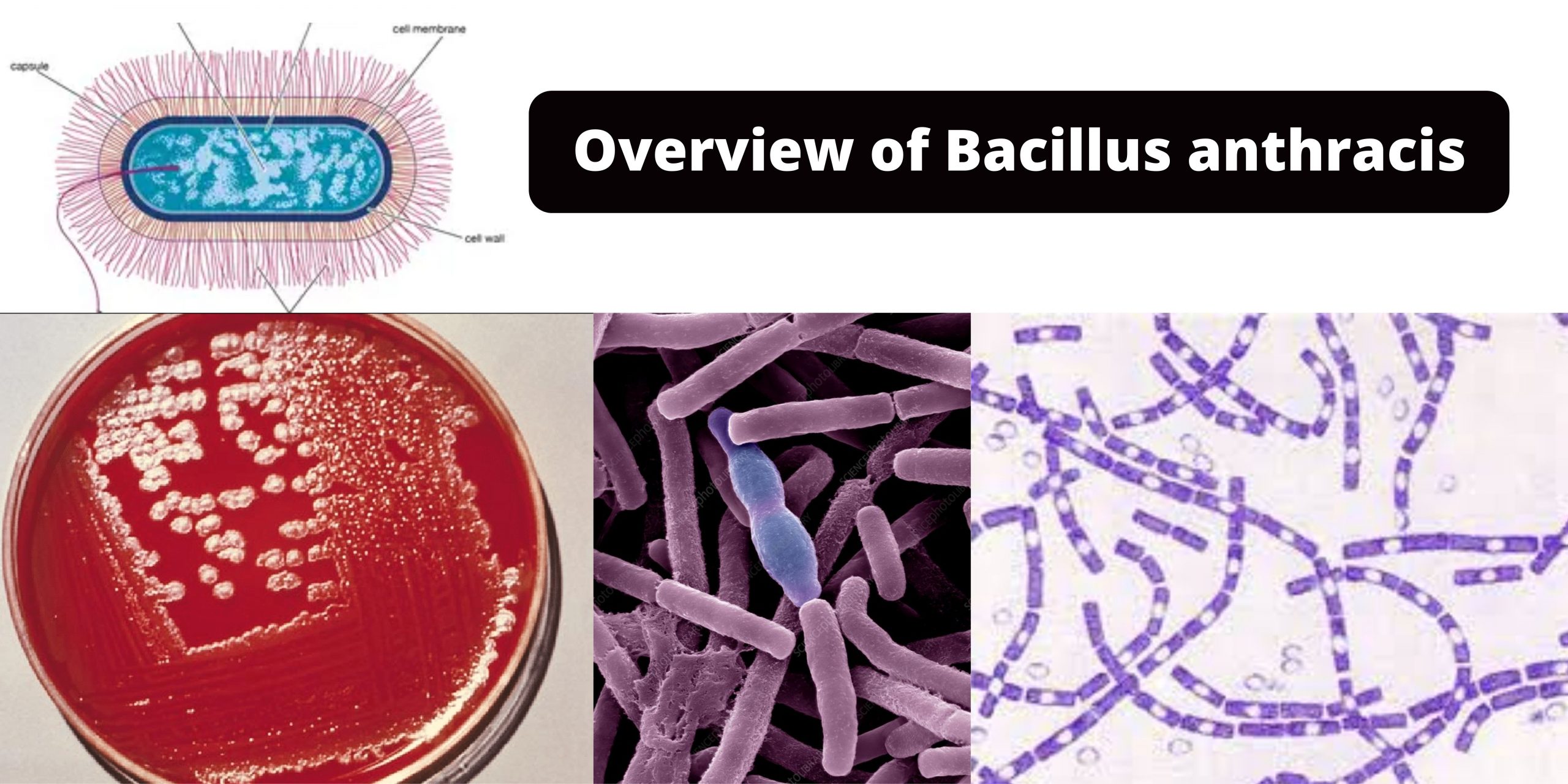
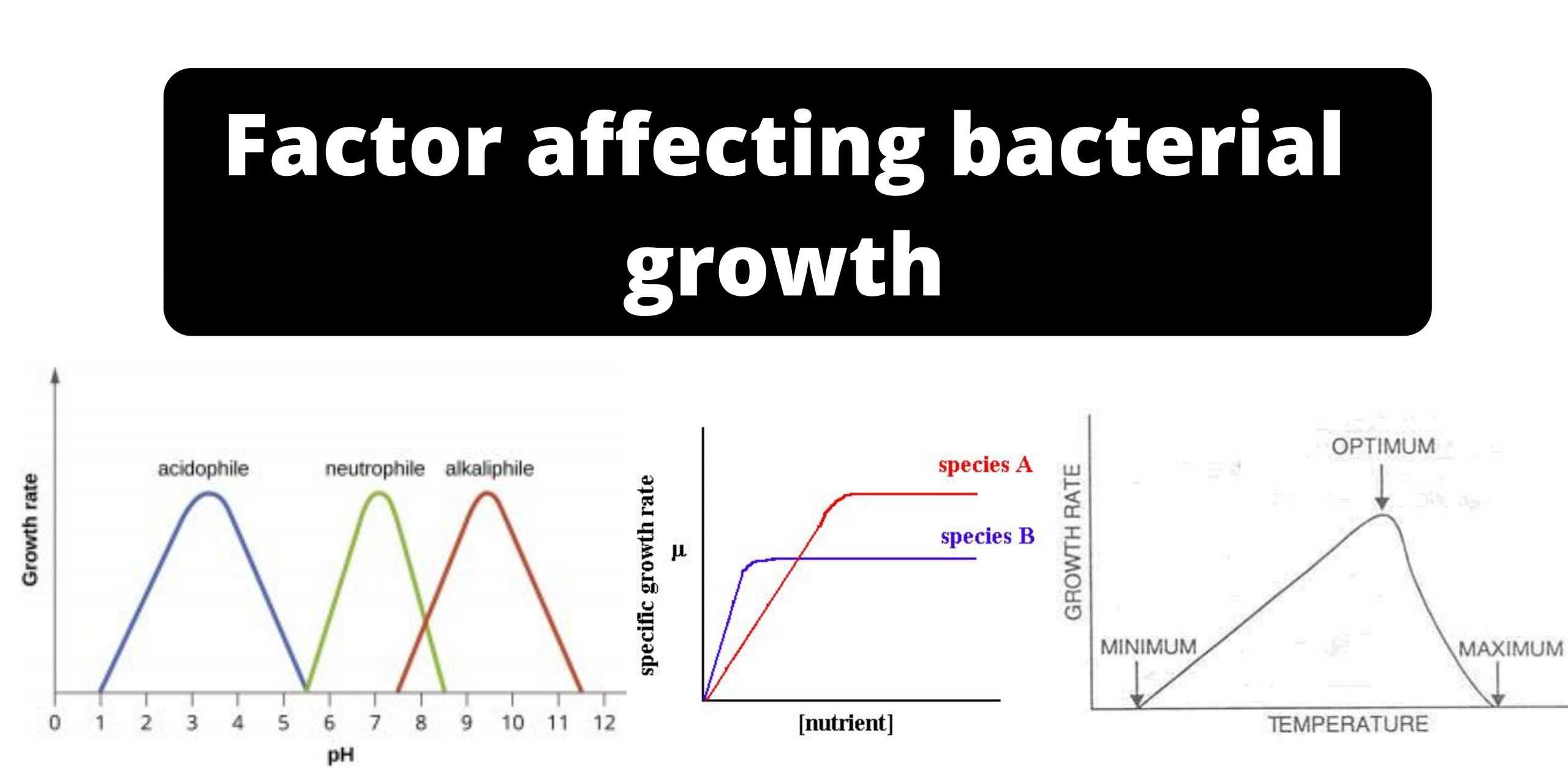
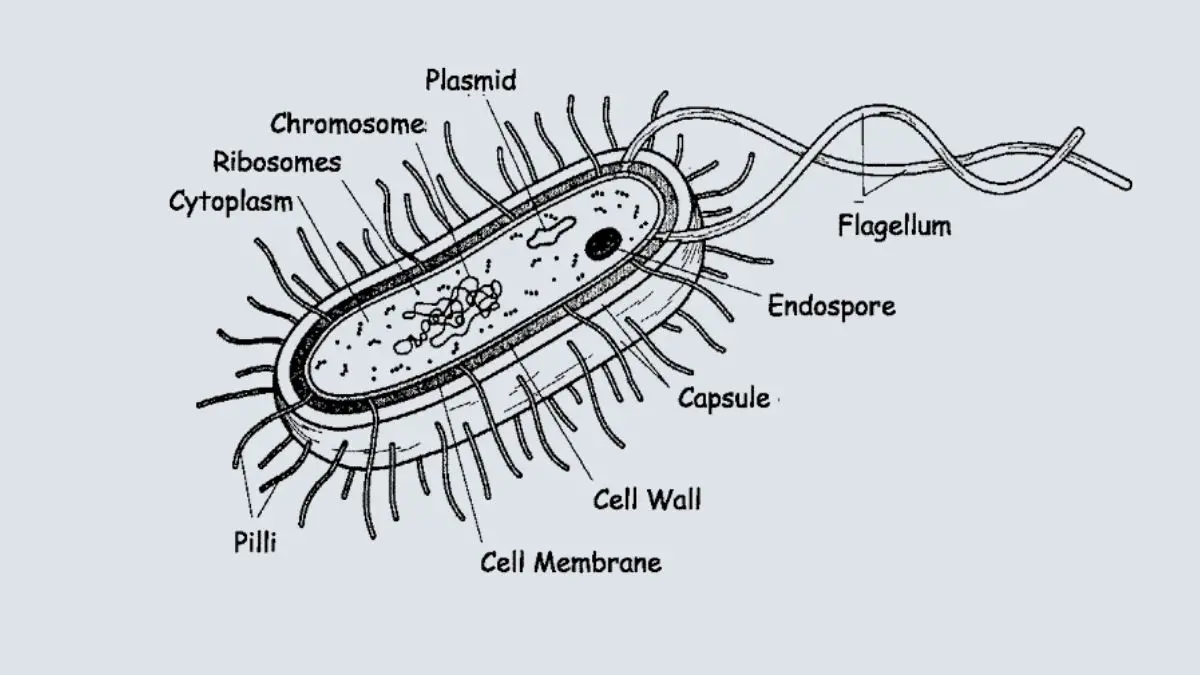
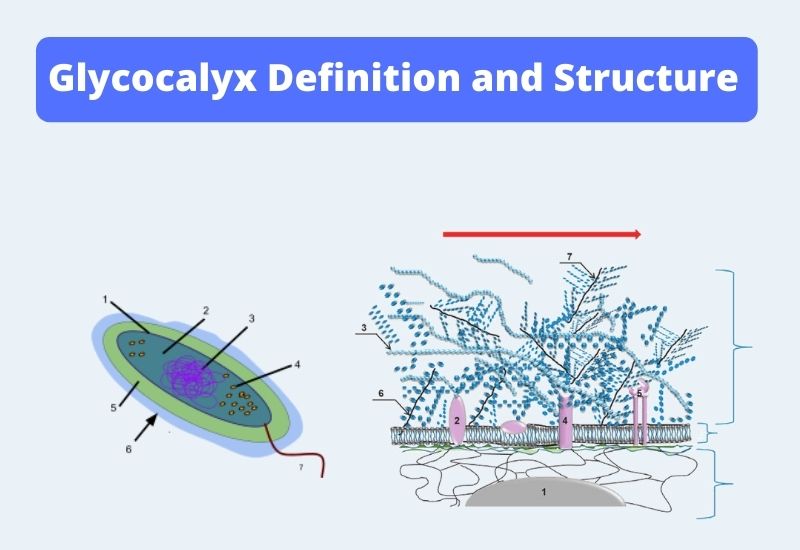
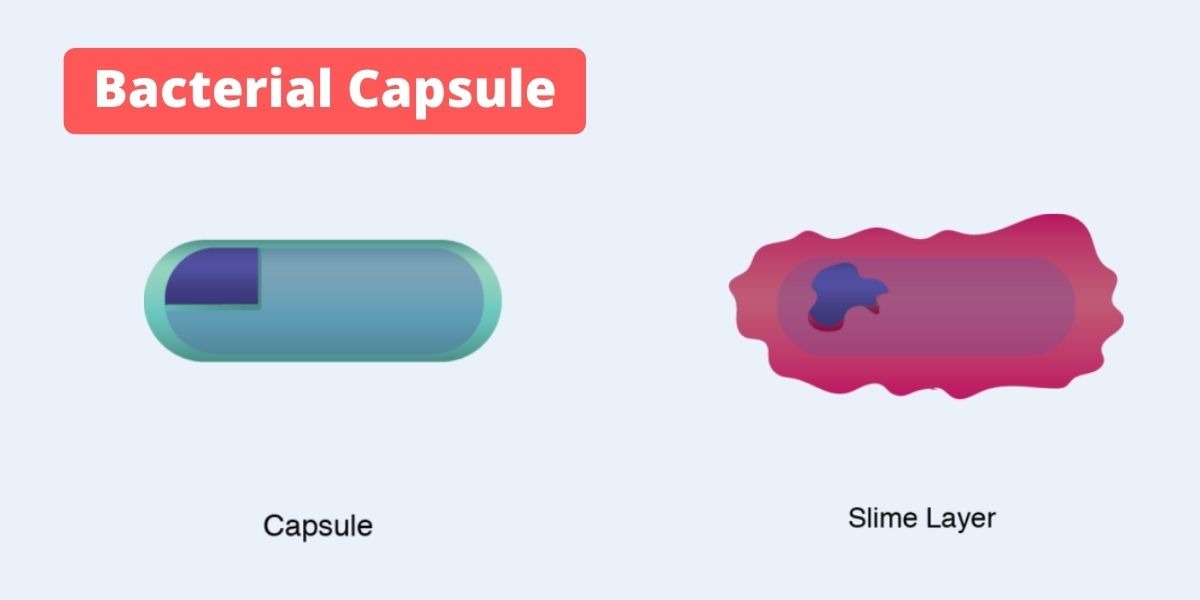
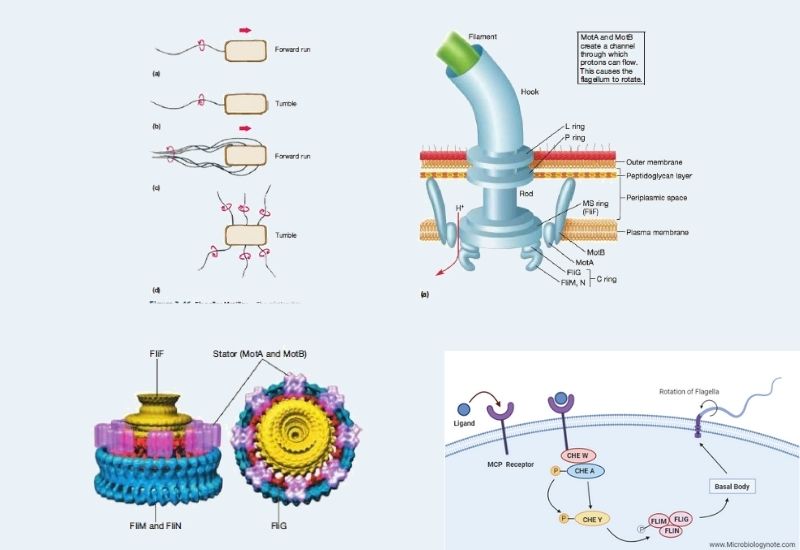
Overview of Bacillus anthracis
Bacillus anthracis the most well-known pathogen in the Genus Bacillus is the cause of a severe zoonotic illness known as anthrax. Anthrax is a primary disease that affects domestic and wild herbivores. It is among the most frequently encountered bioterrorism agents that has been implicated before in the Sverdlovsk the anthrax outbreak of 1979 as … Read more