Before learning about plant tissue culture, first you have to learn about tissue culture and its importance. So, lets jump to the main article-
What is tissue culture?
- The technique in which the tissues or cells are grown on an artificial medium separate from the parent organism is known as tissue culture.
- An American pathologist Montrose Thomas Burrows first coined the term “tissue culture”.
- This technique helps to culture the whole plants and were first created from nutrient solutions.
- The tissue culture technique is also known as micropropagation.
- Liquid, semi-solid, or solid growth medium, such as broth or agar are used to facilitate the tissue culture technique.
- For the animals, this technique is also known as the culture of animal cells and tissues and for the plants, it is known as plant tissue culture.
- In contemporary usage, “tissue culture” usually relates to the extension of cells from a tissue of a multicellular organism in vitro.
- A donor organism (primary cells) or an immortalized cell line provides these cells.
- The cells are immersed in a culture medium, which includes vital nutrients and energy reservoirs essential for the cells’ survival.
- Hence, in its deeper reason, “tissue culture” is frequently used mutually with “cell culture”. On the other hand, the austere definition of “tissue culture” relates to the culturing of tissue parts, i.e. explant culture.
- Example: Some examples of tissue culture media are the root culture medium of White and the callus culture medium of Gautheret. White’s medium was based on Uspenski and Uspenska’s medium for algae, whereas the Gautheret’s medium was based on Knop’s salt solution
Plant tissue culture Definition
Plant tissue culture is a technique that is utilized to sustain or grow plant cells, tissues, or organs in a sterile condition on a nutrient culture medium of known composition.
- The clones of plants are produced by using this method, known as micropropagation.
- Many plant cells possess the capability to reconstruct a whole plant (totipotency), this is the main fact on which the Plant tissue culture technique relies.
- In-Plant tissue culture technique a whole plant or new plant can be generated from plant cells without cell walls (protoplasts), Single cells, stems, or roots, pieces of leaves by providing the required nutrients and plant hormones.
Plant tissue culture techniques
The tissue culture is performed within aseptic conditions under the HEPA filtered air provided by a laminar flow cabinet. The plant tissue culture technique is accomplished in the following steps;
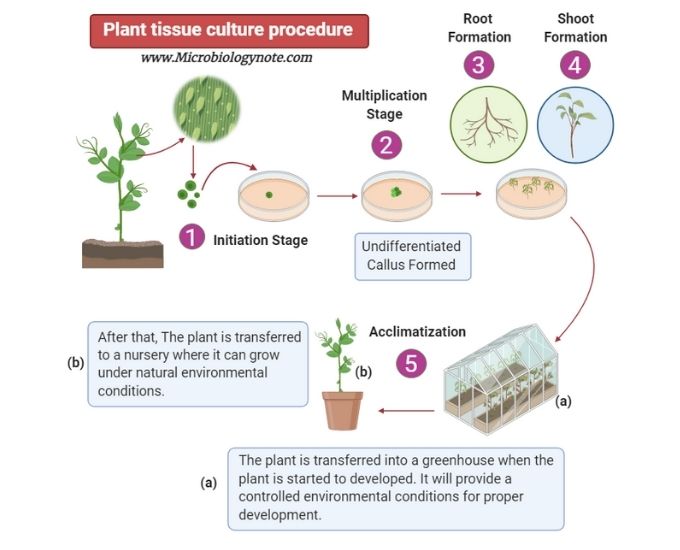
- Initiation Stage: In this step, the desired tissue is collected, added, and sterilized to hinder the method from any contamination.
- Multiplication Stage: In the second step of Plant tissue culture, the sterilized explant is included within a tissue culture medium which is constituted of growth regulators and suitable nutrients. The multiplication of cells occurs within this nutrient-rich medium. This undifferentiated portion of cells is termed as a callus.
- Formation of Root: The root formation is started. Different Plant growth hormones include initiating the development of roots.
- Formation of Shoot: The plant growth hormones are included which help in the development of shoot. The shoot formation will be observed for a week.
- Acclimatization: The plant is transferred into a greenhouse when the plant is started to develop. It will provide controlled environmental conditions for proper development. After that, the plant is sent to a nursery where it can grow under natural environmental conditions.
Types of Plant Tissue Culture Media
There are present different types of Plant Tissue Culture Media such as;
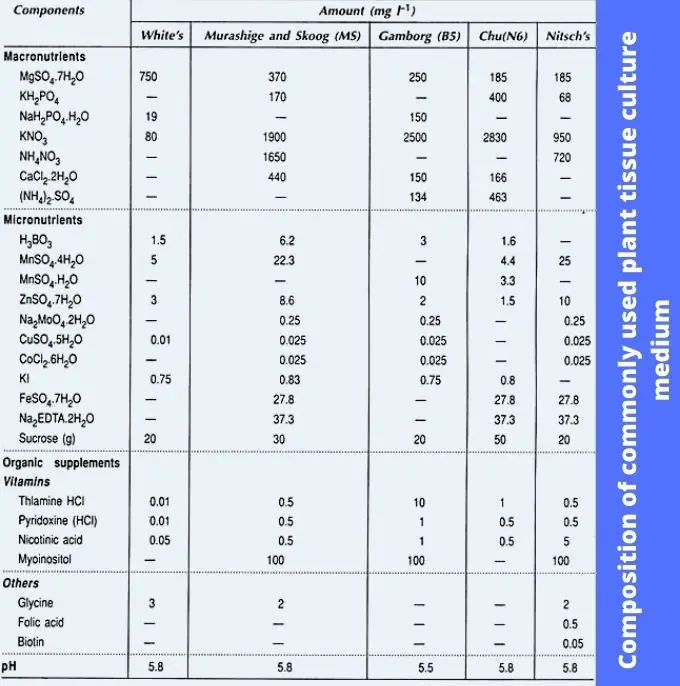
- White’s medium: White’s medium was for the root culture.
- Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium: This medium was developed by Murashige and Skoog to induce organogenesis, and regeneration of plants in cultured tissues.
- B5 medium: Gamborg developed this medium for cell suspension and callus cultures. In modern-day it is used for protoplast culture.
- N6 medium: the medium was developed by Chu for the cereal anther culture, besides other tissue cultures.
- Nitsch’s medium: Nitsch formulated this medium to frequently be used for other cultures. Among the media mentioned above, MS medium is widely employed in plant tissue culture work due to its success with several plant species and culture systems.
Plant Tissue Culture Media Composition
A Plant Tissue Culture Media contain the following components;
Macronutrients (a)
- A Plant Tissue Culture Media should contain the following Macronutrients nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), and sulfur (S) for satisfactory growth and morphogenesis.
Micronutrients (b)
- The vital micronutrients of a plant tissue culture medium are iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), boron (B), copper (Cu), and molybdenum (Mo).
Carbon and energy sources
- 2-5% sucrose is used in Plant Tissue Culture Media as a source of carbon and energy.
- Other carbohydrates such as lactose, galactose, maltose, and starch are also used as the source of carbon and energy. These are less effective than either sucrose or glucose.
Vitamins and Myo-inositol
- Vitamin thiamin (B1), nicotinic acid, and pyridoxine (B6) are used in a Plant Tissue Culture Media.
- In-Plant Tissue Culture Media Vitamins helps for the normal growth and development of plants.
- Plant also use them as a catalyst in various metabolic processes.
Amino acids
- Different amino acid mixtures can be used in this medium such as casein hydrolysate, L-glutamine, L-asparagine, and adenine.
- They function as a source of nitrogen which is assimilated immediately by tissues and cells as compared to inorganic nitrogen sources.
Undefined organic supplements
- Different natural substances or extracts can be used within the medium to check their effect on growth enhancement.
- Different natural substances or extracts include protein hydrolysates, coconut milk, yeast extract, malt extract, ground banana, orange juice, and tomato juice.
Solidifying agents
- Different types of solidifying agents are used in plant tissue culture medium such as agar, agarose, and gellan gum.
Growth regulators
- Growth regulators play an important role in stem elongation, tropism, and apical dominance.
- There are present different groups of Growth regulators which are used in Plant Tissue Culture Media such as;
- Auxins: These are included indole-3- butricacide (IBA), indole-3- acetic acid (IAA), naphthalene- acetic acid (NAA) and 2,4-dichlorophenoxy-acetic acid (2,4-D).
- Cytokinins: These are included TDZ (thiazuron-N-phenyl-N-1,2,3 thiadiazol-5ylurea), BAP (6-benzyloaminopurine), kinetin (N-2-furanylmethyl-1H-purine-6-amine), 2iP (6-dimethylaminopurine) and Zeatin (6-4-hydroxy-3-methyl-trans-2-butenylaminopurine).
- Gibberellins: It is made of more than 20 aggregates, of which GA3 is the most widely engaged gibberellin. These aggregates improve the growth rate of callus and support the elongation of dwarf plantlets
Preparation of Plant Tissue Culture Media
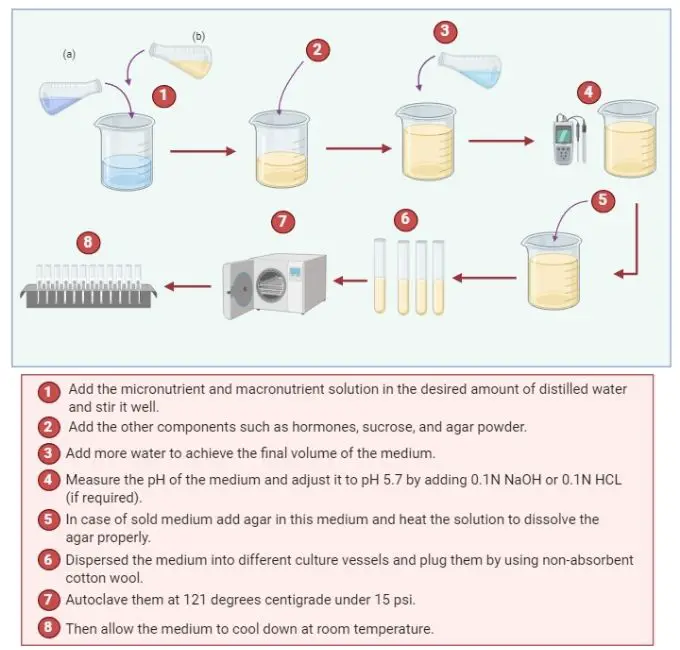
- Prepare the solution of macronutrients and micronutrients separately.
- Add the micronutrient and macronutrient solution in the desired amount of distilled water and stir it well.
- Add the other components such as hormones, sucrose, and agar powder. Add vitamins and auxins after autoclave to achieve better results.
- Add more water to achieve the final volume of the medium.
- Measure the pH of the medium and adjust it to pH 5.7 by adding 0.1N NaOH or 0.1N HCL (if required).
- In case of sold medium add agar in this medium and heat the solution to dissolve the agar properly.
- Dispersed the medium into different culture vessels and plug them by using non-absorbent cotton wool.
- After that autoclave them by wrapping them into cheese-cloth or with any other suitable closer.
- Autoclave them at 121 degrees centigrade under 15 psi.
- Then allow the medium to cool down at room temperature.
Sterilization of Plant Tissue Culture Media
The transmission of plant parasites can be reduced by preventing the contamination of tissue culture media. To control the contamination of culture medium we should follow these steps;
- Add antimicrobial agents, acidification agents to the medium (less employed in plant tissue culture media).
- Use microporous filters for the filtration of the medium.
- To decrease the chances of contamination, it is suggested that sterilization rooms should have the most limited number of openings.
- Perform the Media preparation and sterilization in a separate compartment or in a laminar airflow cabinet.
- The sterilization space should additionally possess walls and floor that withstand moisture, temperature, and vapor.
- Autoclave the medium at a temperature ranging from 115o – 135o C.
Types of Plant tissue culture
There are different types of tissue culture such as;
Embryo Culture
- In this technique, the embryo cell is developing in in-vitro.
- The embryonic cell is collected from a living organism.
- In this technique, both the mature and immature cells are used. The ripe seeds are used to isolate the mature embryos while the seeds that failed to germinate are used to isolate the immature embryo.
- The ovule, seed, or fruit does not need to be sterilized again.
Seed Culture
- In this process, the explants are imported within a laboratory where they can reproduce. These explants are isolated from an in-vitro descended plant.
- To prevent tissue damage the explant must be sterilized.
Callus Culture
- These are unorganized, dividing the mass of cells.
- The callus is collected from the explanations which are cultured in a proper medium.
- The extension of the callus is accompanied by organ differentiation.
- A gel-like medium is used to grow the culture. The medium is composed of agar and precise nutrients which are required for the growth of the cells.
Organ Culture
- In this process, the shoot, leaf, or any organ of the plant is used as an explant.
- Different methods are used for Organ culture such as plasma clot method, raft method, grid method, and agar gel method.
- This process is applied to conserve the structure and functions of an organism.
Protoplast Culture
- The cell is lacking a cell wall.
- The hanging-drop method, or micro-culture chambers are used to cultured a protoplast.
- There are different phases such as the construction of cell walls, cell division, reconstruction of a whole plant.
Except those 5, There are many types of plant tissue culture techniques such as Pollen Culture, Anther Culture, Single Cell Culture, Suspension Culture, Somatic Embryogenesis.
Advantages of Plant tissue culture
There are several advantages of plant tissue culture such as;
- It can produce the same copy of the plant which can provide especially good flowers, fruits, or have other desirable traits.
- Mature plants are prepared quickly.
- The reproduction of multiples of plants in the deficiency of grains or necessary pollinators to produce grains.
- The whole plants are regenerated from the plant cells which are genetically modified.
- The reproduction of plants in a sterilized vessel that permits them considerably reduced the risks of spreading diseases, pests, and pathogens. I one word it produces disease-free plants.
- To refine distinct plants of viral and other diseases and to instantly multiply these plants as ‘cleaned stock’ for farming and horticulture.
- The plantlets are achieved in a brief time by a minute volume of plant tissue.
- It gives the plants the ability to grow throughout the year, irrespective of the season.
- In the tissue culture technique, a large space is not required to grow plants.
- The production of the latest variations in the marketplace speeds up.
- Ornamental plants such as dahlia, chrysanthemum, orchids, etc. are produced by using this technique.
Plant tissue culture applications
The tissue culture plays a vital role in plant sciences, forestry, and in horticulture.
- The profitable product of plants used as potting, landscape, and florist subjects, which manages meristem and shoot culture to generate a huge number of identical individuals.
- It also helps in the preservation of rare or endangered plant species.
- A farmer may practice tissue culture techniques to eliminate cells rather than plants for beneficial characteristics, e.g. herbicide resistance/tolerance.
- Biopharmaceuticals such as plant-derived secondary metabolites and recombinant proteins can be produced by growing plant cells in liquid culture in bioreactors.
- Help in regeneration of the novel hybrid by fusing the protoplast of distantly related species.
- It helps to study different mechanisms in plants such as molecular basis study for physiological, biochemical, and reproductive mechanisms in plants. It assists the in vitro selection for stress-tolerant plants.
- Plant tissue culture help to cross-pollinate distantly associated species and next tissue culture the resulting embryo which would usually die.
- The chromosome doubling and induction of polyploidy is achieved by Plant tissue culture such as doubled haploids, tetraploids, and other forms of polyploids. Different antimitotic agents (colchicine or oryzalin) are used to achieve this.
- Being a tissue for transformation, accompanied by the short-term experiment of genetic constructs or by the reconstruction of transgenic plants.
- To regeneration clean plant material from a virus-infected one (sugarcane, potatoes, and many species of soft fruit.) can be done by the meristem tip culture techniques.
- By using this technique an identical sterile hybrid species can be produced.
- The artificial seeds can be produced on a large scale by using somatic embryogenesis.
- Help in the production of Synthetic seeds. In this method, an artificial endosperm and artificial seed coat encapsulate the somatic embryo.
FAQ
What is plant tissue culture?
Plant tissue culture is a technique used to grow and maintain plant cells, tissues, or organs in a sterile, controlled environment.
What are the applications of plant tissue culture?
Plant tissue culture has many applications, including micropropagation, somatic embryogenesis, protoplast fusion, anther culture, and the production of secondary metabolites.
What is micropropagation?
Micropropagation is the rapid production of large numbers of identical plants for agricultural or horticultural purposes using plant tissue culture.
What is somatic embryogenesis?
Somatic embryogenesis is the production of embryos from plant cells other than the egg and sperm cells, using plant tissue culture techniques.
What is protoplast fusion?
Protoplast fusion is the fusion of protoplasts, or cells with their cell walls removed, from different plant species to create hybrid plants.
What is anther culture?
Anther culture is the production of haploid plants from pollen grains using plant tissue culture techniques.
What are the advantages of plant tissue culture?
The advantages of plant tissue culture include the ability to produce large numbers of genetically identical plants, the ability to produce disease-resistant and genetically uniform plants, and the ability to produce plants with desirable traits.
What are the disadvantages of plant tissue culture?
The disadvantages of plant tissue culture include the potential for genetic uniformity, the high cost and technical expertise required, and the potential for contamination.
What are the steps involved in plant tissue culture?
The steps involved in plant tissue culture include the selection of plant material, sterilization, culture initiation, and subculturing.
What is the importance of plant tissue culture?
Plant tissue culture is important for the production of disease-resistant and genetically uniform plants, the preservation of rare or endangered plant species, and the production of compounds with medicinal or industrial value.

Great information to me