Contents
Overview
You must be thinking what is a bacterial smear? Let me clear you donut, A bacterial smear is a thin layer of bacterial cell/culture which is placed on a clean, grease-free microscopic slide to observe a clear image under a microscope.
Bacterial cells are colorless, hence to observe them under the microscope we need to apply color on them adding some staining reagents. Once the bacterial cells are stained with reagents we can easily observe them under a microscope.
The preparation of a stained bacteria smear involves different steps, such as, first placed the bacterial cells on slide, apply heat to fix them on slide, then apply basic stain (simple staining).
Each of these steps has a different purpose, so, you need to be careful during the preparation.
Bacterial smear purpose
The main purpose of bacterial smear preparation is to fix the bacterial cell on the slide and prevent the loss of bacterial cells during the staining procedure.
Bacterial Smear Preparation Principle
Bacterial smear preparation involves the spreading of bacterial culture on slide, air drying, heat fixing before staining, and microscopic observation. The heat fixing in smear preparation has a purpose, it kills the bacterial cells in the smear, tightly adheres the smear to the slide, and allows the sample to more easily take up stains.
Bacterial Smear Preparation Requirements
- Clean and Grease or oil free slide
- Bacterial culture
- Inoculating loop.
- Bunsen burner.
- Distilled water.
Bacterial Smear Preparation Steps
Bacterial Smear Preparation from a Broth Medium
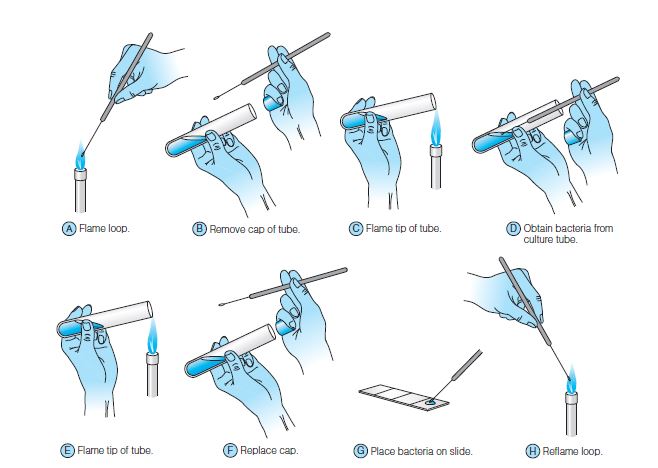
- Take a clean slide and Make it grease-free or oil-free by washing the slides with soap and water. Then rinse the slide with 95% alcohol and air dry it. After making it oil-free, hold the slide by its edge. Avoid touching the surface of slide (because we have an oily hand).
- Now, use a marking pencil, to mark the smear area on a clean slide and label the slide with the organism’s name.
- Now, use your other hand to hold the culture tube, remove the cap from tube. Hold the tip of tube on flame for a few seconds, this will kill r air-born organism that might cause containation.
- Insert the sterile loop into the tube, and gently dip the tip into the culture medium, remove the loop, reflame the tube tip, replace the cap.
- Transfer the loopful bacterial culture at the center of slide, spread it over the slide by using the loop.
- Now, air dry the slide by keeping it at room temperature.
- Heat fix the smear by quickly passing the slide through the bunsen burner flame, three-time. It will kill the bacterial cells on slide.
- Now bacteria smear is ready to apply stain and microscopy.
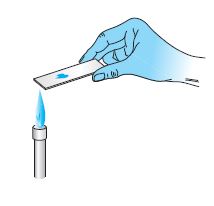
Bacterial Smears preparation from a Solid Medium
- To prepare bacterial smear from solid medium perform the 1, 2, and 3 steps from above procedure.
- Placed a drop of distilled water at the center of the slide.
- Now, gently insert the loop tip into the slant tube, and touch the main portion of the slant. Avoid dig into the medium or scrape on it. Take a small portion of bacterial cell on the tip of the loop and transfer it into the droplet of sterile distilled water. Mix this properly by using the loop tip.
- Perform the 6,7 and 8 steps from the previous procedure.
The Fixation of smear can be done by Alcohol. During alcohol fixation, first air-dry the slide then one or two drops of 70% alcohol, and leave it for 2 minutes until the alcohol dries up.
Limitation
- The smear should be thin.
- Avoid overheating during heat fix.
- Only transfer a loopful culture.
- The glass slide must be grease-free or oil-free, otherwise it will create difficulties during the smear preparation.