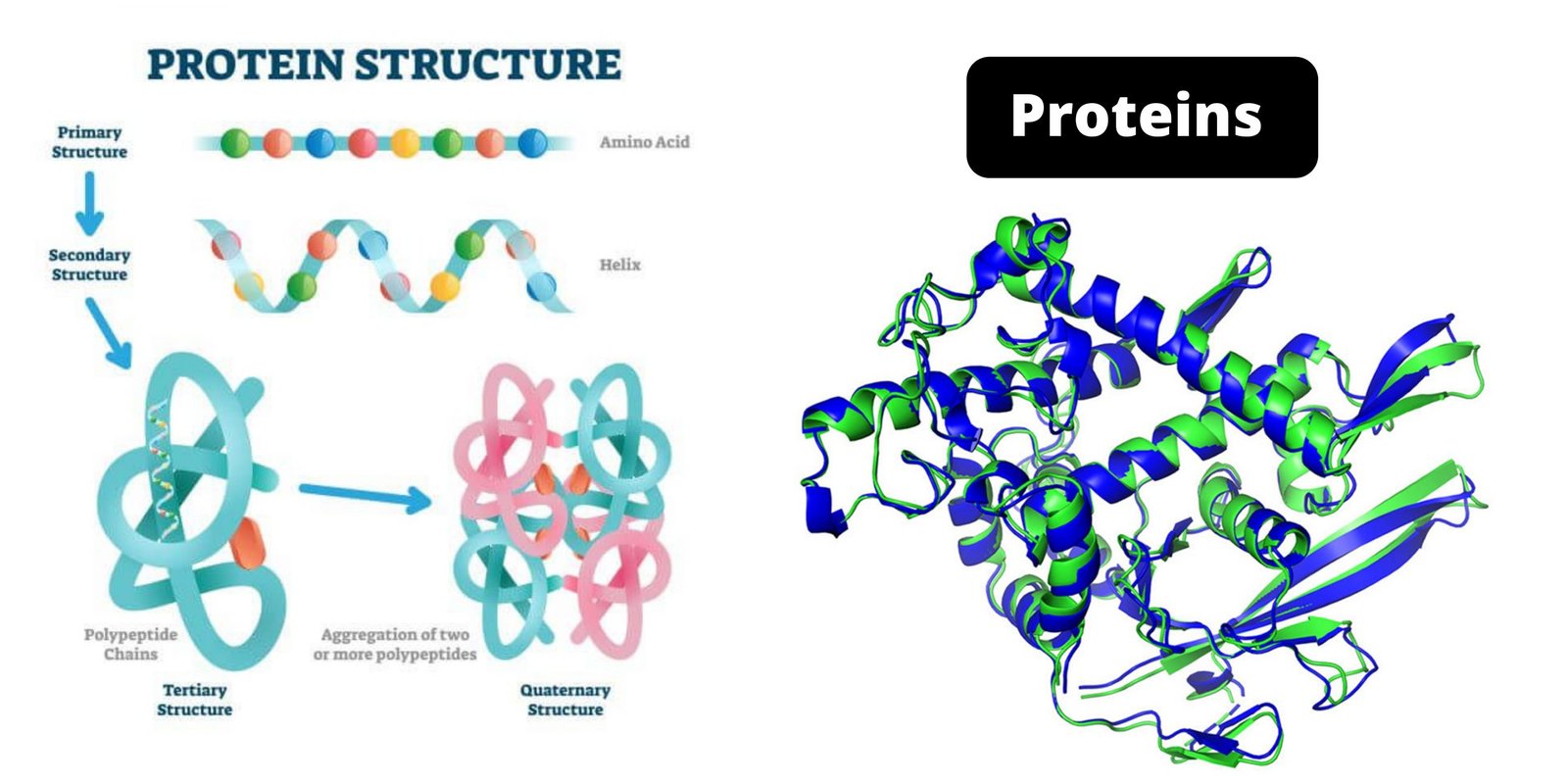
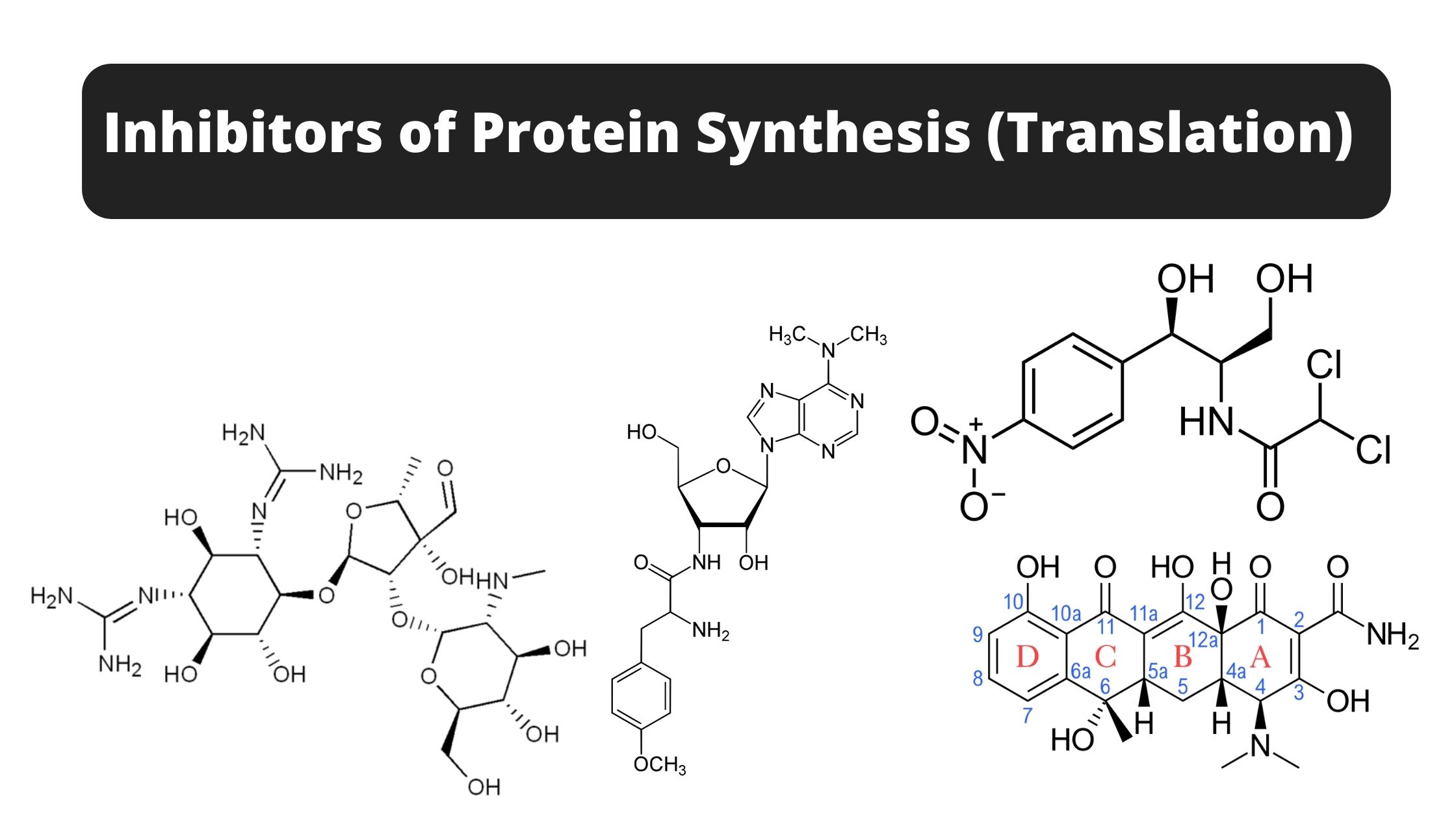
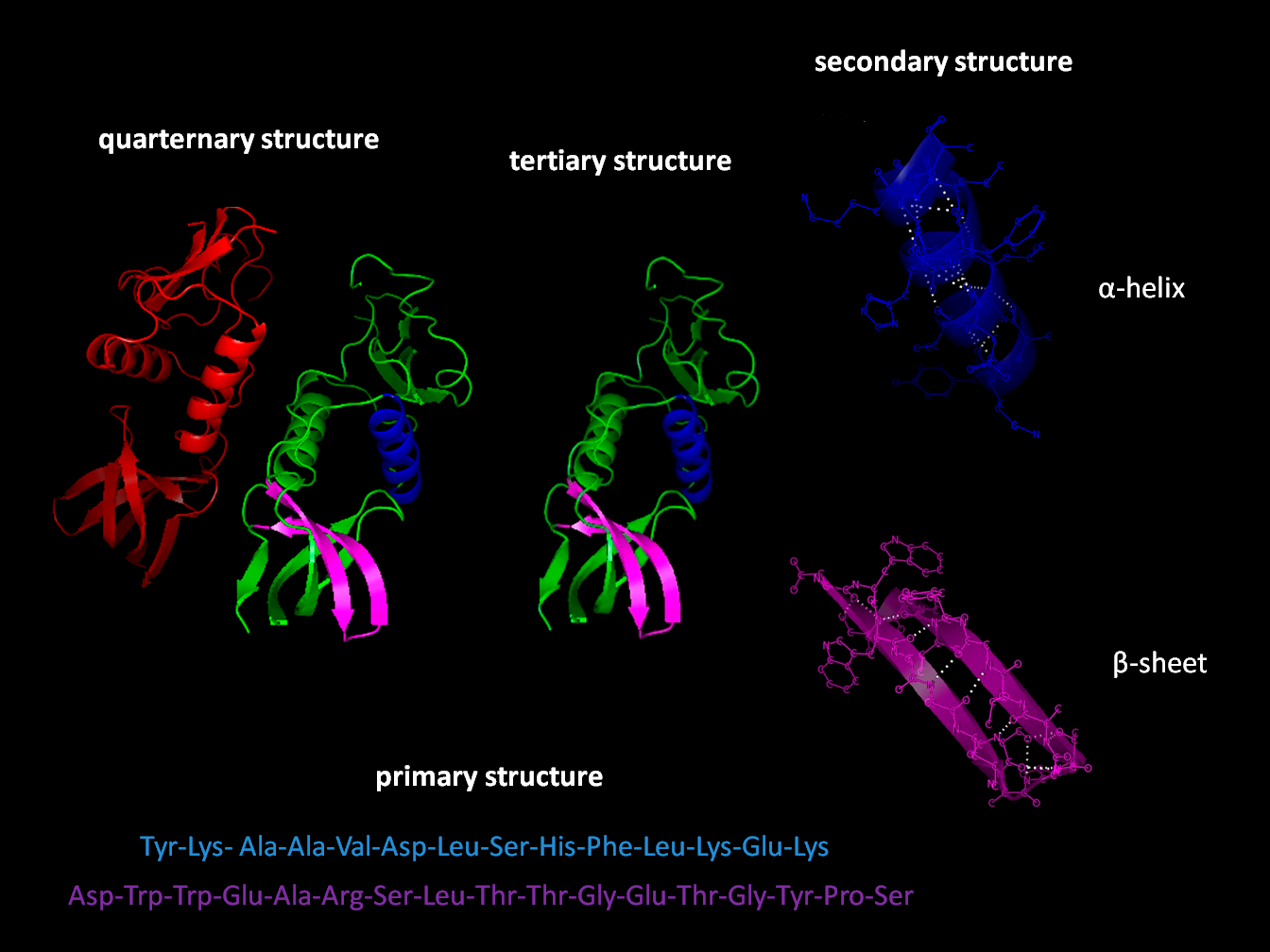
Proteins – Structure, Properties, Type, Denaturation, Functions
What are Proteins? Definition of Proteins Proteins are large, complex molecules composed of amino acid chains that perform a vast array of functions in living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, providing structural support, and facilitating cell signaling and transport. Properties of Proteins Synthesis of peptides Peptides are short chains composed of amino acids. These chains, … Read more