Giardia is an infectious parasite and responsible for the diarrheal illness known as giardiasis. Giardia mainly infects humans, cats, and dogs.
Giardia Classification
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| (unranked): | Excavata |
| Phylum: | Metamonada |
| Order: | Diplomonadida |
| Family: | Hexamitidae |
| Subfamily: | Giardiinae |
| Genus: | Giardia |
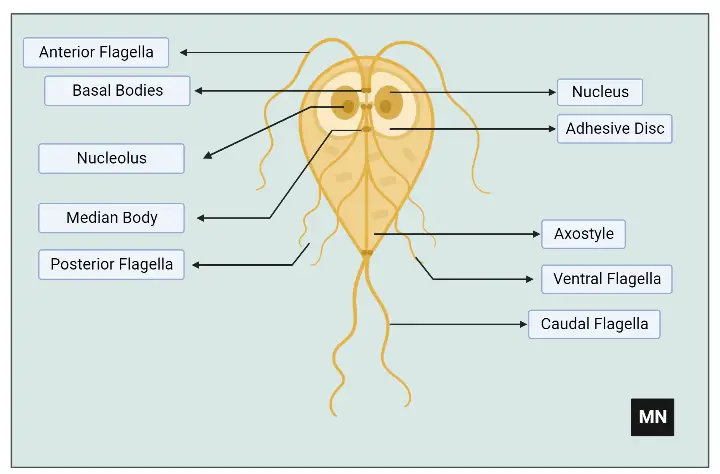
Giardia
- It is an anaerobic flagellated protozoan parasite.
- This microscopic parasite causes a diarrheal illness in the small intestines of vertebrates called giardiasis.
- They are mainly found on soil, food, or contaminated water.
- In 1681, the Dutch microscopist Antonie van Leeuwenhoek first described the Giardia.
Giardia Characteristics
- They contain two nuclei.
- They have four associated flagella.
- They are thought to lack both mitochondria and a Golgi apparatus.
- They contain a complex endomembrane system as well as mitochondrial remnants, called mitosomes.
- The mitosomes help in the maturation of iron-sulfur proteins.
Giardia infection/Giardiasis
- It is also known as beaver fever.
- The microscopic parasite Giardia is responsible for Giardiasis. It is a diarrheal disease.
- They feed off of another to survive.
- They live in the intestine of an infected person or animals such as cats, dogs, cattle, deer, and beavers. They are passed in feces (poop).
- They can survive for weeks or months on the outside of the body.
Giardiasis definition
Giardiasis is an intestinal infection caused by the protozoan Giardia lamblia. They are spread through contaminated water, foods, etc. Giardiasis is characterized by abdominal discomfort and prolonged, intermittent diarrhea.
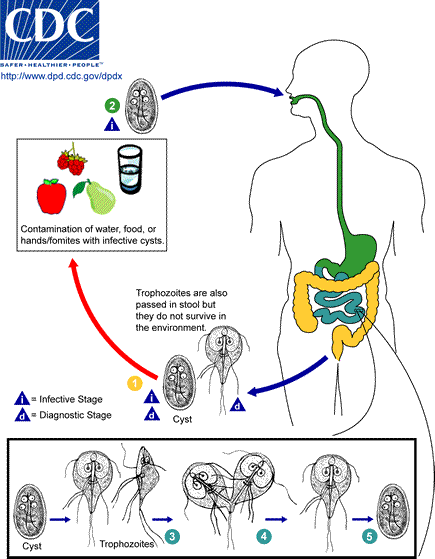
Giardia life cycle
- During the life cycle of giardia two distinct forms are developed such as a cyst form and a trophozoite form. Among the two forms, the cyst is an infection and within-host body it transform into trophozoite form.
- Now, these trophozoites get attached to the intestinal wall and started to multiply within the gut.
- After that, the trophozoites are transformed back into cyst form and excrete through the feces.
- The giardia infection results in
- Decreased the expression of brush border enzymes.
- The morphological changes to the microvillus.
- Increased intestinal permeability.
- Programmed cell death of small intestinal epithelial cell.
- The trophozoites and cysts do not invade beyond the gastrointestinal tract.
Causes of Giardiasis
The protozoan Giardia duodenalis is responsible for the diarrheal infection known as Giardiasis. Giardia duodenalis cause infection in many animals such as beavers (hence its nickname), as well as cows, other rodents, and sheep.
Giardia symptoms/Giardiasis symptoms
The symptoms of Giardiasis are; Diarrhea, Gas or flatulence, Greasy stool that can float, Stomach or abdominal cramps, Upset stomach or nausea, Dehydration.
After infection, it takes 1 to 3 weeks to develops signs or symptoms. The symptoms can last 2 to 6 weeks in healthy people. The amount of time symptoms last can be reduced by Medications.
Giardiasis spread/transmission
- It can transmit through the feces of infected animals or persons.
- Through the Drinking water contaminted with Giardiasis parasite.
- Swallowing lakes, rivers, springs, ponds, and streams water swimming.
- By eating contaminated foods.
- Having contact with the Giardiasis infected patients.
- By traveling in giardiasis common countries.
Giardiasis diagnosis
- Giardia can detect from the stools of an infected person by using the concentration methods and trichrome staining method. However, these two methods are not effective.
- Fecal immunoassays are used to detect Giardia in stools. It is the most sensitive test for the detection of Giardiasis.
- Rapid immune-chromatographic cartridge assays, molecular testing (e.g., polymerase chain reaction) can also be used for the detection of Giardia.
Giardiasis treatment
- There are several effective drugs that can be used for the treatment of Giardiasis such as metronidazole, tinidazole, and nitazoxanide.
- Some alternative drugs of these medications are paromomycin, quinacrine, and furazolidone.
Giardiasis prevention
- Wash your hand thoroughly in places where germs can easily spread. Wash hand before eat, after toilet, during, and after preparing food, After touching garbage.
- Do not swallow water of Ponds, streams, rivers during swimming.
- Avoid drinking untreated water such as water from lakes, rivers, springs, ponds, streams, or shallow wells.
- Wash vegetables and fruits then peel them before eating.
- During traveling avoid eating of untreated or uncooked foods.
- Be cautious about sexual practices associated with the spread of this infection, such as anal sex. Use a condom to reduce the chance of contracting giardiasis.
Giardiasis in dogs
- A common, microscopic (intestinal) parasite Giardia intestinalis is responsible for infection in humans, dogs, and cats.
- The common symptoms of Giardiasis in dogs are diarrhea, gas, abdominal discomfort, nausea, and vomiting.
- The transmission risk of Giardia from dogs and cats to humans is very low. The type of giardia infection in both humans and dogs are different.
- A dog can get infected with giardia when they come in contact with infected feces (poop), during rolling and playing in contaminated soil, by licking contaminated surfaces, by drinking contaminated water.
Related Posts
- Ascaris lumbricoides – Structure, Reproduction, Life Cycle, Characteristics
- Ancylostoma duodenale – Structure, Life Cycle, Habitat, Characteristics
- Cysticercosis – Definition, Symptoms, Treatment, Diagnosis
- Host-Parasite Interactions – Definition, Types, Mechanism
- Fasciola hepatica – Definition, Structure, Reproducation, Life Cycle
