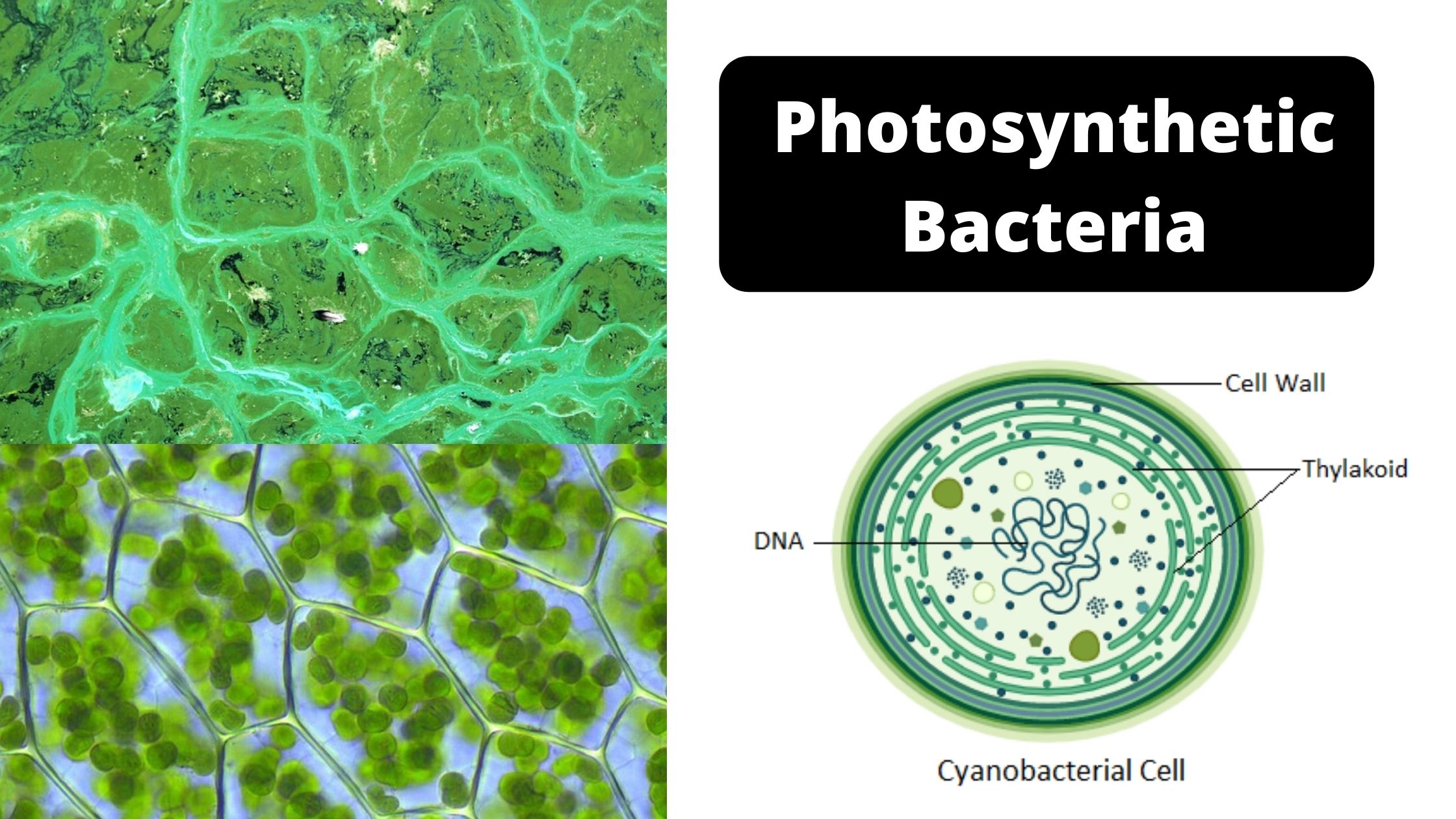
What is Sphaeroplast? A Spheroplast (or sphaeroplast according to British use) can be described as a microbe organism with a cell wall that is almost entirely gone through the penicillin or Lysozyme. According to certain definitions the term is employed to refer to Gram-negative bacteria. In other definitions, the word also includes yeasts. Spheroplast’s name … Read more