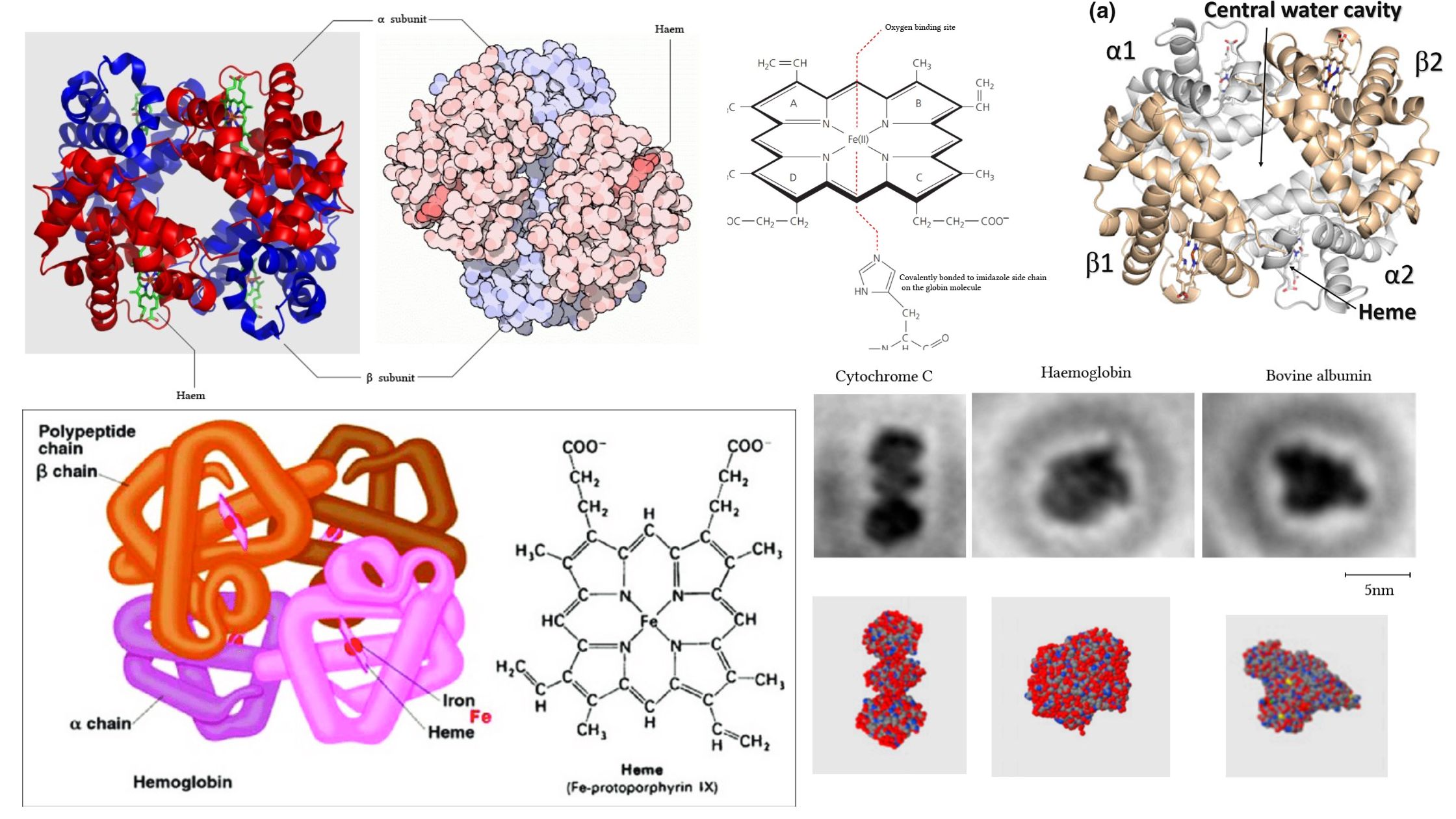
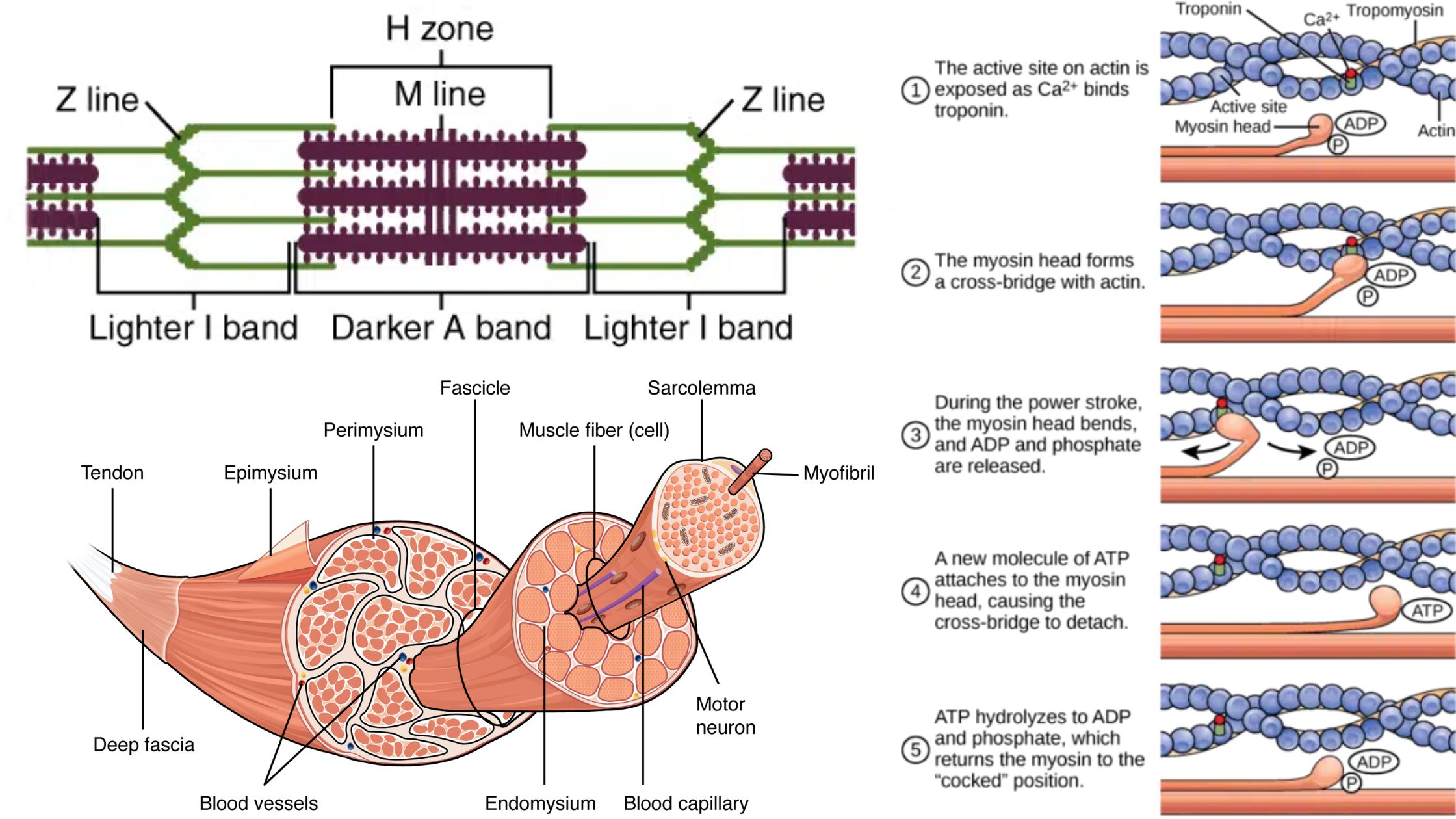
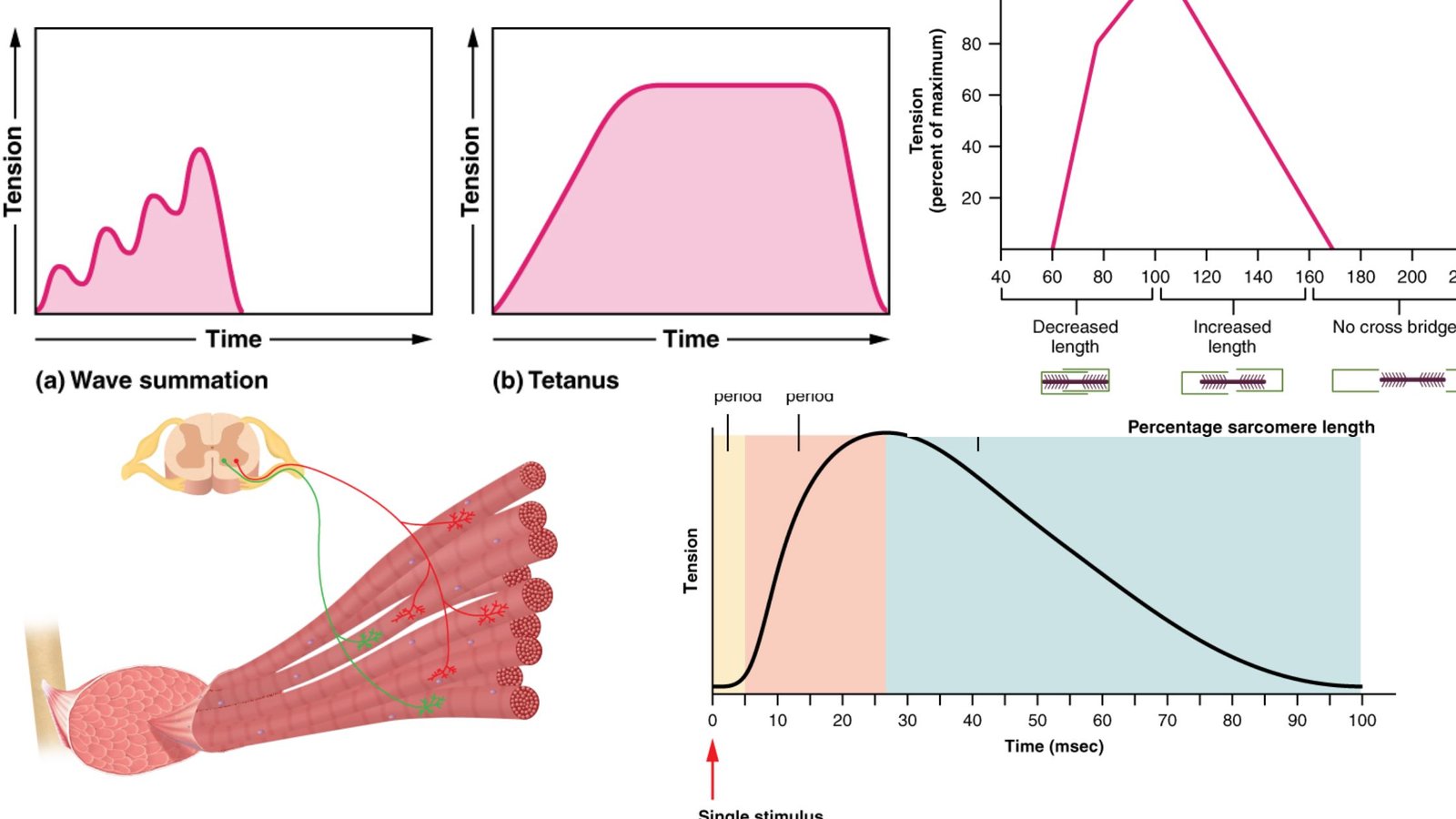
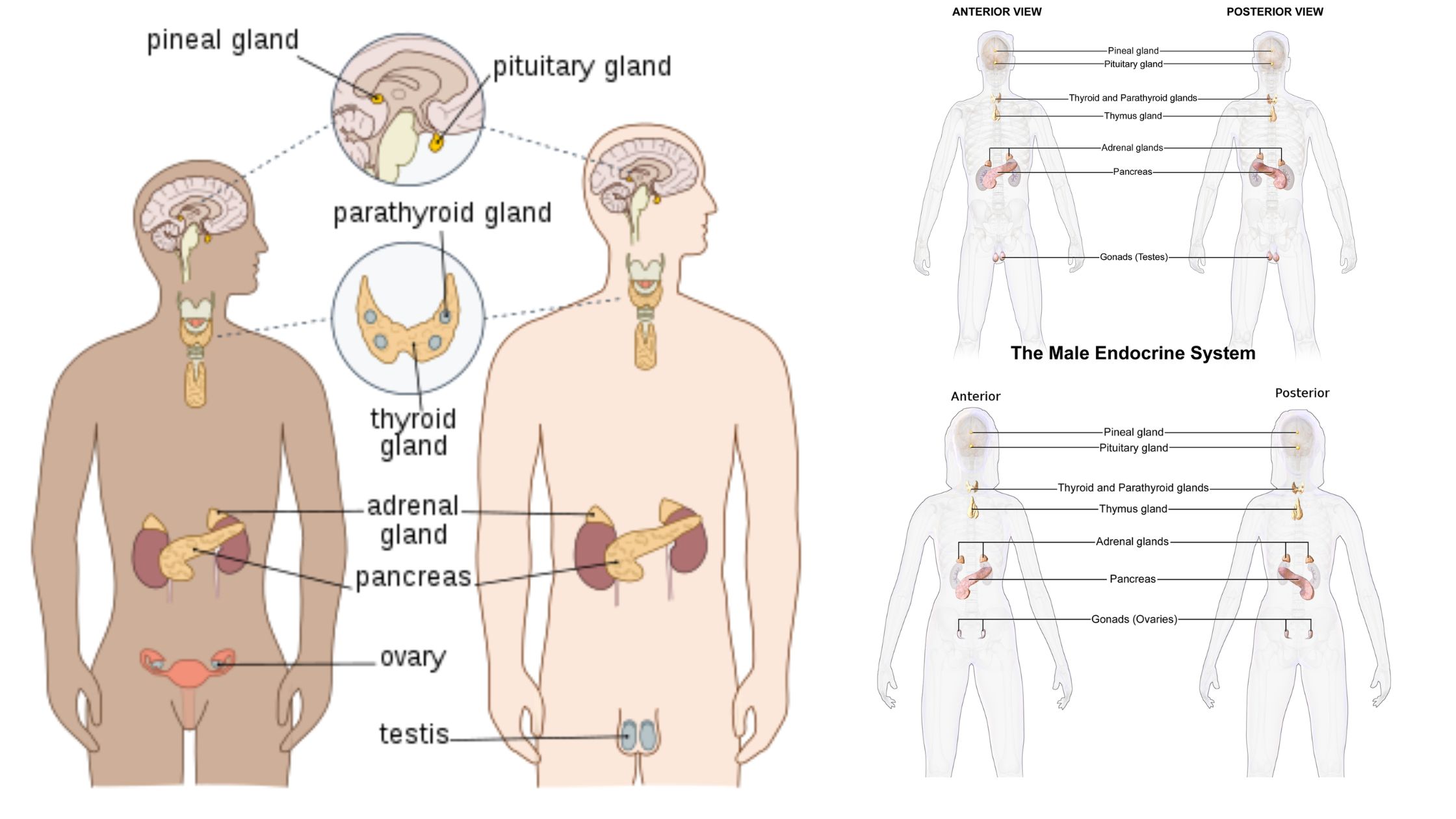
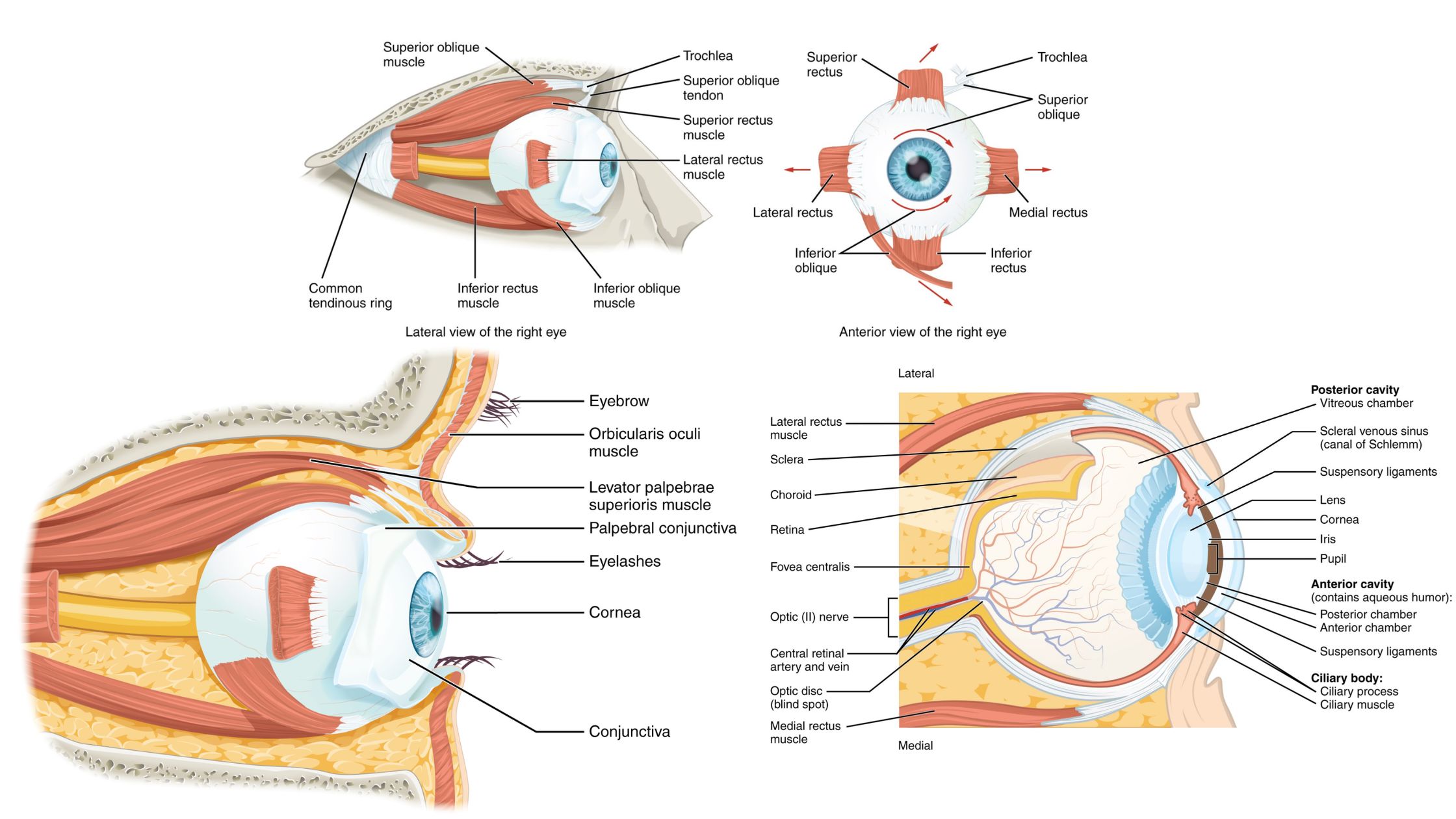
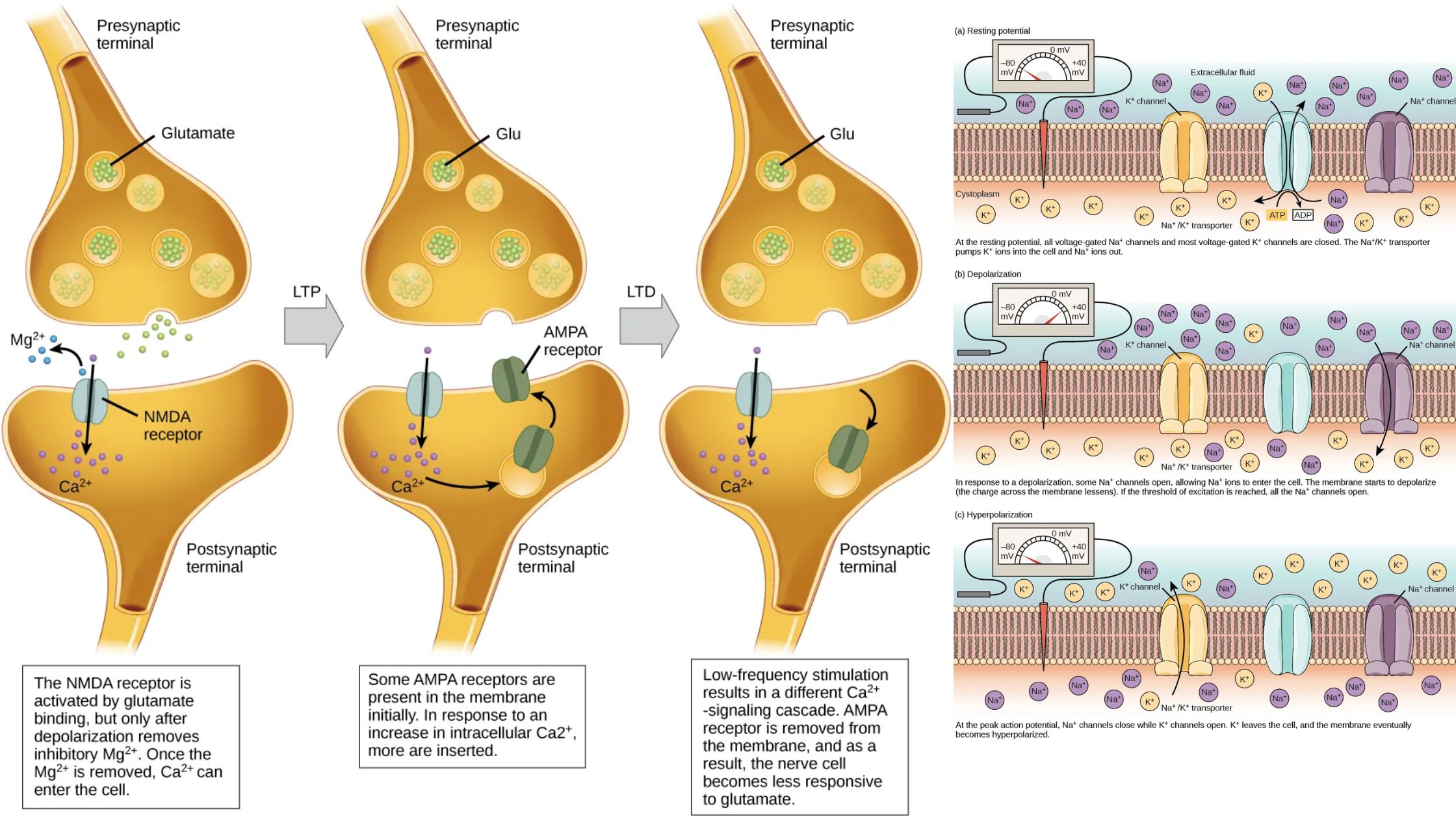
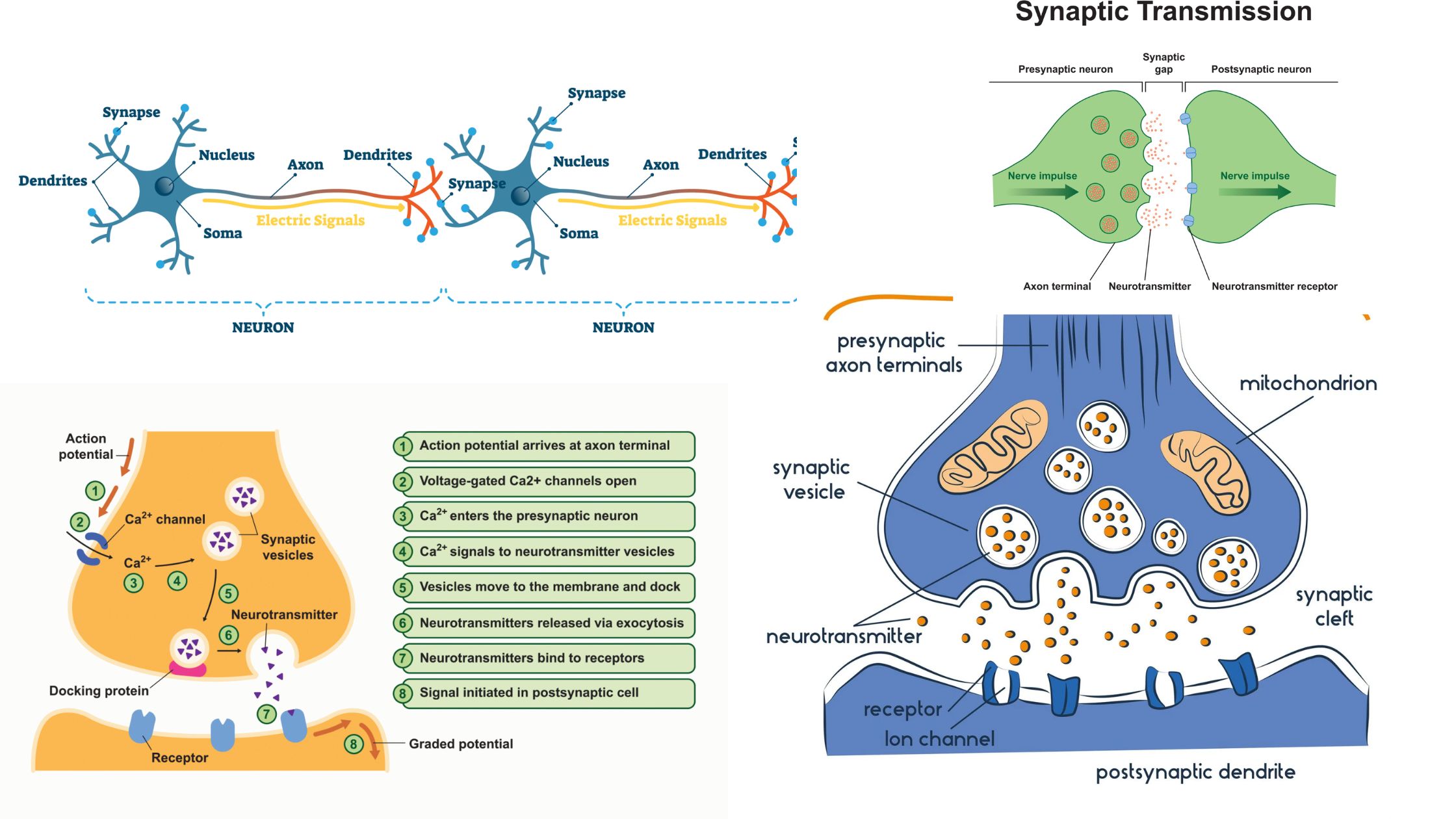
Hemoglobin – Definition, Structure and Function
What is Hemoglobin? What is Globin Chain? The globin chain refers to the specific combination of protein subunits that make up different types of hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is composed of four globin chains, which can vary depending on the specific type of hemoglobin. The different types of hemoglobin and their corresponding globin chains are as follows: … Read more