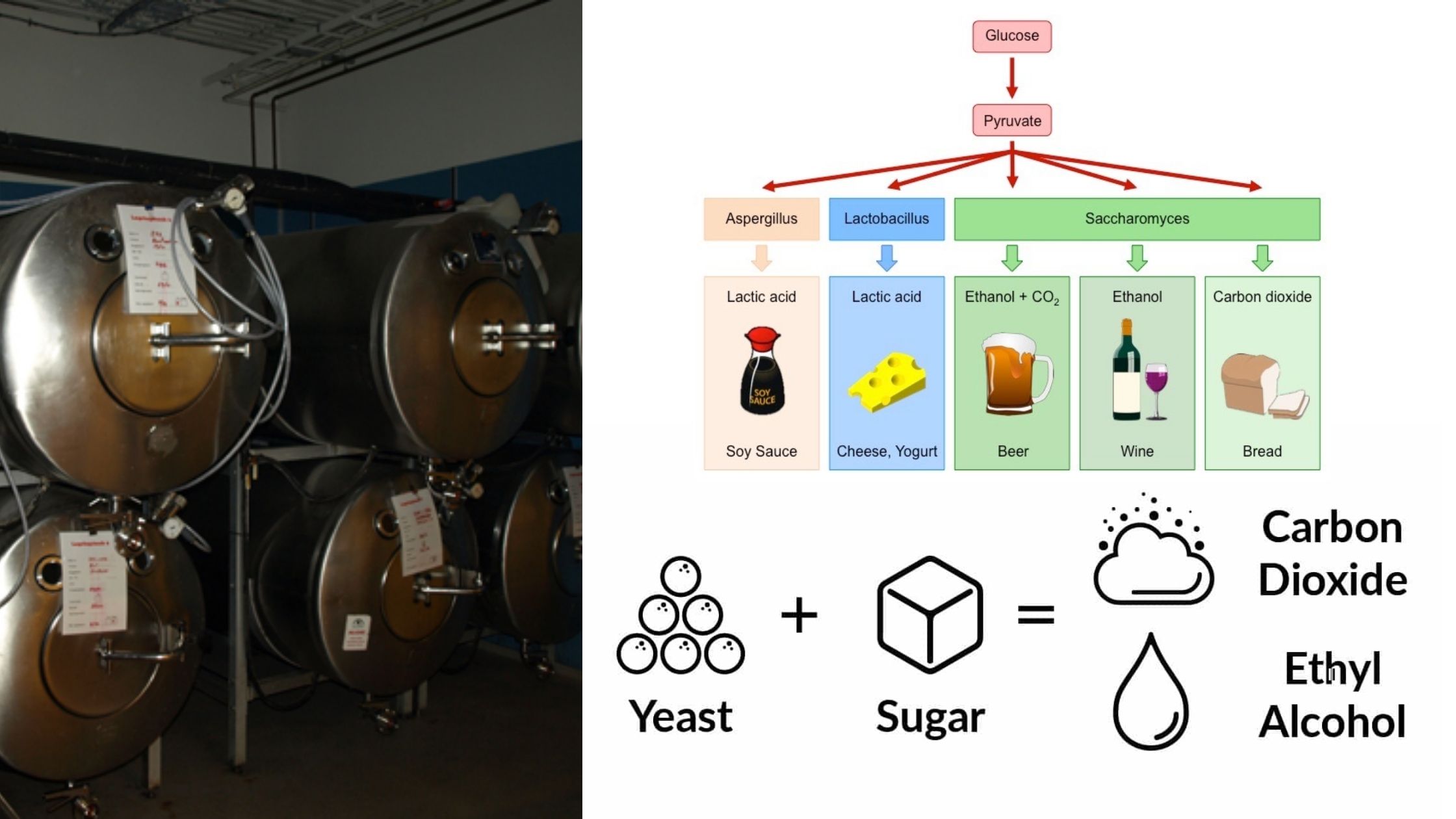
Food Spoilage General Principles – Chemical Changes Caused by Microorganisms
When food is called “spoiled”, it usually means that there is decay or decomposition of an unfavorable nature. Foods unfit for consumption are not considered spoiled. Spoiling could be caused by one or more of these: